Calvin Barrett
Measuring and mitigating voting access disparities: a study of race and polling locations in Florida and North Carolina
May 30, 2022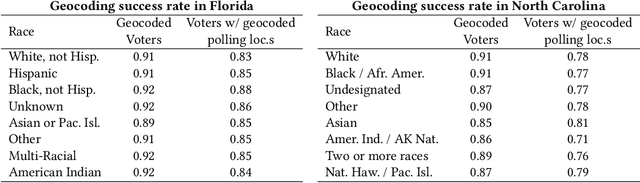
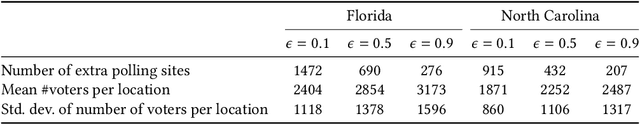
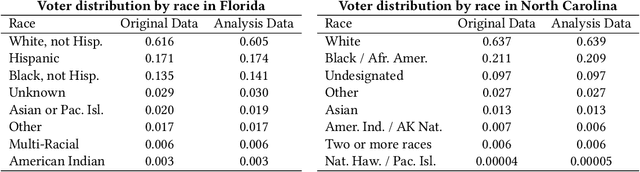

Abstract:Voter suppression and associated racial disparities in access to voting are long-standing civil rights concerns in the United States. Barriers to voting have taken many forms over the decades. A history of violent explicit discouragement has shifted to more subtle access limitations that can include long lines and wait times, long travel times to reach a polling station, and other logistical barriers to voting. Our focus in this work is on quantifying disparities in voting access pertaining to the overall time-to-vote, and how they could be remedied via a better choice of polling location or provisioning more sites where voters can cast ballots. However, appropriately calibrating access disparities is difficult because of the need to account for factors such as population density and different community expectations for reasonable travel times. In this paper, we quantify access to polling locations, developing a methodology for the calibrated measurement of racial disparities in polling location "load" and distance to polling locations. We apply this methodology to a study of real-world data from Florida and North Carolina to identify disparities in voting access from the 2020 election. We also introduce algorithms, with modifications to handle scale, that can reduce these disparities by suggesting new polling locations from a given list of identified public locations (including schools and libraries). Applying these algorithms on the 2020 election location data also helps to expose and explore tradeoffs between the cost of allocating more polling locations and the potential impact on access disparities. The developed voting access measurement methodology and algorithmic remediation technique is a first step in better polling location assignment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge