Bradley P. Allen
A Benchmark for the Detection of Metalinguistic Disagreements between LLMs and Knowledge Graphs
Feb 05, 2025
Abstract:Evaluating large language models (LLMs) for tasks like fact extraction in support of knowledge graph construction frequently involves computing accuracy metrics using a ground truth benchmark based on a knowledge graph (KG). These evaluations assume that errors represent factual disagreements. However, human discourse frequently features metalinguistic disagreement, where agents differ not on facts but on the meaning of the language used to express them. Given the complexity of natural language processing and generation using LLMs, we ask: do metalinguistic disagreements occur between LLMs and KGs? Based on an investigation using the T-REx knowledge alignment dataset, we hypothesize that metalinguistic disagreement does in fact occur between LLMs and KGs, with potential relevance for the practice of knowledge graph engineering. We propose a benchmark for evaluating the detection of factual and metalinguistic disagreements between LLMs and KGs. An initial proof of concept of such a benchmark is available on Github.
Evaluating Class Membership Relations in Knowledge Graphs using Large Language Models
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:A backbone of knowledge graphs are their class membership relations, which assign entities to a given class. As part of the knowledge engineering process, we propose a new method for evaluating the quality of these relations by processing descriptions of a given entity and class using a zero-shot chain-of-thought classifier that uses a natural language intensional definition of a class. We evaluate the method using two publicly available knowledge graphs, Wikidata and CaLiGraph, and 7 large language models. Using the gpt-4-0125-preview large language model, the method's classification performance achieves a macro-averaged F1-score of 0.830 on data from Wikidata and 0.893 on data from CaLiGraph. Moreover, a manual analysis of the classification errors shows that 40.9% of errors were due to the knowledge graphs, with 16.0% due to missing relations and 24.9% due to incorrectly asserted relations. These results show how large language models can assist knowledge engineers in the process of knowledge graph refinement. The code and data are available on Github.
SHROOM-INDElab at SemEval-2024 Task 6: Zero- and Few-Shot LLM-Based Classification for Hallucination Detection
Apr 04, 2024



Abstract:We describe the University of Amsterdam Intelligent Data Engineering Lab team's entry for the SemEval-2024 Task 6 competition. The SHROOM-INDElab system builds on previous work on using prompt programming and in-context learning with large language models (LLMs) to build classifiers for hallucination detection, and extends that work through the incorporation of context-specific definition of task, role, and target concept, and automated generation of examples for use in a few-shot prompting approach. The resulting system achieved fourth-best and sixth-best performance in the model-agnostic track and model-aware tracks for Task 6, respectively, and evaluation using the validation sets showed that the system's classification decisions were consistent with those of the crowd-sourced human labellers. We further found that a zero-shot approach provided better accuracy than a few-shot approach using automatically generated examples. Code for the system described in this paper is available on Github.
Standardizing Knowledge Engineering Practices with a Reference Architecture
Apr 04, 2024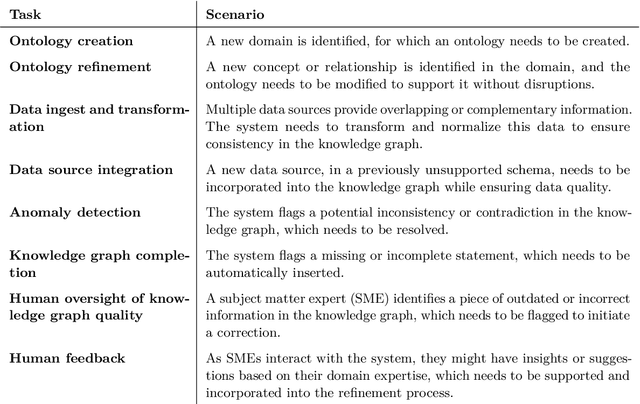
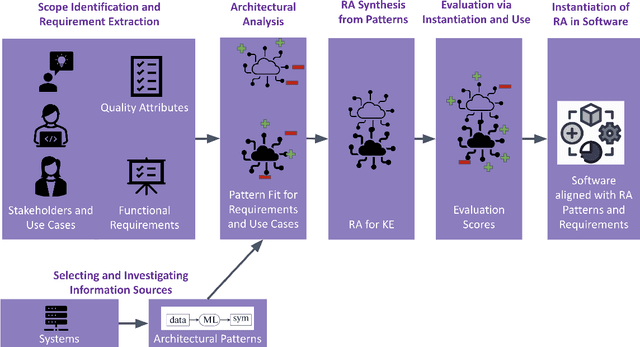
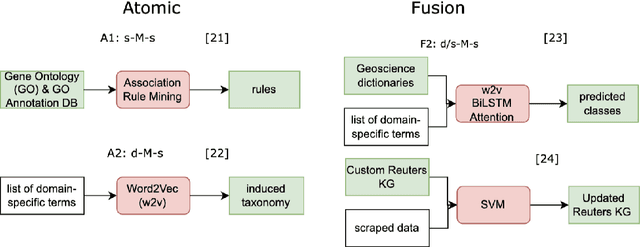
Abstract:Knowledge engineering is the process of creating and maintaining knowledge-producing systems. Throughout the history of computer science and AI, knowledge engineering workflows have been widely used given the importance of high-quality knowledge for reliable intelligent agents. Meanwhile, the scope of knowledge engineering, as apparent from its target tasks and use cases, has been shifting, together with its paradigms such as expert systems, semantic web, and language modeling. The intended use cases and supported user requirements between these paradigms have not been analyzed globally, as new paradigms often satisfy prior pain points while possibly introducing new ones. The recent abstraction of systemic patterns into a boxology provides an opening for aligning the requirements and use cases of knowledge engineering with the systems, components, and software that can satisfy them best. This paper proposes a vision of harmonizing the best practices in the field of knowledge engineering by leveraging the software engineering methodology of creating reference architectures. We describe how a reference architecture can be iteratively designed and implemented to associate user needs with recurring systemic patterns, building on top of existing knowledge engineering workflows and boxologies. We provide a six-step roadmap that can enable the development of such an architecture, providing an initial design and outcome of the definition of architectural scope, selection of information sources, and analysis. We expect that following through on this vision will lead to well-grounded reference architectures for knowledge engineering, will advance the ongoing initiatives of organizing the neurosymbolic knowledge engineering space, and will build new links to the software architectures and data science communities.
Conceptual Engineering Using Large Language Models
Dec 01, 2023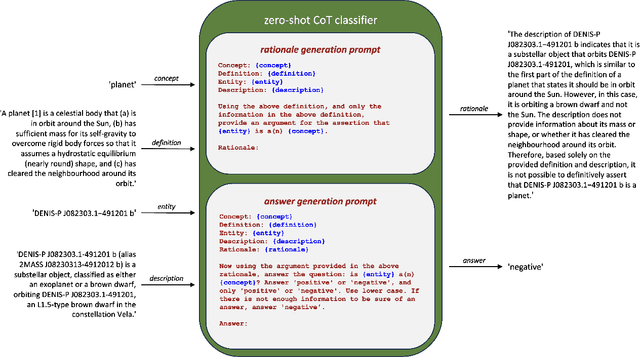
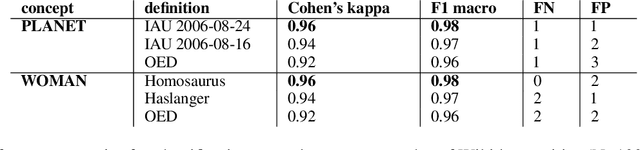
Abstract:We describe a method, based on Jennifer Nado's definition of classification procedures as targets of conceptual engineering, that implements such procedures using a large language model. We then apply this method using data from the Wikidata knowledge graph to evaluate concept definitions from two paradigmatic conceptual engineering projects: the International Astronomical Union's redefinition of PLANET and Haslanger's ameliorative analysis of WOMAN. We discuss implications of this work for the theory and practice of conceptual engineering. The code and data can be found on GitHub.
Knowledge Engineering using Large Language Models
Oct 01, 2023Abstract:Knowledge engineering is a discipline that focuses on the creation and maintenance of processes that generate and apply knowledge. Traditionally, knowledge engineering approaches have focused on knowledge expressed in formal languages. The emergence of large language models and their capabilities to effectively work with natural language, in its broadest sense, raises questions about the foundations and practice of knowledge engineering. Here, we outline the potential role of LLMs in knowledge engineering, identifying two central directions: 1) creating hybrid neuro-symbolic knowledge systems; and 2) enabling knowledge engineering in natural language. Additionally, we formulate key open research questions to tackle these directions.
Identifying and Consolidating Knowledge Engineering Requirements
Jun 27, 2023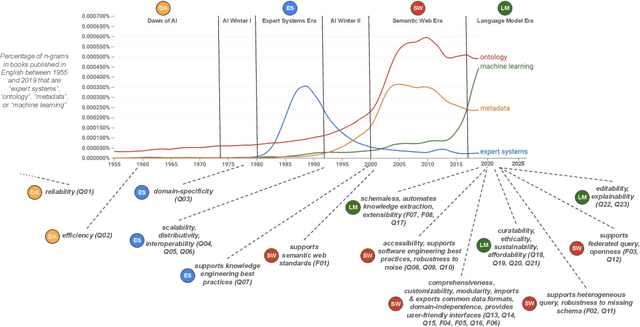
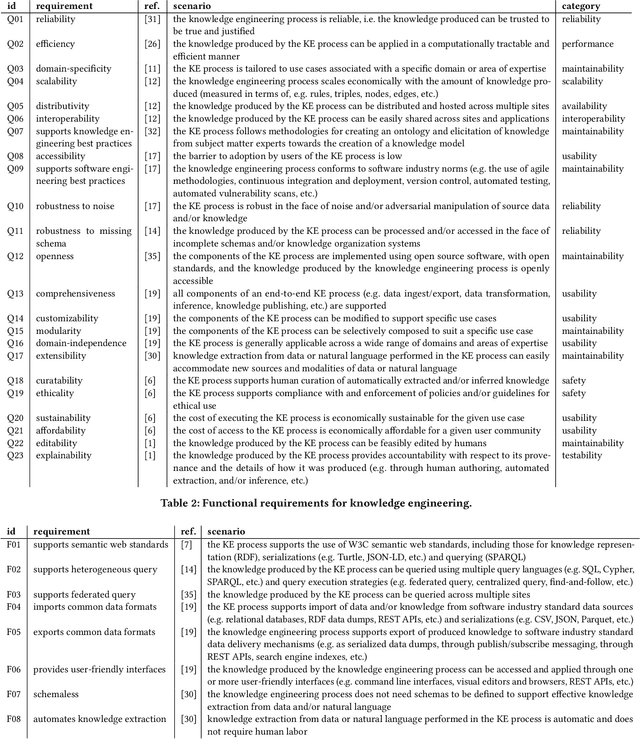
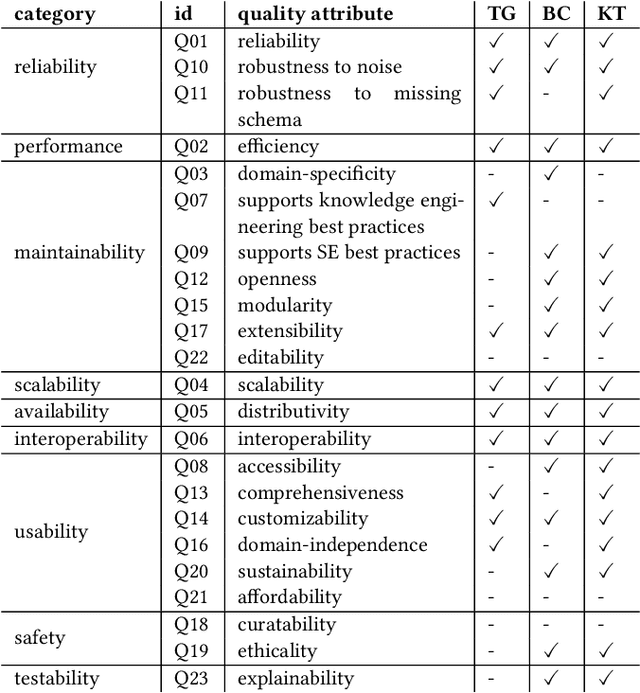
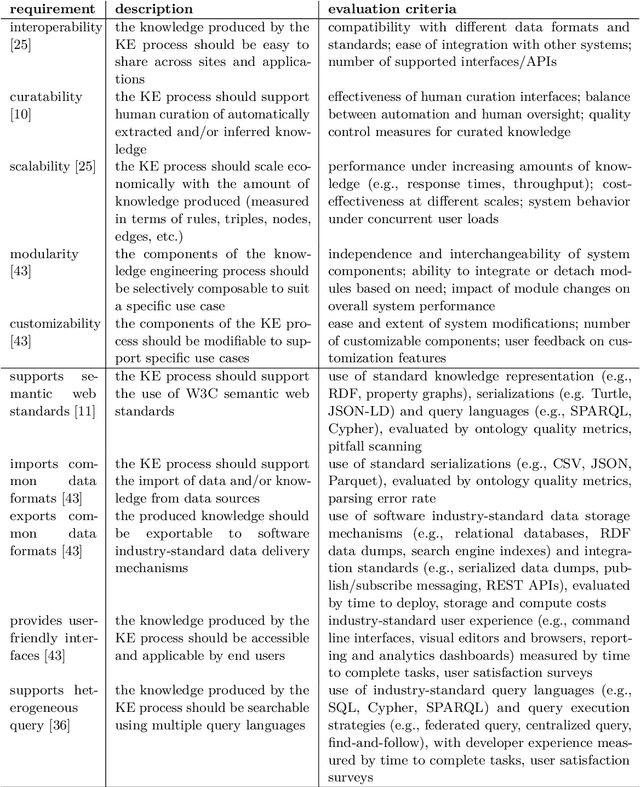
Abstract:Knowledge engineering is the process of creating and maintaining knowledge-producing systems. Throughout the history of computer science and AI, knowledge engineering workflows have been widely used because high-quality knowledge is assumed to be crucial for reliable intelligent agents. However, the landscape of knowledge engineering has changed, presenting four challenges: unaddressed stakeholder requirements, mismatched technologies, adoption barriers for new organizations, and misalignment with software engineering practices. In this paper, we propose to address these challenges by developing a reference architecture using a mainstream software methodology. By studying the requirements of different stakeholders and eras, we identify 23 essential quality attributes for evaluating reference architectures. We assess three candidate architectures from recent literature based on these attributes. Finally, we discuss the next steps towards a comprehensive reference architecture, including prioritizing quality attributes, integrating components with complementary strengths, and supporting missing socio-technical requirements. As this endeavor requires a collaborative effort, we invite all knowledge engineering researchers and practitioners to join us.
End-to-End Learning for Answering Structured Queries Directly over Text
Nov 16, 2018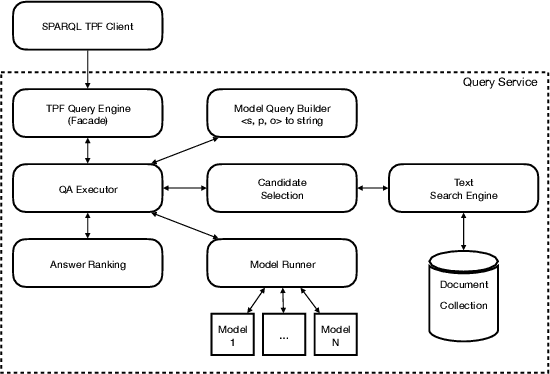
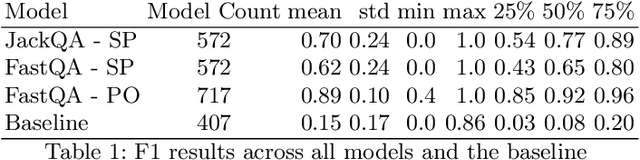
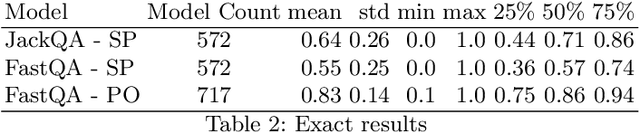
Abstract:Structured queries expressed in languages (such as SQL, SPARQL, or XQuery) offer a convenient and explicit way for users to express their information needs for a number of tasks. In this work, we present an approach to answer these directly over text data without storing results in a database. We specifically look at the case of knowledge bases where queries are over entities and the relations between them. Our approach combines distributed query answering (e.g. Triple Pattern Fragments) with models built for extractive question answering. Importantly, by applying distributed querying answering we are able to simplify the model learning problem. We train models for a large portion (572) of the relations within Wikidata and achieve an average 0.70 F1 measure across all models. We also present a systematic method to construct the necessary training data for this task from knowledge graphs and describe a prototype implementation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge