Bora Bozkurt
Theoretical and Experimental Assessment of Large Beam Codebook at mmWave Devices: How Much is Enough?
May 14, 2025Abstract:Modern millimeter wave (mmWave) transceivers come with a large number of antennas, each of which can support thousands of phase shifter configurations. This capability enables beam sweeping with fine angular resolution, but results in large codebook sizes that can span more than six orders of magnitude. On the other hand, the mobility of user terminals and their randomly changing orientations require constantly adjusting the beam direction. A key focus of recent research has been on the design of beam sweeping codebooks that balance a trade-off between the achievable gain and the beam search time, governed by the codebook size. In this paper, we investigate the extent to which a large codebook can be reduced to fewer steering vectors while covering the entire angular space and maintaining performance close to the maximum array gain. We derive a closed-form expression for the angular coverage range of a steering vector, subject to maintaining a gain loss within \(\gamma\) dB (e.g., 2\, dB) with respect to the maximum gain achieved by an infinitely large codebook. We demonstrate, both theoretically and experimentally, that a large beam-steering codebooks (such as the \(1024^{16}\) set considered in our experiment) can be reduced to just a few steering vectors. This framework serves as a proof that only a few steering vectors are sufficient to achieve near-maximum gain, challenging the common belief that a large codebook with fine angular resolution is essential to fully reap the benefits of an antenna array.
Beam Codebook Refinement for mmWave Devices with Random Orientations: Concept and Experimental Validation
Dec 30, 2024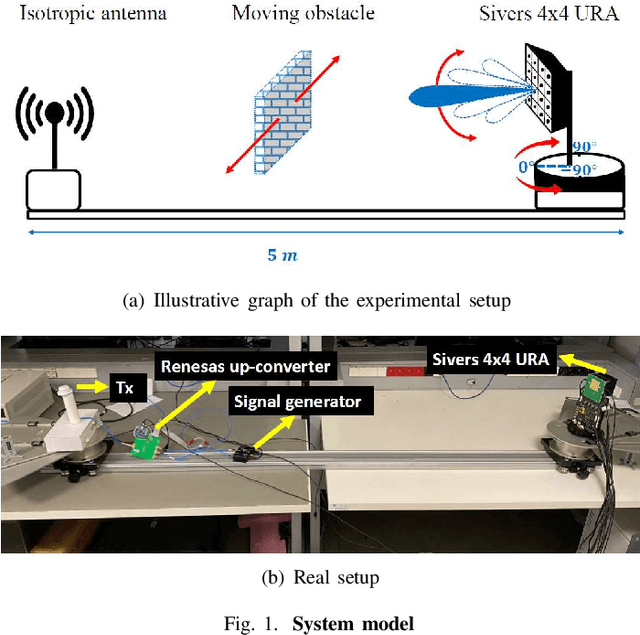
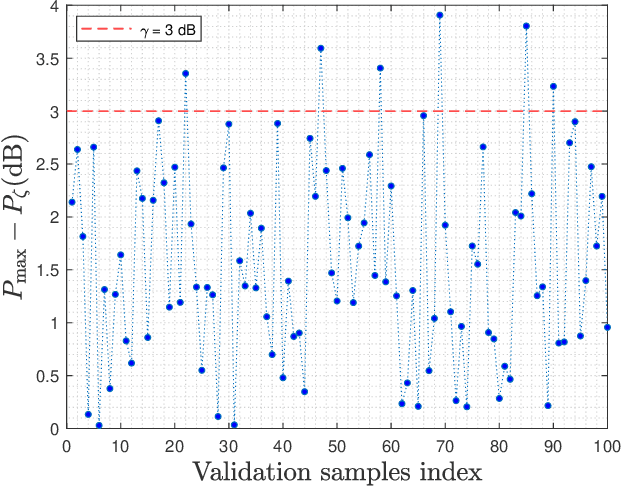
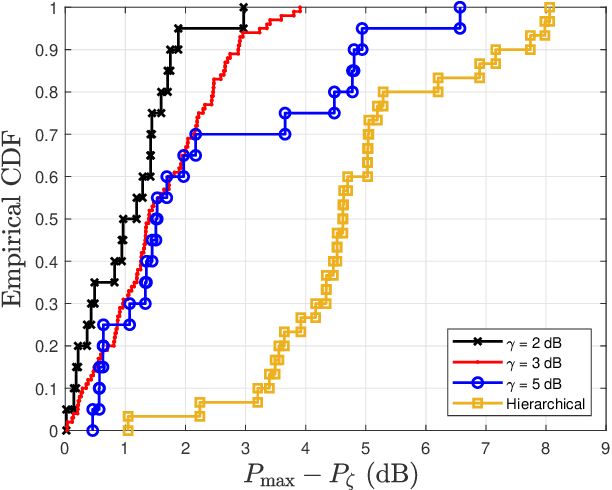
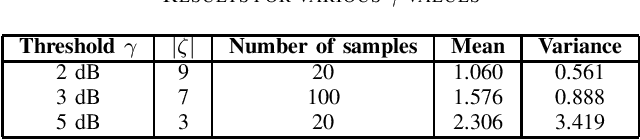
Abstract:There is a growing interest in codebook-based beam-steering for millimeter-wave (mmWave) systems due to its potential for low complexity and rapid beam search. A key focus of recent research has been the design of codebooks that strike a trade-off between achievable gain and codebook size, which directly impacts beam search time. Statistical approaches have shown promise by leveraging the likelihood that certain beam directions (equivalently, sets of phase-shifter configurations) are more probable than others. Such approaches are shown to be valid for static, non-rotating transmission stations such as base stations. However, for the case of user terminals that are constantly changing orientation, the possible phase-shifter configurations become equally probable, rendering statistical methods less relevant. On the other hand, user terminals come with a large number of possible steering vector configurations, which can span up to six orders of magnitude. Therefore, efficient solutions to reduce the codebook size (set of possible steering vectors) without compromising array gain are needed. We address this challenge by proposing a novel and practical codebook refinement technique, aiming to reduce the codebook size while maintaining array gain within $\gamma$ dB of the maximum achievable gain at any random orientation of the user terminal. We project that a steering vector at a given angle could effectively cover adjacent angles with a small gain loss compared to the maximum achievable gain. We demonstrate experimentally that it is possible to reduce the codebook size from $1024^{16}$ to just a few configurations (e.g., less than ten), covering all angles while maintaining the gain within $\gamma=3$ dB of the maximum achievable gain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge