Chang-tsun Li
Atypical Facial Landmark Localisation with Stacked Hourglass Networks: A Study on 3D Facial Modelling for Medical Diagnosis
Sep 05, 2019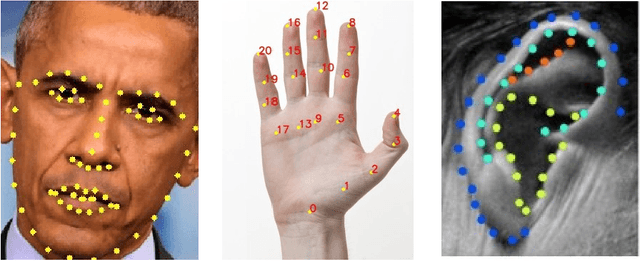

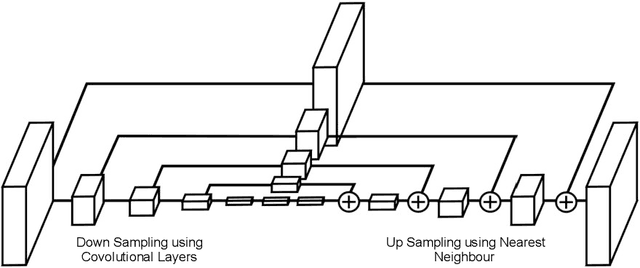
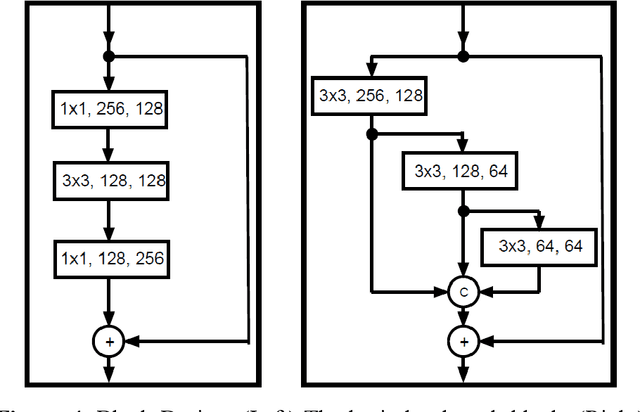
Abstract:While facial biometrics has been widely used for identification purpose, it has recently been researched as medical biometrics for a range of diseases. In this chapter, we investigate the facial landmark detection for atypical 3D facial modelling in facial palsy cases, while potentially such modelling can assist the medical diagnosis using atypical facial features. In our work, a study of landmarks localisation methods such as stacked hourglass networks is conducted and evaluated to ascertain their accuracy when presented with unseen atypical faces. The evaluation highlights that the state-of-the-art stacked hourglass architecture outperforms other traditional methods.
* In press, 2019
Homogeneous Feature Transfer and Heterogeneous Location Fine-tuning for Cross-City Property Appraisal Framework
Dec 11, 2018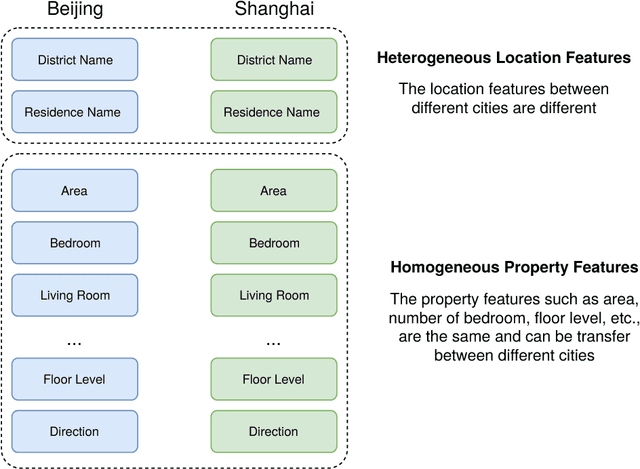
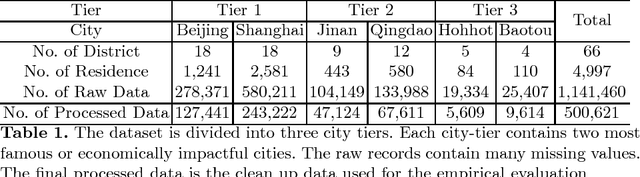
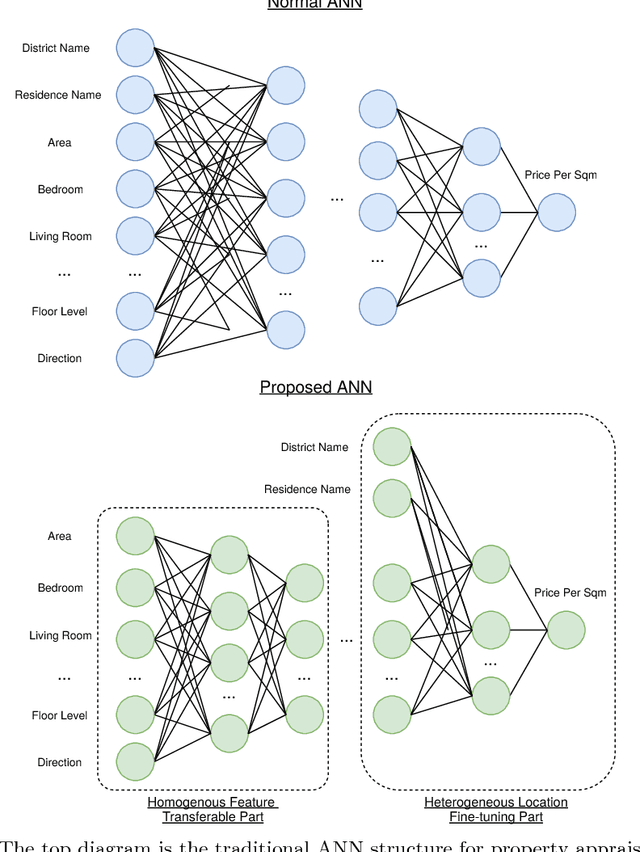
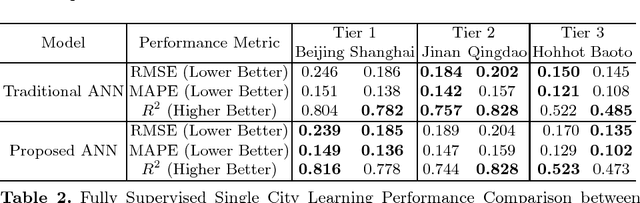
Abstract:Most existing real estate appraisal methods focus on building accuracy and reliable models from a given dataset but pay little attention to the extensibility of their trained model. As different cities usually contain a different set of location features (district names, apartment names), most existing mass appraisal methods have to train a new model from scratch for different cities or regions. As a result, these approaches require massive data collection for each city and the total training time for a multi-city property appraisal system will be extremely long. Besides, some small cities may not have enough data for training a robust appraisal model. To overcome these limitations, we develop a novel Homogeneous Feature Transfer and Heterogeneous Location Fine-tuning (HFT+HLF) cross-city property appraisal framework. By transferring partial neural network learning from a source city and fine-tuning on the small amount of location information of a target city, our semi-supervised model can achieve similar or even superior performance compared to a fully supervised Artificial neural network (ANN) method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge