Brian Henn
SamudrACE: Fast and Accurate Coupled Climate Modeling with 3D Ocean and Atmosphere Emulators
Sep 15, 2025


Abstract:Traditional numerical global climate models simulate the full Earth system by exchanging boundary conditions between separate simulators of the atmosphere, ocean, sea ice, land surface, and other geophysical processes. This paradigm allows for distributed development of individual components within a common framework, unified by a coupler that handles translation between realms via spatial or temporal alignment and flux exchange. Following a similar approach adapted for machine learning-based emulators, we present SamudrACE: a coupled global climate model emulator which produces centuries-long simulations at 1-degree horizontal, 6-hourly atmospheric, and 5-daily oceanic resolution, with 145 2D fields spanning 8 atmospheric and 19 oceanic vertical levels, plus sea ice, surface, and top-of-atmosphere variables. SamudrACE is highly stable and has low climate biases comparable to those of its components with prescribed boundary forcing, with realistic variability in coupled climate phenomena such as ENSO that is not possible to simulate in uncoupled mode.
ACE2: Accurately learning subseasonal to decadal atmospheric variability and forced responses
Nov 18, 2024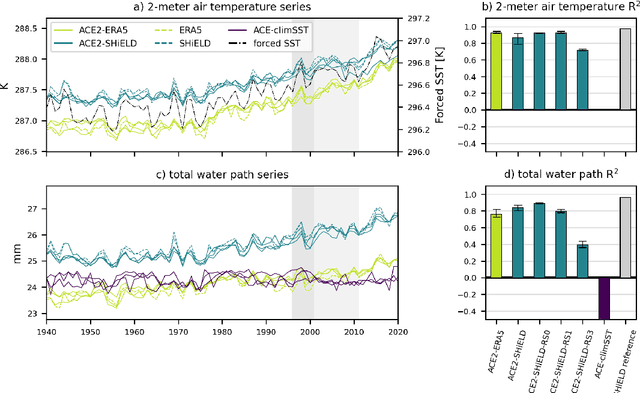
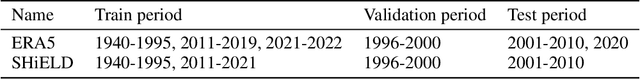
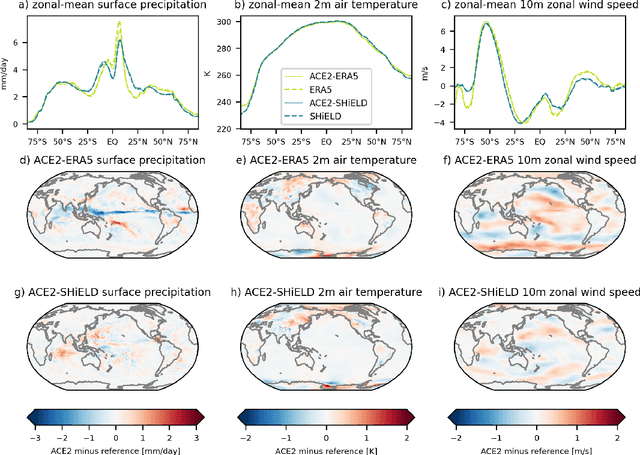

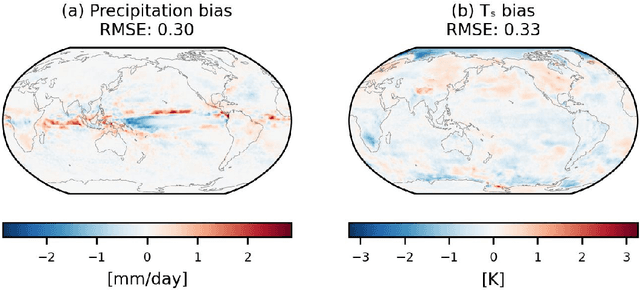
Abstract:Existing machine learning models of weather variability are not formulated to enable assessment of their response to varying external boundary conditions such as sea surface temperature and greenhouse gases. Here we present ACE2 (Ai2 Climate Emulator version 2) and its application to reproducing atmospheric variability over the past 80 years on timescales from days to decades. ACE2 is a 450M-parameter autoregressive machine learning emulator, operating with 6-hour temporal resolution, 1{\deg} horizontal resolution and eight vertical layers. It exactly conserves global dry air mass and moisture and can be stepped forward stably for arbitrarily many steps with a throughput of about 1500 simulated years per wall clock day. ACE2 generates emergent phenomena such as tropical cyclones, the Madden Julian Oscillation, and sudden stratospheric warmings. Furthermore, it accurately reproduces the atmospheric response to El Ni\~no variability and global trends of temperature over the past 80 years. However, its sensitivities to separately changing sea surface temperature and carbon dioxide are not entirely realistic.
Probabilistic Emulation of a Global Climate Model with Spherical DYffusion
Jun 21, 2024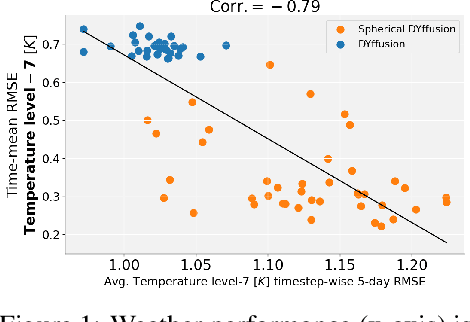
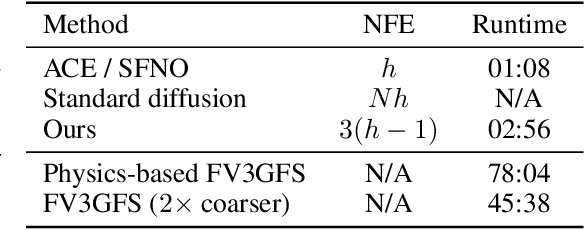
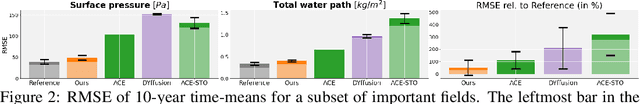
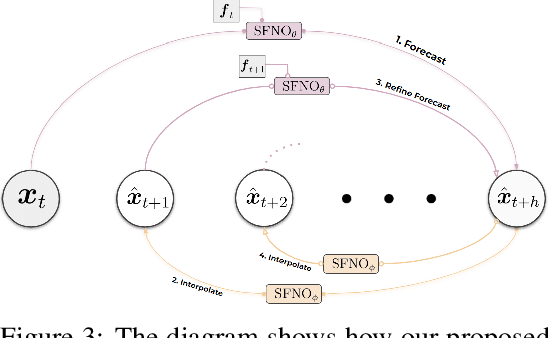
Abstract:Data-driven deep learning models are on the verge of transforming global weather forecasting. It is an open question if this success can extend to climate modeling, where long inference rollouts and data complexity pose significant challenges. Here, we present the first conditional generative model able to produce global climate ensemble simulations that are accurate and physically consistent. Our model runs at 6-hourly time steps and is shown to be stable for 10-year-long simulations. Our approach beats relevant baselines and nearly reaches a gold standard for successful climate model emulation. We discuss the key design choices behind our dynamics-informed diffusion model-based approach which enables this significant step towards efficient, data-driven climate simulations that can help us better understand the Earth and adapt to a changing climate.
ACE: A fast, skillful learned global atmospheric model for climate prediction
Oct 03, 2023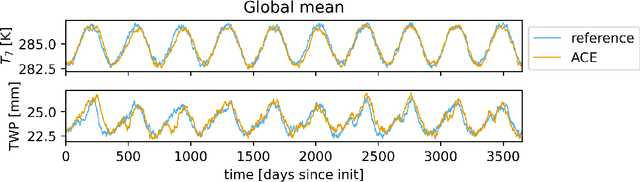
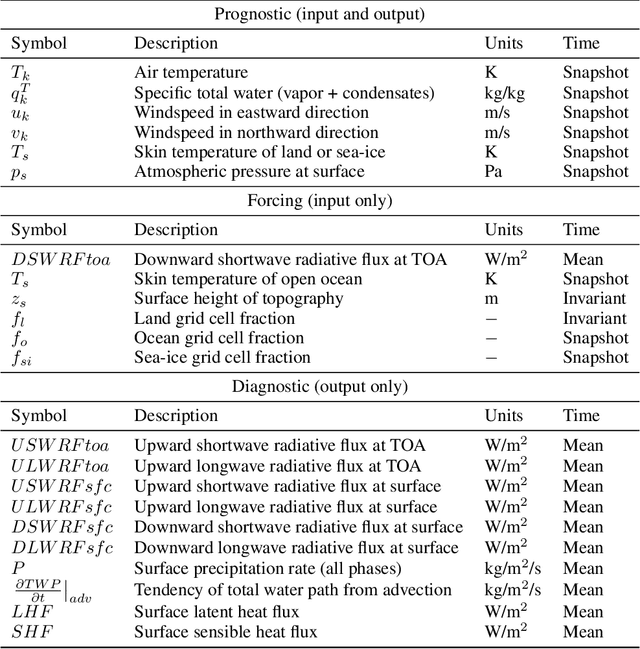
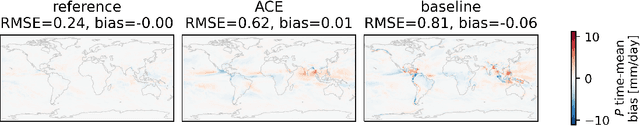

Abstract:Existing ML-based atmospheric models are not suitable for climate prediction, which requires long-term stability and physical consistency. We present ACE (AI2 Climate Emulator), a 200M-parameter, autoregressive machine learning emulator of an existing comprehensive 100-km resolution global atmospheric model. The formulation of ACE allows evaluation of physical laws such as the conservation of mass and moisture. The emulator is stable for 10 years, nearly conserves column moisture without explicit constraints and faithfully reproduces the reference model's climate, outperforming a challenging baseline on over 80% of tracked variables. ACE requires nearly 100x less wall clock time and is 100x more energy efficient than the reference model using typically available resources.
Machine-learned climate model corrections from a global storm-resolving model
Nov 21, 2022Abstract:Due to computational constraints, running global climate models (GCMs) for many years requires a lower spatial grid resolution (${\gtrsim}50$ km) than is optimal for accurately resolving important physical processes. Such processes are approximated in GCMs via subgrid parameterizations, which contribute significantly to the uncertainty in GCM predictions. One approach to improving the accuracy of a coarse-grid global climate model is to add machine-learned state-dependent corrections at each simulation timestep, such that the climate model evolves more like a high-resolution global storm-resolving model (GSRM). We train neural networks to learn the state-dependent temperature, humidity, and radiative flux corrections needed to nudge a 200 km coarse-grid climate model to the evolution of a 3~km fine-grid GSRM. When these corrective ML models are coupled to a year-long coarse-grid climate simulation, the time-mean spatial pattern errors are reduced by 6-25% for land surface temperature and 9-25% for land surface precipitation with respect to a no-ML baseline simulation. The ML-corrected simulations develop other biases in climate and circulation that differ from, but have comparable amplitude to, the baseline simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge