Camelia Constantin
Leiden-Fusion Partitioning Method for Effective Distributed Training of Graph Embeddings
Sep 15, 2024Abstract:In the area of large-scale training of graph embeddings, effective training frameworks and partitioning methods are critical for handling large networks. However, they face two major challenges: 1) existing synchronized distributed frameworks require continuous communication to access information from other machines, and 2) the inability of current partitioning methods to ensure that subgraphs remain connected components without isolated nodes, which is essential for effective training of GNNs since training relies on information aggregation from neighboring nodes. To address these issues, we introduce a novel partitioning method, named Leiden-Fusion, designed for large-scale training of graphs with minimal communication. Our method extends the Leiden community detection algorithm with a greedy algorithm that merges the smallest communities with highly connected neighboring communities. Our method guarantees that, for an initially connected graph, each partition is a densely connected subgraph with no isolated nodes. After obtaining the partitions, we train a GNN for each partition independently, and finally integrate all embeddings for node classification tasks, which significantly reduces the need for network communication and enhances the efficiency of distributed graph training. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through extensive evaluations on several benchmark datasets, achieving high efficiency while preserving the quality of the graph embeddings for node classification tasks.
ATEM: A Topic Evolution Model for the Detection of Emerging Topics in Scientific Archives
Jun 04, 2023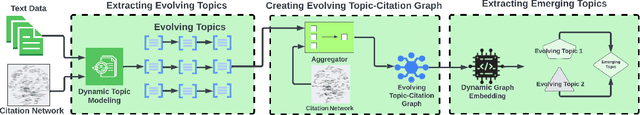

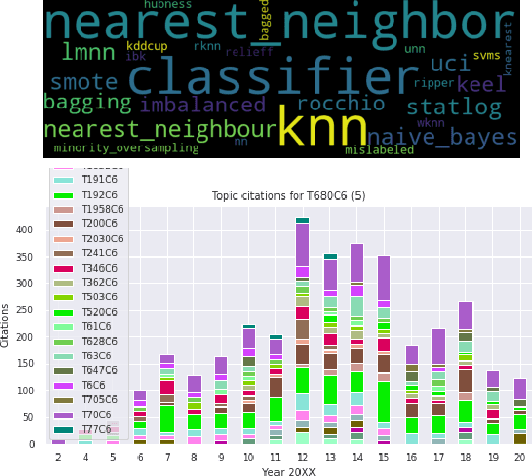
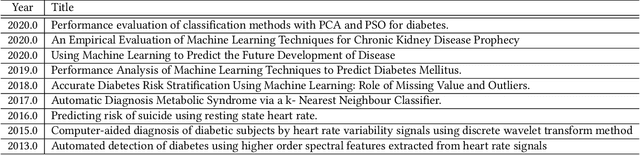
Abstract:This paper presents ATEM, a novel framework for studying topic evolution in scientific archives. ATEM is based on dynamic topic modeling and dynamic graph embedding techniques that explore the dynamics of content and citations of documents within a scientific corpus. ATEM explores a new notion of contextual emergence for the discovery of emerging interdisciplinary research topics based on the dynamics of citation links in topic clusters. Our experiments show that ATEM can efficiently detect emerging cross-disciplinary topics within the DBLP archive of over five million computer science articles.
Contextualized Topic Coherence Metrics
May 23, 2023Abstract:The recent explosion in work on neural topic modeling has been criticized for optimizing automated topic evaluation metrics at the expense of actual meaningful topic identification. But human annotation remains expensive and time-consuming. We propose LLM-based methods inspired by standard human topic evaluations, in a family of metrics called Contextualized Topic Coherence (CTC). We evaluate both a fully automated version as well as a semi-automated CTC that allows human-centered evaluation of coherence while maintaining the efficiency of automated methods. We evaluate CTC relative to five other metrics on six topic models and find that it outperforms automated topic coherence methods, works well on short documents, and is not susceptible to meaningless but high-scoring topics.
ANTM: An Aligned Neural Topic Model for Exploring Evolving Topics
Feb 03, 2023
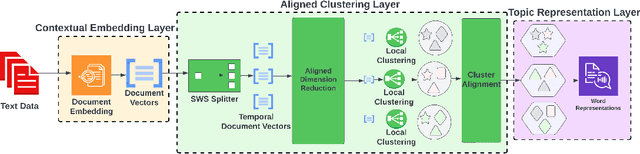
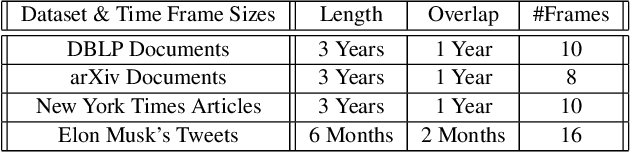
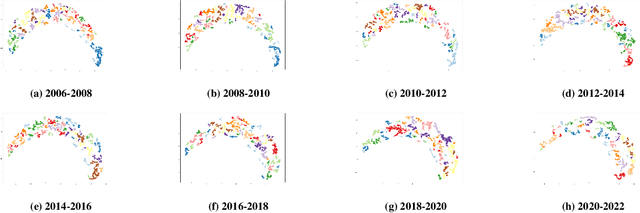
Abstract:As the amount of text data generated by humans and machines increases, the necessity of understanding large corpora and finding a way to extract insights from them is becoming more crucial than ever. Dynamic topic models are effective methods that primarily focus on studying the evolution of topics present in a collection of documents. These models are widely used for understanding trends, exploring public opinion in social networks, or tracking research progress and discoveries in scientific archives. Since topics are defined as clusters of semantically similar documents, it is necessary to observe the changes in the content or themes of these clusters in order to understand how topics evolve as new knowledge is discovered over time. In this paper, we introduce the Aligned Neural Topic Model (ANTM), a dynamic neural topic model that uses document embeddings to compute clusters of semantically similar documents at different periods and to align document clusters to represent their evolution. This alignment procedure preserves the temporal similarity of document clusters over time and captures the semantic change of words characterized by their context within different periods. Experiments on four different datasets show that ANTM outperforms probabilistic dynamic topic models (e.g. DTM, DETM) and significantly improves topic coherence and diversity over other existing dynamic neural topic models (e.g. BERTopic).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge