Chanran Kim
Sparse Bayesian Message Passing under Structural Uncertainty
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Semi-supervised learning on real-world graphs is frequently challenged by heterophily, where the observed graph is unreliable or label-disassortative. Many existing graph neural networks either rely on a fixed adjacency structure or attempt to handle structural noise through regularization. In this work, we explicitly capture structural uncertainty by modeling a posterior distribution over signed adjacency matrices, allowing each edge to be positive, negative, or absent. We propose a sparse signed message passing network that is naturally robust to edge noise and heterophily, which can be interpreted from a Bayesian perspective. By combining (i) posterior marginalization over signed graph structures with (ii) sparse signed message aggregation, our approach offers a principled way to handle both edge noise and heterophily. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms strong baseline models on heterophilic benchmarks under both synthetic and real-world structural noise.
InstantFamily: Masked Attention for Zero-shot Multi-ID Image Generation
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:In the field of personalized image generation, the ability to create images preserving concepts has significantly improved. Creating an image that naturally integrates multiple concepts in a cohesive and visually appealing composition can indeed be challenging. This paper introduces "InstantFamily," an approach that employs a novel masked cross-attention mechanism and a multimodal embedding stack to achieve zero-shot multi-ID image generation. Our method effectively preserves ID as it utilizes global and local features from a pre-trained face recognition model integrated with text conditions. Additionally, our masked cross-attention mechanism enables the precise control of multi-ID and composition in the generated images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of InstantFamily through experiments showing its dominance in generating images with multi-ID, while resolving well-known multi-ID generation problems. Additionally, our model achieves state-of-the-art performance in both single-ID and multi-ID preservation. Furthermore, our model exhibits remarkable scalability with a greater number of ID preservation than it was originally trained with.
StyLandGAN: A StyleGAN based Landscape Image Synthesis using Depth-map
May 13, 2022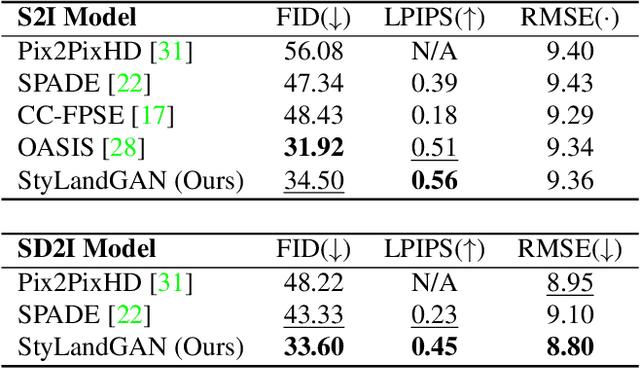
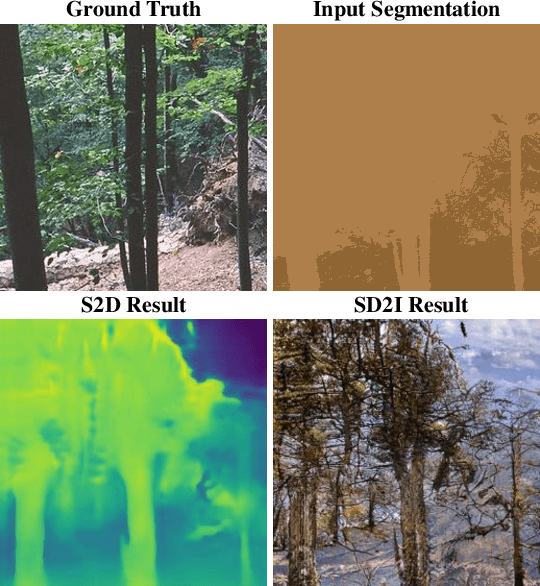
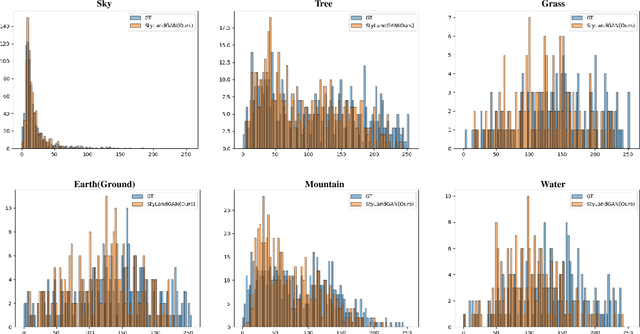
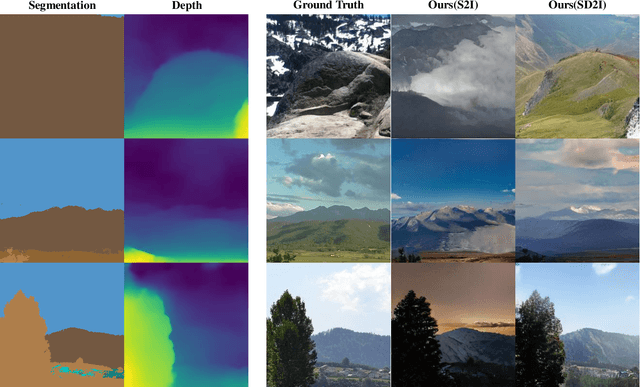
Abstract:Despite recent success in conditional image synthesis, prevalent input conditions such as semantics and edges are not clear enough to express `Linear (Ridges)' and `Planar (Scale)' representations. To address this problem, we propose a novel framework StyLandGAN, which synthesizes desired landscape images using a depth map which has higher expressive power. Our StyleLandGAN is extended from the unconditional generation model to accept input conditions. We also propose a '2-phase inference' pipeline which generates diverse depth maps and shifts local parts so that it can easily reflect user's intend. As a comparison, we modified the existing semantic image synthesis models to accept a depth map as well. Experimental results show that our method is superior to existing methods in quality, diversity, and depth-accuracy.
Data-Efficient Deep Learning Method for Image Classification Using Data Augmentation, Focal Cosine Loss, and Ensemble
Jul 15, 2020



Abstract:In general, sufficient data is essential for the better performance and generalization of deep-learning models. However, lots of limitations(cost, resources, etc.) of data collection leads to lack of enough data in most of the areas. In addition, various domains of each data sources and licenses also lead to difficulties in collection of sufficient data. This situation makes us hard to utilize not only the pre-trained model, but also the external knowledge. Therefore, it is important to leverage small dataset effectively for achieving the better performance. We applied some techniques in three aspects: data, loss function, and prediction to enable training from scratch with less data. With these methods, we obtain high accuracy by leveraging ImageNet data which consist of only 50 images per class. Furthermore, our model is ranked 4th in Visual Inductive Printers for Data-Effective Computer Vision Challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge