Changqi Sun
A knowledge-based data-driven framework for all-day identification of cloud types using satellite remote sensing
Dec 01, 2023
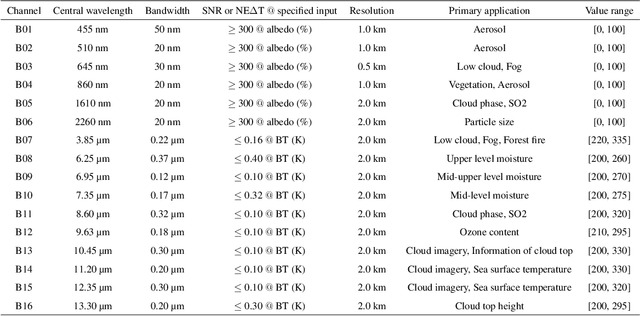
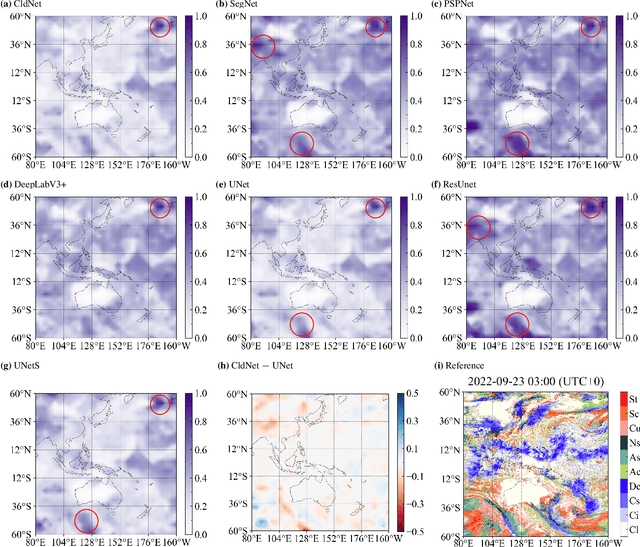
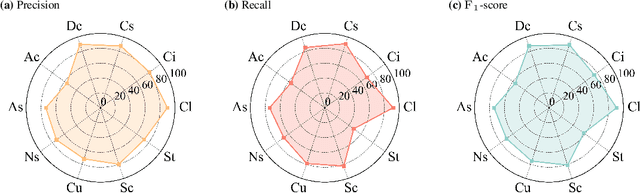
Abstract:Cloud types, as a type of meteorological data, are of particular significance for evaluating changes in rainfall, heatwaves, water resources, floods and droughts, food security and vegetation cover, as well as land use. In order to effectively utilize high-resolution geostationary observations, a knowledge-based data-driven (KBDD) framework for all-day identification of cloud types based on spectral information from Himawari-8/9 satellite sensors is designed. And a novel, simple and efficient network, named CldNet, is proposed. Compared with widely used semantic segmentation networks, including SegNet, PSPNet, DeepLabV3+, UNet, and ResUnet, our proposed model CldNet with an accuracy of 80.89+-2.18% is state-of-the-art in identifying cloud types and has increased by 32%, 46%, 22%, 2%, and 39%, respectively. With the assistance of auxiliary information (e.g., satellite zenith/azimuth angle, solar zenith/azimuth angle), the accuracy of CldNet-W using visible and near-infrared bands and CldNet-O not using visible and near-infrared bands on the test dataset is 82.23+-2.14% and 73.21+-2.02%, respectively. Meanwhile, the total parameters of CldNet are only 0.46M, making it easy for edge deployment. More importantly, the trained CldNet without any fine-tuning can predict cloud types with higher spatial resolution using satellite spectral data with spatial resolution 0.02{\deg}*0.02{\deg}, which indicates that CldNet possesses a strong generalization ability. In aggregate, the KBDD framework using CldNet is a highly effective cloud-type identification system capable of providing a high-fidelity, all-day, spatiotemporal cloud-type database for many climate assessment fields.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge