Bo Xing
Tensor-Networks-based Learning of Probabilistic Cellular Automata Dynamics
Apr 17, 2024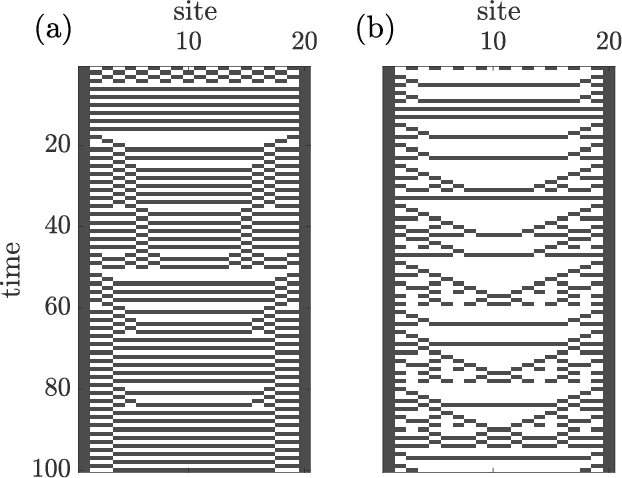
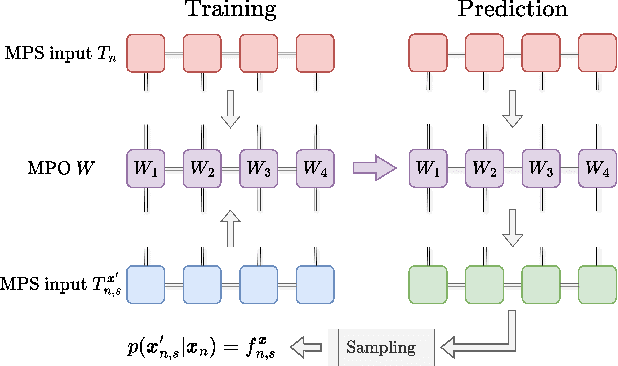
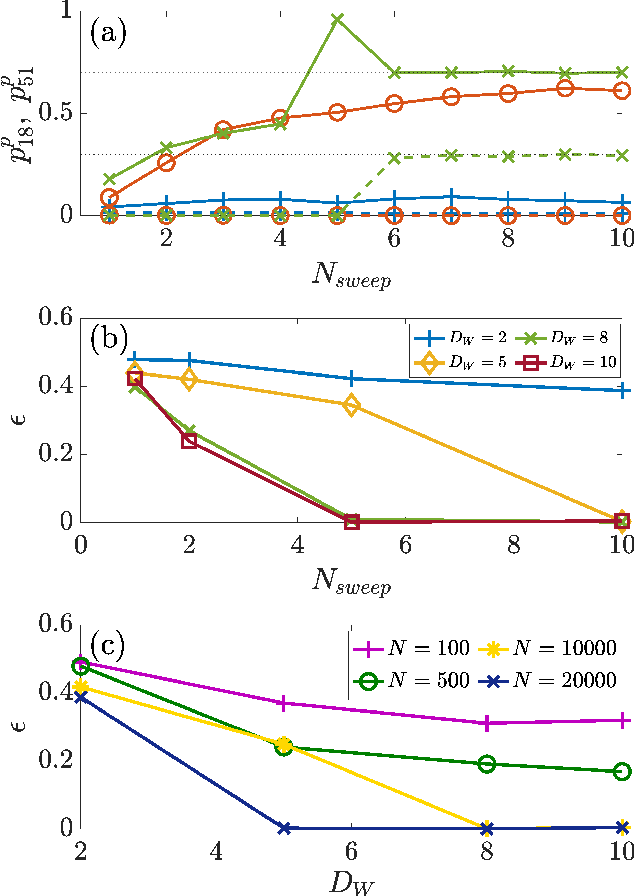
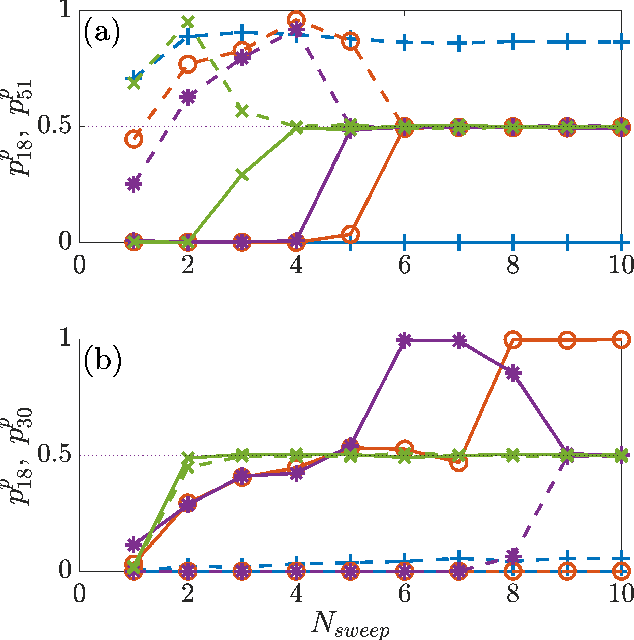
Abstract:Algorithms developed to solve many-body quantum problems, like tensor networks, can turn into powerful quantum-inspired tools to tackle problems in the classical domain. In this work, we focus on matrix product operators, a prominent numerical technique to study many-body quantum systems, especially in one dimension. It has been previously shown that such a tool can be used for classification, learning of deterministic sequence-to-sequence processes and of generic quantum processes. We further develop a matrix product operator algorithm to learn probabilistic sequence-to-sequence processes and apply this algorithm to probabilistic cellular automata. This new approach can accurately learn probabilistic cellular automata processes in different conditions, even when the process is a probabilistic mixture of different chaotic rules. In addition, we find that the ability to learn these dynamics is a function of the bit-wise difference between the rules and whether one is much more likely than the other.
Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence
Oct 23, 2018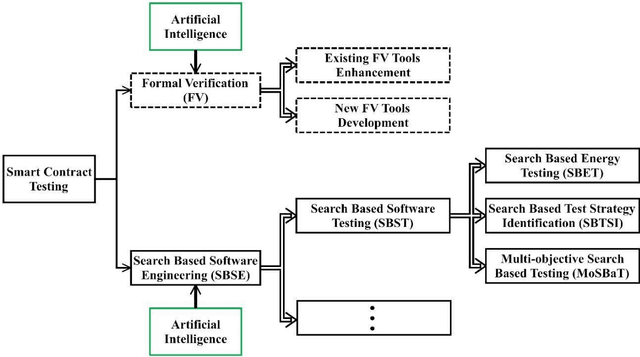
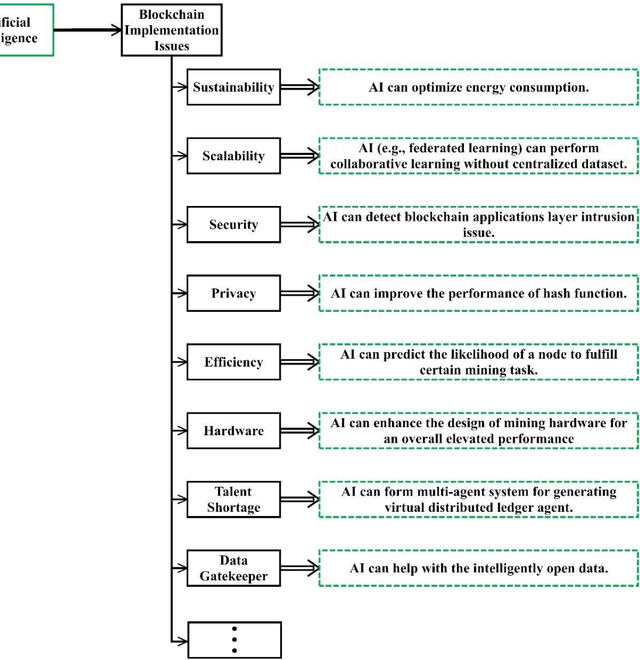
Abstract:It is undeniable that artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain concepts are spreading at a phenomenal rate. Both technologies have distinct degree of technological complexity and multi-dimensional business implications. However, a common misunderstanding about blockchain concept, in particular, is that blockchain is decentralized and is not controlled by anyone. But the underlying development of a blockchain system is still attributed to a cluster of core developers. Take smart contract as an example, it is essentially a collection of codes (or functions) and data (or states) that are programmed and deployed on a blockchain (say, Ethereum) by different human programmers. It is thus, unfortunately, less likely to be free of loopholes and flaws. In this article, through a brief overview about how artificial intelligence could be used to deliver bug-free smart contract so as to achieve the goal of blockchain 2.0, we to emphasize that the blockchain implementation can be assisted or enhanced via various AI techniques. The alliance of AI and blockchain is expected to create numerous possibilities.
Creativity and Artificial Intelligence: A Digital Art Perspective
Jul 21, 2018Abstract:This paper describes the application of artificial intelligence to the creation of digital art. AI is a computational paradigm that codifies intelligence into machines. There are generally three types of artificial intelligence and these are machine learning, evolutionary programming and soft computing. Machine learning is the statistical approach to building intelligent systems. Evolutionary programming is the use of natural evolutionary systems to design intelligent machines. Some of the evolutionary programming systems include genetic algorithm which is inspired by the principles of evolution and swarm optimization which is inspired by the swarming of birds, fish, ants etc. Soft computing includes techniques such as agent based modelling and fuzzy logic. Opportunities on the applications of these to digital art are explored.
Artificial Intelligence in Reverse Supply Chain Management: The State of the Art
Dec 18, 2010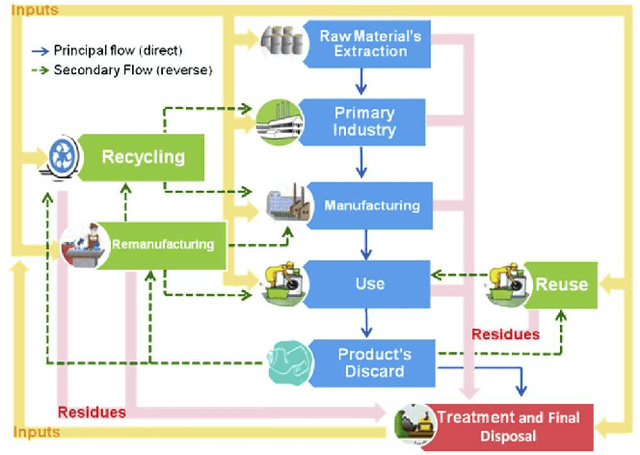
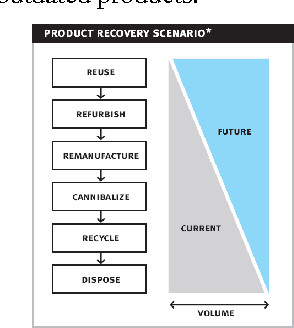
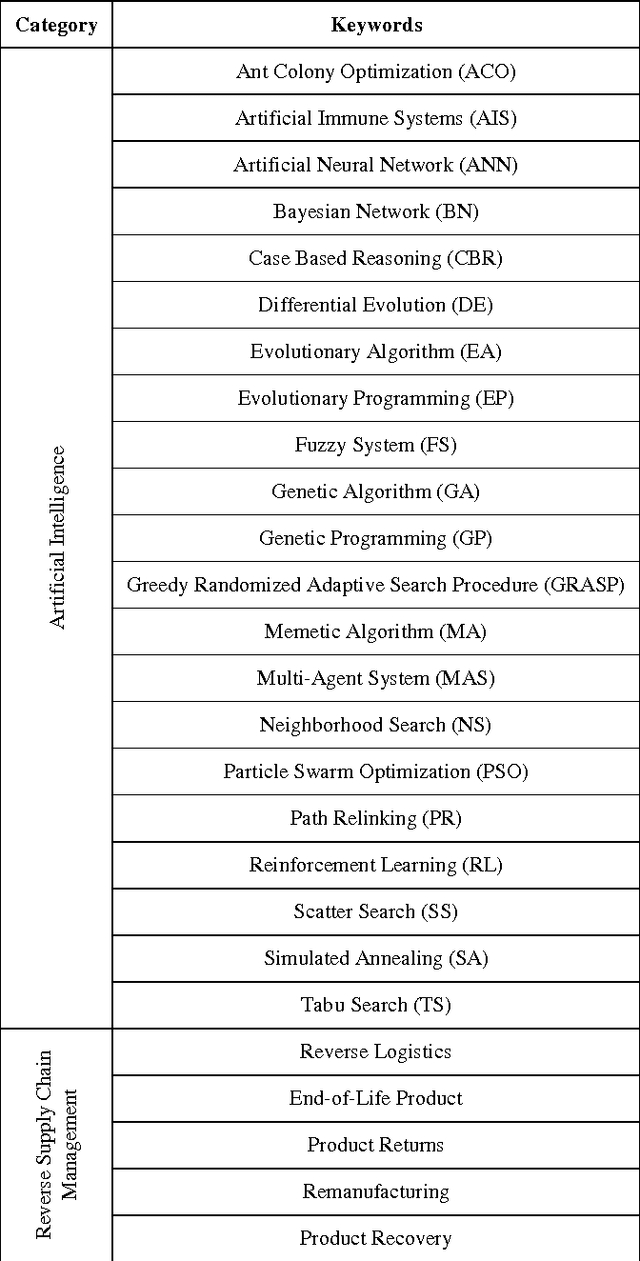
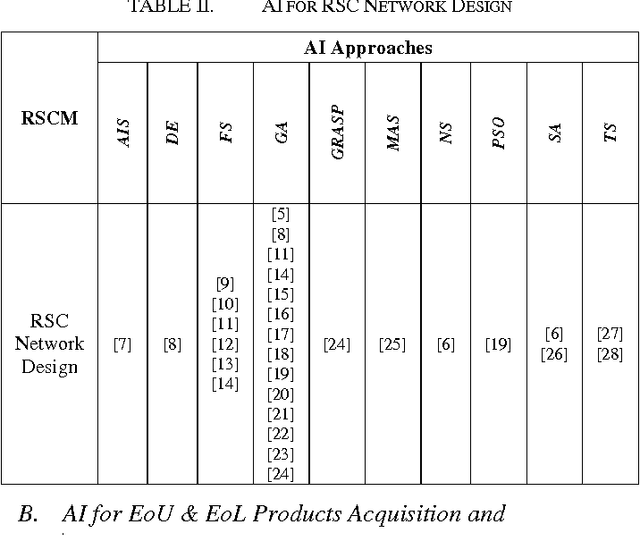
Abstract:Product take-back legislation forces manufacturers to bear the costs of collection and disposal of products that have reached the end of their useful lives. In order to reduce these costs, manufacturers can consider reuse, remanufacturing and/or recycling of components as an alternative to disposal. The implementation of such alternatives usually requires an appropriate reverse supply chain management. With the concepts of reverse supply chain are gaining popularity in practice, the use of artificial intelligence approaches in these areas is also becoming popular. As a result, the purpose of this paper is to give an overview of the recent publications concerning the application of artificial intelligence techniques to reverse supply chain with emphasis on certain types of product returns.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge