Changdong Wang
EdgeGFL: Rethinking Edge Information in Graph Feature Preference Learning
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have significant advantages in handling non-Euclidean data and have been widely applied across various areas, thus receiving increasing attention in recent years. The framework of GNN models mainly includes the information propagation phase and the aggregation phase, treating nodes and edges as information entities and propagation channels, respectively. However, most existing GNN models face the challenge of disconnection between node and edge feature information, as these models typically treat the learning of edge and node features as independent tasks. To address this limitation, we aim to develop an edge-empowered graph feature preference learning framework that can capture edge embeddings to assist node embeddings. By leveraging the learned multidimensional edge feature matrix, we construct multi-channel filters to more effectively capture accurate node features, thereby obtaining the non-local structural characteristics and fine-grained high-order node features. Specifically, the inclusion of multidimensional edge information enhances the functionality and flexibility of the GNN model, enabling it to handle complex and diverse graph data more effectively. Additionally, integrating relational representation learning into the message passing framework allows graph nodes to receive more useful information, thereby facilitating node representation learning. Finally, experiments on four real-world heterogeneous graphs demonstrate the effectiveness of theproposed model.
PRSI: Privacy-Preserving Recommendation Model Based on Vector Splitting and Interactive Protocols
Nov 27, 2024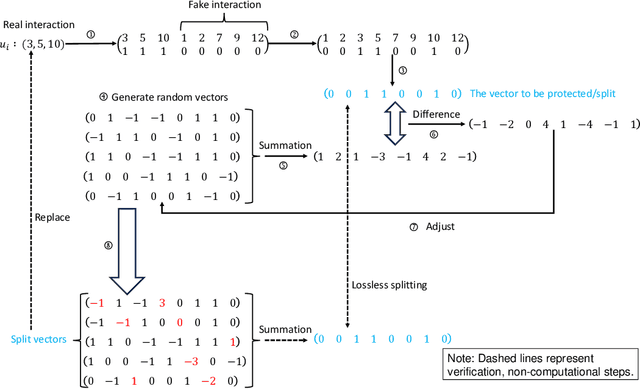

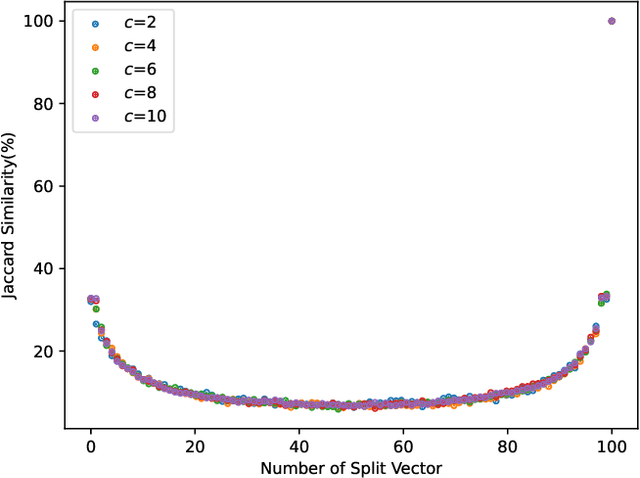
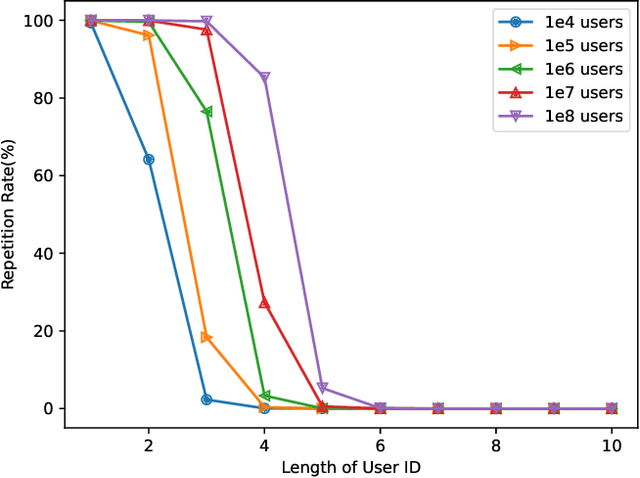
Abstract:With the development of the internet, recommending interesting products to users has become a highly valuable research topic for businesses. Recommendation systems play a crucial role in addressing this issue. To prevent the leakage of each user's (client's) private data, Federated Recommendation Systems (FedRec) have been proposed and widely used. However, extensive research has shown that FedRec suffers from security issues such as data privacy leakage, and it is challenging to train effective models with FedRec when each client only holds interaction information for a single user. To address these two problems, this paper proposes a new privacy-preserving recommendation system (PRSI), which includes a preprocessing module and two main phases. The preprocessing module employs split vectors and fake interaction items to protect clients' interaction information and recommendation results. The two main phases are: (1) the collection of interaction information and (2) the sending of recommendation results. In the interaction information collection phase, each client uses the preprocessing module and random communication methods (according to the designed interactive protocol) to protect their ID information and IP addresses. In the recommendation results sending phase, the central server uses the preprocessing module and triplets to distribute recommendation results to each client under secure conditions, following the designed interactive protocol. Finally, we conducted multiple sets of experiments to verify the security, accuracy, and communication cost of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge