Brian Bingham
DAVE Aquatic Virtual Environment: Toward a General Underwater Robotics Simulator
Sep 06, 2022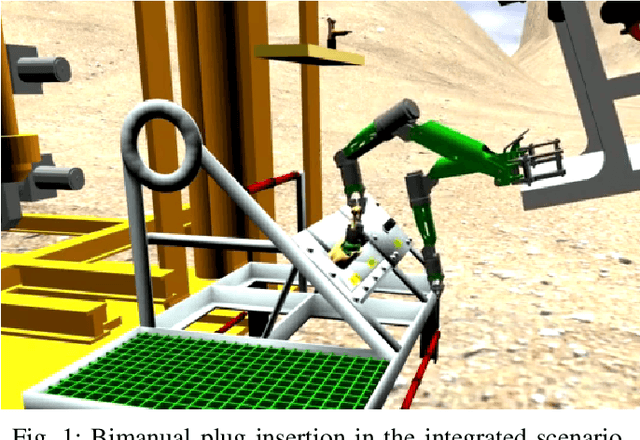
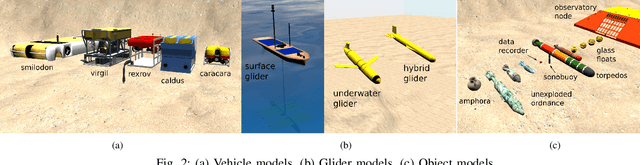

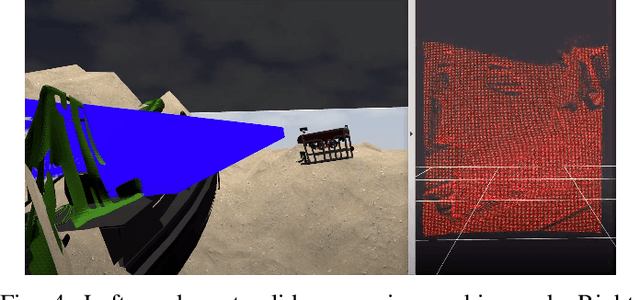
Abstract:We present DAVE Aquatic Virtual Environment (DAVE), an open source simulation stack for underwater robots, sensors, and environments. Conventional robotics simulators are not designed to address unique challenges that come with the marine environment, including but not limited to environment conditions that vary spatially and temporally, impaired or challenging perception, and the unavailability of data in a generally unexplored environment. Given the variety of sensors and platforms, wheels are often reinvented for specific use cases that inevitably resist wider adoption. Building on existing simulators, we provide a framework to help speed up the development and evaluation of algorithms that would otherwise require expensive and time-consuming operations at sea. The framework includes basic building blocks (e.g., new vehicles, water-tracking Doppler Velocity Logger, physics-based multibeam sonar) as well as development tools (e.g., dynamic bathymetry spawning, ocean currents), which allows the user to focus on methodology rather than software infrastructure. We demonstrate usage through example scenarios, bathymetric data import, user interfaces for data inspection and motion planning for manipulation, and visualizations.
Ocean Plume Tracking with Unmanned Surface Vessels: Algorithms and Experiments
Apr 23, 2018



Abstract:Pollution plume monitoring using autonomous vehicles is important due to the adverse effect of pollution plumes on the environment and associated monetary losses. Using the advection-diffusion plume dispersion model, we present a control law design to track dynamic concentration level curves. We also present a gradient and divergence estimation method to enable this control law from concentration measurement only. We then present the field testing results of the control law to track concentration level curves in a plume generated using Rhodamine dye as a pollution surrogate in a near-shore marine environment. These plumes are then autonomously tracked using an unmanned surface vessel equipped with fluorometer sensors. Field experimental results are shown to evaluate the performance of the controller, and complexities of field experiments in real-world marine environments are discussed in the paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge