Chenglong Dai
A Sparse Cross Attention-based Graph Convolution Network with Auxiliary Information Awareness for Traffic Flow Prediction
Dec 14, 2023Abstract:Deep graph convolution networks (GCNs) have recently shown excellent performance in traffic prediction tasks. However, they face some challenges. First, few existing models consider the influence of auxiliary information, i.e., weather and holidays, which may result in a poor grasp of spatial-temporal dynamics of traffic data. Second, both the construction of a dynamic adjacent matrix and regular graph convolution operations have quadratic computation complexity, which restricts the scalability of GCN-based models. To address such challenges, this work proposes a deep encoder-decoder model entitled AIMSAN. It contains an auxiliary information-aware module (AIM) and sparse cross attention-based graph convolution network (SAN). The former learns multi-attribute auxiliary information and obtains its embedded presentation of different time-window sizes. The latter uses a cross-attention mechanism to construct dynamic adjacent matrices by fusing traffic data and embedded auxiliary data. Then, SAN applies diffusion GCN on traffic data to mine rich spatial-temporal dynamics. Furthermore, AIMSAN considers and uses the spatial sparseness of traffic nodes to reduce the quadratic computation complexity. Experimental results on three public traffic datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other counterparts in terms of various performance indices. Specifically, the proposed method has competitive performance with the state-of-the-art algorithms but saves 35.74% of GPU memory usage, 42.25% of training time, and 45.51% of validation time on average.
Brain EEG Time Series Selection: A Novel Graph-Based Approach for Classification
Feb 09, 2018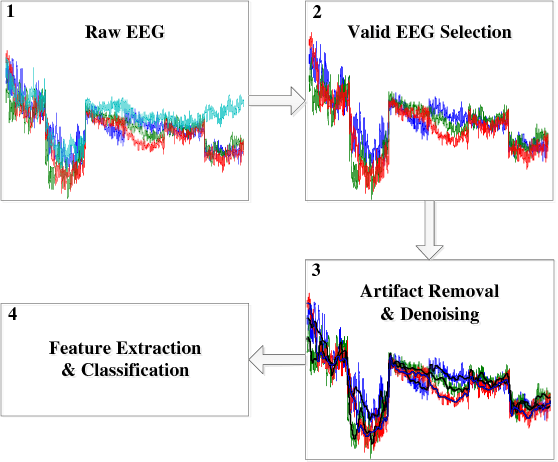
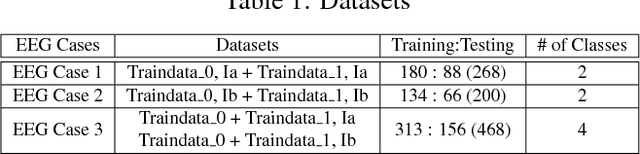
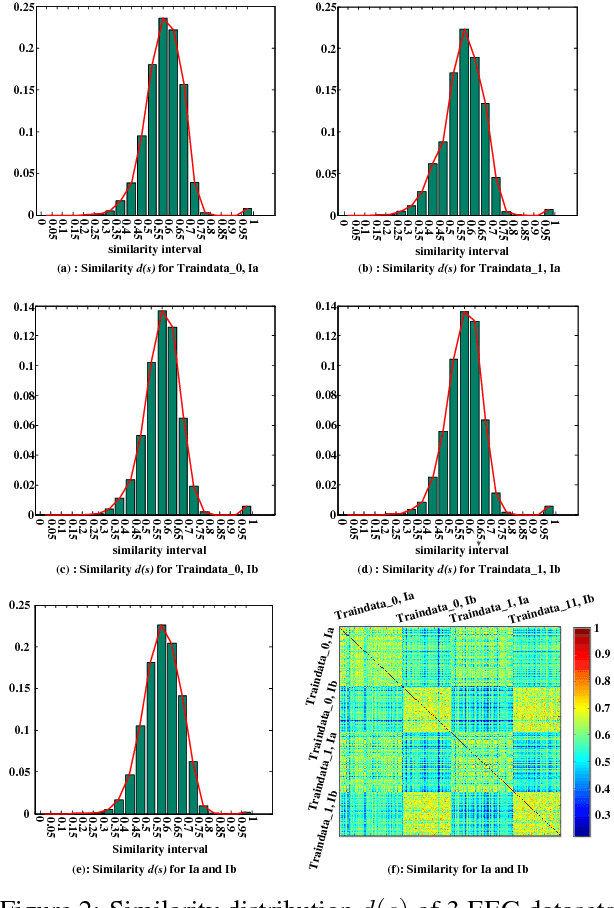
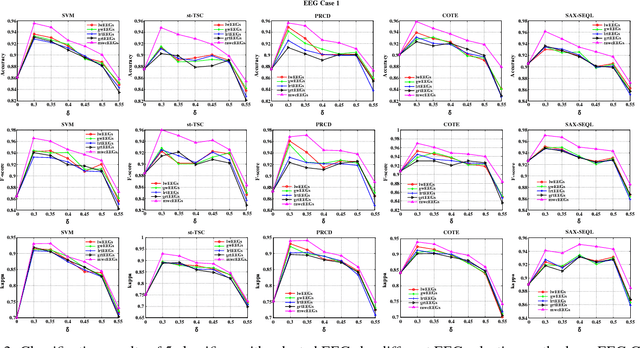
Abstract:Brain Electroencephalography (EEG) classification is widely applied to analyze cerebral diseases in recent years. Unfortunately, invalid/noisy EEGs degrade the diagnosis performance and most previously developed methods ignore the necessity of EEG selection for classification. To this end, this paper proposes a novel maximum weight clique-based EEG selection approach, named mwcEEGs, to map EEG selection to searching maximum similarity-weighted cliques from an improved Fr\'{e}chet distance-weighted undirected EEG graph simultaneously considering edge weights and vertex weights. Our mwcEEGs improves the classification performance by selecting intra-clique pairwise similar and inter-clique discriminative EEGs with similarity threshold $\delta$. Experimental results demonstrate the algorithm effectiveness compared with the state-of-the-art time series selection algorithms on real-world EEG datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge