C. Zhang
Transformer Language Models with LSTM-based Cross-utterance Information Representation
Feb 12, 2021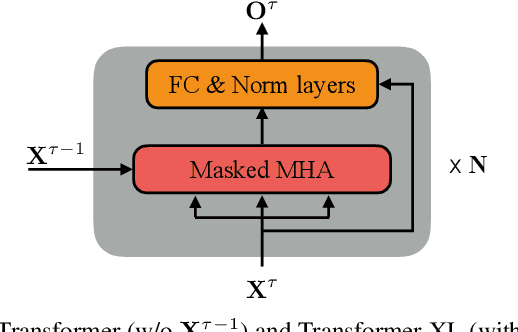
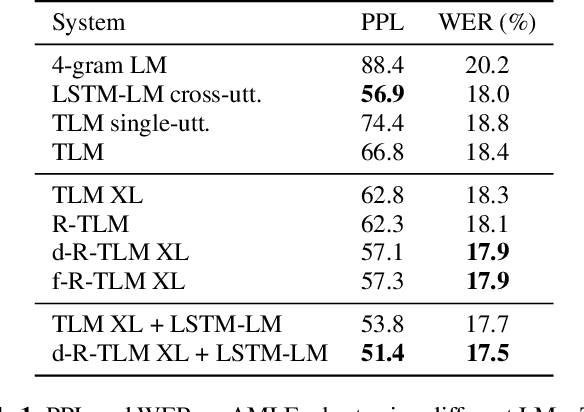
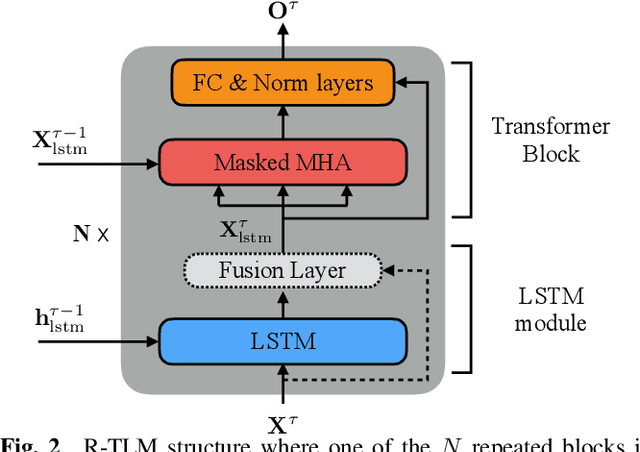
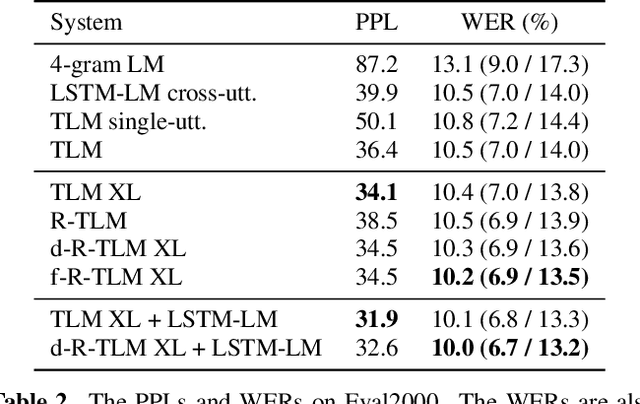
Abstract:The effective incorporation of cross-utterance information has the potential to improve language models (LMs) for automatic speech recognition (ASR). To extract more powerful and robust cross-utterance representations for the Transformer LM (TLM), this paper proposes the R-TLM which uses hidden states in a long short-term memory (LSTM) LM. To encode the cross-utterance information, the R-TLM incorporates an LSTM module together with a segment-wise recurrence in some of the Transformer blocks. In addition to the LSTM module output, a shortcut connection using a fusion layer that bypasses the LSTM module is also investigated. The proposed system was evaluated on the AMI meeting corpus, the Eval2000 and the RT03 telephone conversation evaluation sets. The best R-TLM achieved 0.9%, 0.6%, and 0.8% absolute WER reductions over the single-utterance TLM baseline, and 0.5%, 0.3%, 0.2% absolute WER reductions over a strong cross-utterance TLM baseline on the AMI evaluation set, Eval2000 and RT03 respectively. Improvements on Eval2000 and RT03 were further supported by significance tests. R-TLMs were found to have better LM scores on words where recognition errors are more likely to occur. The R-TLM WER can be further reduced by interpolation with an LSTM-LM.
Content-Aware Speaker Embeddings for Speaker Diarisation
Feb 12, 2021
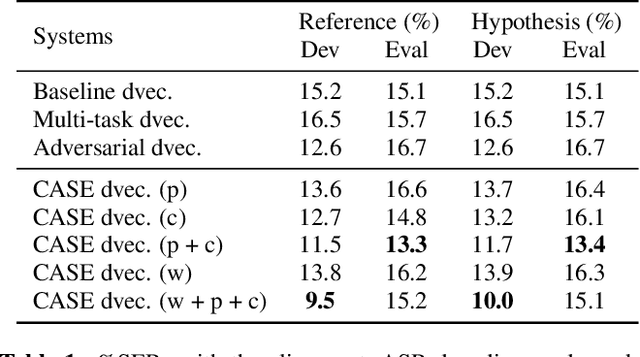
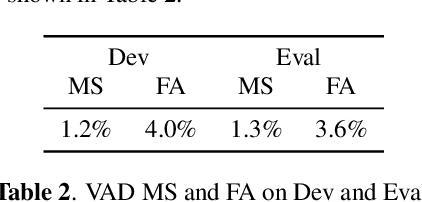

Abstract:Recent speaker diarisation systems often convert variable length speech segments into fixed-length vector representations for speaker clustering, which are known as speaker embeddings. In this paper, the content-aware speaker embeddings (CASE) approach is proposed, which extends the input of the speaker classifier to include not only acoustic features but also their corresponding speech content, via phone, character, and word embeddings. Compared to alternative methods that leverage similar information, such as multitask or adversarial training, CASE factorises automatic speech recognition (ASR) from speaker recognition to focus on modelling speaker characteristics and correlations with the corresponding content units to derive more expressive representations. CASE is evaluated for speaker re-clustering with a realistic speaker diarisation setup using the AMI meeting transcription dataset, where the content information is obtained by performing ASR based on an automatic segmentation. Experimental results showed that CASE achieved a 17.8% relative speaker error rate reduction over conventional methods.
Cross-Utterance Language Models with Acoustic Error Sampling
Aug 19, 2020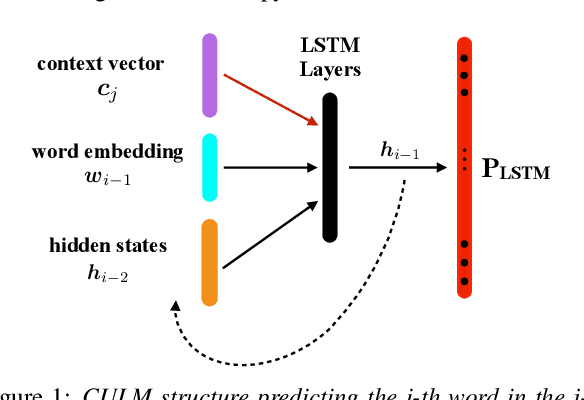

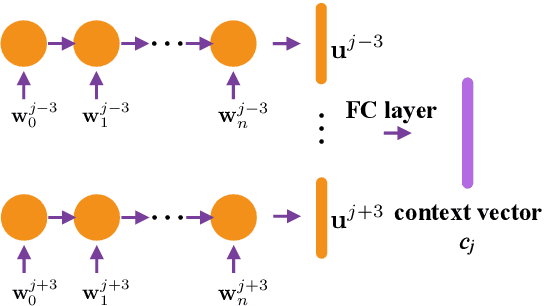

Abstract:The effective exploitation of richer contextual information in language models (LMs) is a long-standing research problem for automatic speech recognition (ASR). A cross-utterance LM (CULM) is proposed in this paper, which augments the input to a standard long short-term memory (LSTM) LM with a context vector derived from past and future utterances using an extraction network. The extraction network uses another LSTM to encode surrounding utterances into vectors which are integrated into a context vector using either a projection of LSTM final hidden states, or a multi-head self-attentive layer. In addition, an acoustic error sampling technique is proposed to reduce the mismatch between training and test-time. This is achieved by considering possible ASR errors into the model training procedure, and can therefore improve the word error rate (WER). Experiments performed on both AMI and Switchboard datasets show that CULMs outperform the LSTM LM baseline WER. In particular, the CULM with a self-attentive layer-based extraction network and acoustic error sampling achieves 0.6% absolute WER reduction on AMI, 0.3% WER reduction on the Switchboard part and 0.9% WER reduction on the Callhome part of Eval2000 test set over the respective baselines.
A Deep Neural Network for Pixel-Level Electromagnetic Particle Identification in the MicroBooNE Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber
Aug 22, 2018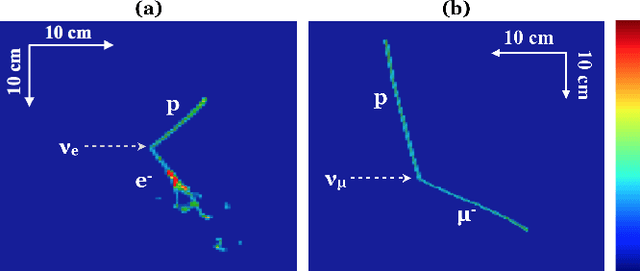
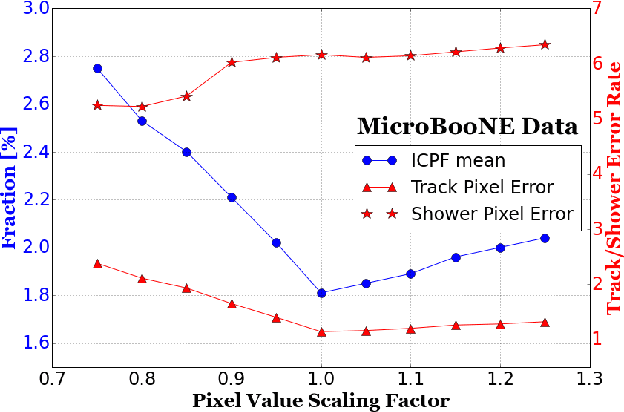
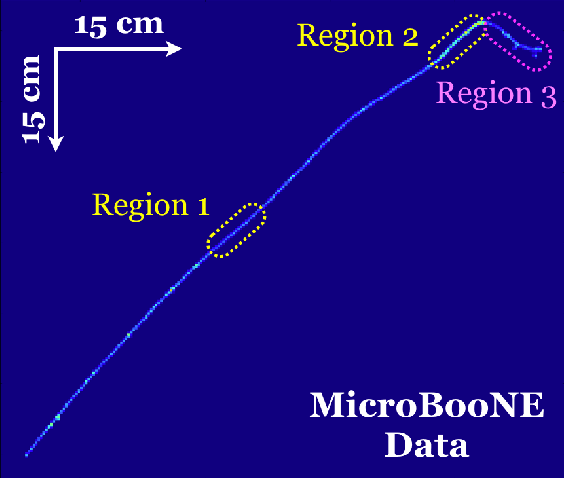
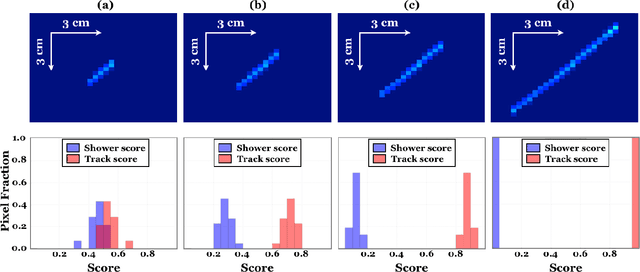
Abstract:We have developed a convolutional neural network (CNN) that can make a pixel-level prediction of objects in image data recorded by a liquid argon time projection chamber (LArTPC) for the first time. We describe the network design, training techniques, and software tools developed to train this network. The goal of this work is to develop a complete deep neural network based data reconstruction chain for the MicroBooNE detector. We show the first demonstration of a network's validity on real LArTPC data using MicroBooNE collection plane images. The demonstration is performed for stopping muon and a $\nu_\mu$ charged current neutral pion data samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge