Bocheng Wang
Towards Learnable Anchor for Deep Multi-View Clustering
Mar 16, 2025


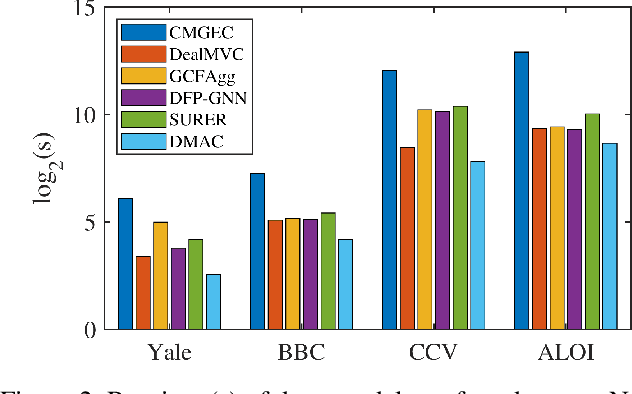
Abstract:Deep multi-view clustering incorporating graph learning has presented tremendous potential. Most methods encounter costly square time consumption w.r.t. data size. Theoretically, anchor-based graph learning can alleviate this limitation, but related deep models mainly rely on manual discretization approaches to select anchors, which indicates that 1) the anchors are fixed during model training and 2) they may deviate from the true cluster distribution. Consequently, the unreliable anchors may corrupt clustering results. In this paper, we propose the Deep Multi-view Anchor Clustering (DMAC) model that performs clustering in linear time. Concretely, the initial anchors are intervened by the positive-incentive noise sampled from Gaussian distribution, such that they can be optimized with a newly designed anchor learning loss, which promotes a clear relationship between samples and anchors. Afterwards, anchor graph convolution is devised to model the cluster structure formed by the anchors, and the mutual information maximization loss is built to provide cross-view clustering guidance. In this way, the learned anchors can better represent clusters. With the optimal anchors, the full sample graph is calculated to derive a discriminative embedding for clustering. Extensive experiments on several datasets demonstrate the superior performance and efficiency of DMAC compared to state-of-the-art competitors.
Multi-Task Curriculum Graph Contrastive Learning with Clustering Entropy Guidance
Aug 22, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in unsupervised deep graph clustering have been significantly promoted by contrastive learning. Despite the strides, most graph contrastive learning models face challenges: 1) graph augmentation is used to improve learning diversity, but commonly used random augmentation methods may destroy inherent semantics and cause noise; 2) the fixed positive and negative sample selection strategy is limited to deal with complex real data, thereby impeding the model's capability to capture fine-grained patterns and relationships. To reduce these problems, we propose the Clustering-guided Curriculum Graph contrastive Learning (CCGL) framework. CCGL uses clustering entropy as the guidance of the following graph augmentation and contrastive learning. Specifically, according to the clustering entropy, the intra-class edges and important features are emphasized in augmentation. Then, a multi-task curriculum learning scheme is proposed, which employs the clustering guidance to shift the focus from the discrimination task to the clustering task. In this way, the sample selection strategy of contrastive learning can be adjusted adaptively from early to late stage, which enhances the model's flexibility for complex data structure. Experimental results demonstrate that CCGL has achieved excellent performance compared to state-of-the-art competitors.
Deep Contrastive Graph Learning with Clustering-Oriented Guidance
Feb 25, 2024Abstract:Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) has exhibited remarkable potential in improving graph-based clustering. To handle the general clustering scenario without a prior graph, these models estimate an initial graph beforehand to apply GCN. Throughout the literature, we have witnessed that 1) most models focus on the initial graph while neglecting the original features. Therefore, the discriminability of the learned representation may be corrupted by a low-quality initial graph; 2) the training procedure lacks effective clustering guidance, which may lead to the incorporation of clustering-irrelevant information into the learned graph. To tackle these problems, the Deep Contrastive Graph Learning (DCGL) model is proposed for general data clustering. Specifically, we establish a pseudo-siamese network, which incorporates auto-encoder with GCN to emphasize both the graph structure and the original features. On this basis, feature-level contrastive learning is introduced to enhance the discriminative capacity, and the relationship between samples and centroids is employed as the clustering-oriented guidance. Afterward, a two-branch graph learning mechanism is designed to extract the local and global structural relationships, which are further embedded into a unified graph under the cluster-level contrastive guidance. Experimental results on several benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of DCGL against state-of-the-art algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge