Charles F. Lynch
Deriving Enhanced Geographical Representations via Similarity-based Spectral Analysis: Predicting Colorectal Cancer Survival Curves in Iowa
Sep 06, 2018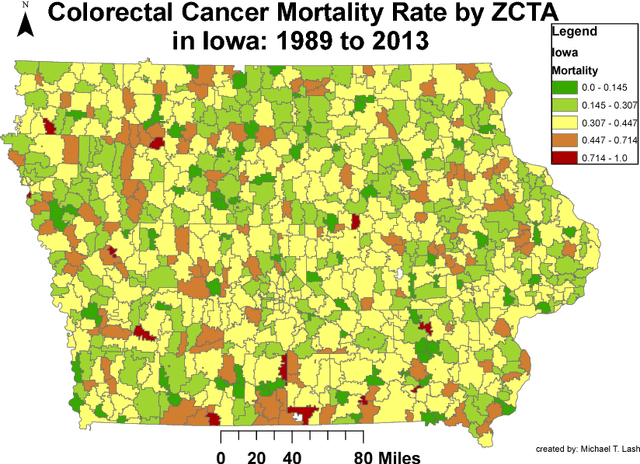
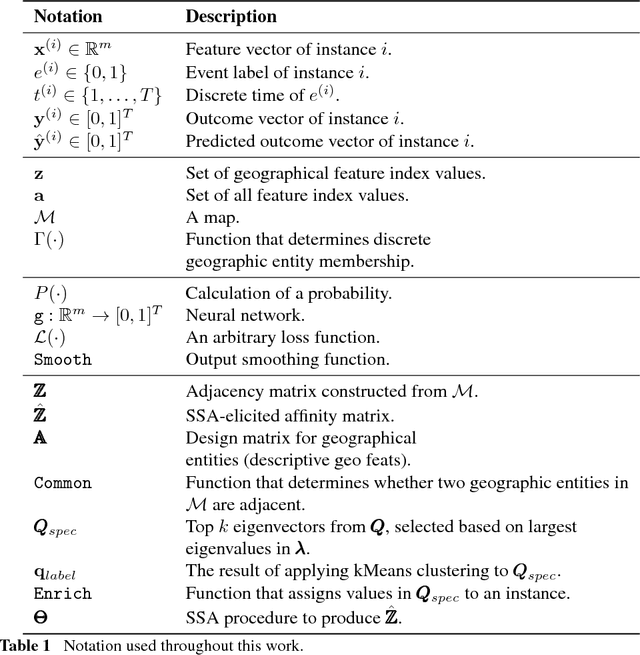
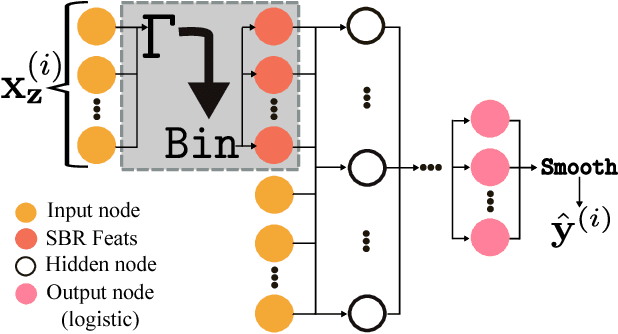
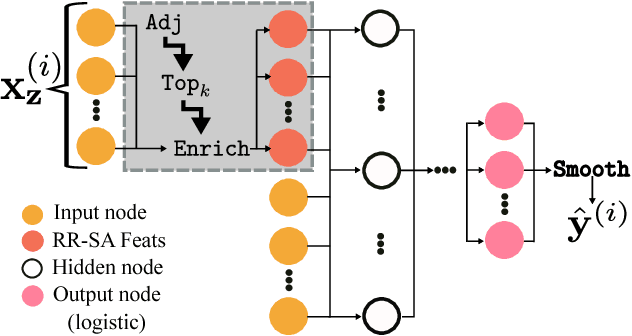
Abstract:Neural networks are capable of learning rich, nonlinear feature representations shown to be beneficial in many predictive tasks. In this work, we use such models to explore different geographical feature representations in the context of predicting colorectal cancer survival curves for patients in the state of Iowa, spanning the years 1989 to 2013. Specifically, we compare model performance using "area between the curves" (ABC) to assess (a) whether survival curves can be reasonably predicted for colorectal cancer patients in the state of Iowa, (b) whether geographical features improve predictive performance, (c) whether a simple binary representation, or a richer, spectral analysis-elicited representation perform better, and (d) whether spectral analysis-based representations can be improved upon by leveraging geographically-descriptive features. In exploring (d), we devise a similarity-based spectral analysis procedure, which allows for the combination of geographically relational and geographically descriptive features. Our findings suggest that survival curves can be reasonably estimated on average, with predictive performance deviating at the five-year survival mark among all models. We also find that geographical features improve predictive performance, and that better performance is obtained using richer, spectral analysis-elicited features. Furthermore, we find that similarity-based spectral analysis-elicited representations improve upon the original spectral analysis results by approximately 40%.
Learning Rich Geographical Representations: Predicting Colorectal Cancer Survival in the State of Iowa
Aug 15, 2017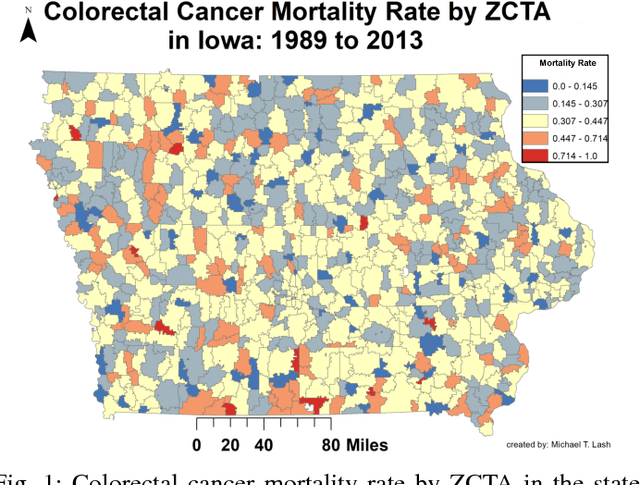
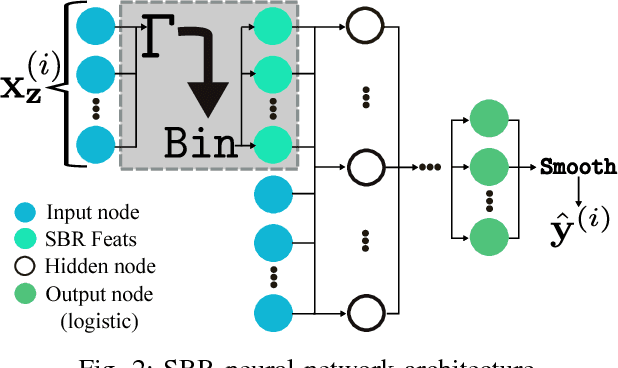
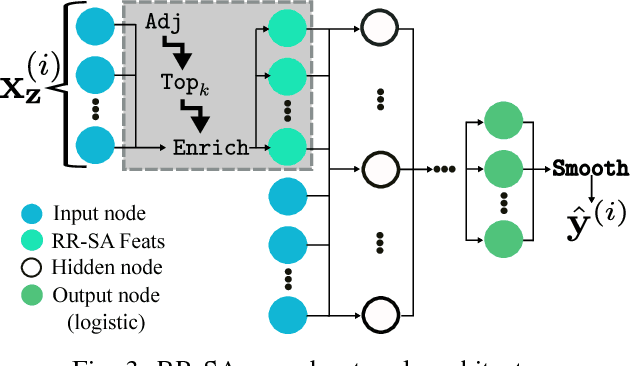
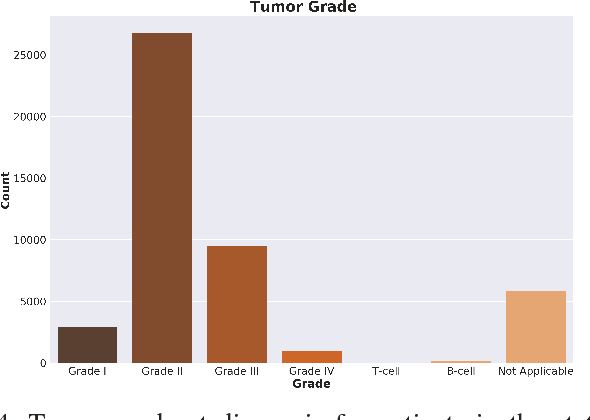
Abstract:Neural networks are capable of learning rich, nonlinear feature representations shown to be beneficial in many predictive tasks. In this work, we use these models to explore the use of geographical features in predicting colorectal cancer survival curves for patients in the state of Iowa, spanning the years 1989 to 2012. Specifically, we compare model performance using a newly defined metric -- area between the curves (ABC) -- to assess (a) whether survival curves can be reasonably predicted for colorectal cancer patients in the state of Iowa, (b) whether geographical features improve predictive performance, and (c) whether a simple binary representation or richer, spectral clustering-based representation perform better. Our findings suggest that survival curves can be reasonably estimated on average, with predictive performance deviating at the five-year survival mark. We also find that geographical features improve predictive performance, and that the best performance is obtained using richer, spectral analysis-elicited features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge