Bipasha Kundu
Multi-Scale Feature Fusion with Image-Driven Spatial Integration for Left Atrium Segmentation from Cardiac MRI Images
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Accurate segmentation of the left atrium (LA) from late gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging plays a vital role in visualizing diseased atrial structures, enabling the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular diseases. It is particularly essential for planning treatment with ablation therapy, a key intervention for atrial fibrillation (AF). However, manual segmentation is time-intensive and prone to inter-observer variability, underscoring the need for automated solutions. Class-agnostic foundation models like DINOv2 have demonstrated remarkable feature extraction capabilities in vision tasks. However, their lack of domain specificity and task-specific adaptation can reduce spatial resolution during feature extraction, impacting the capture of fine anatomical detail in medical imaging. To address this limitation, we propose a segmentation framework that integrates DINOv2 as an encoder with a UNet-style decoder, incorporating multi-scale feature fusion and input image integration to enhance segmentation accuracy. The learnable weighting mechanism dynamically prioritizes hierarchical features from different encoder blocks of the foundation model, optimizing feature selection for task relevance. Additionally, the input image is reintroduced during the decoding stage to preserve high-resolution spatial details, addressing limitations of downsampling in the encoder. We validate our approach on the LAScarQS 2022 dataset and demonstrate improved performance with a 92.3% Dice and 84.1% IoU score for giant architecture compared to the nnUNet baseline model. These findings emphasize the efficacy of our approach in advancing the field of automated left atrium segmentation from cardiac MRI.
Assessing the Performance of the DINOv2 Self-supervised Learning Vision Transformer Model for the Segmentation of the Left Atrium from MRI Images
Nov 14, 2024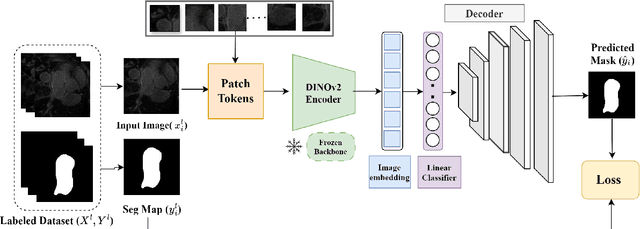
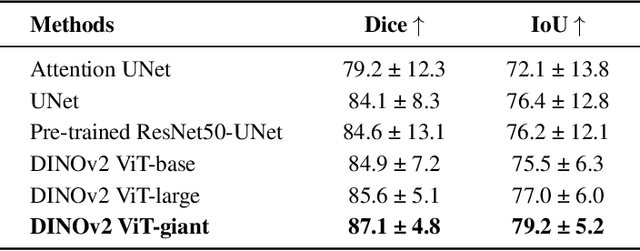
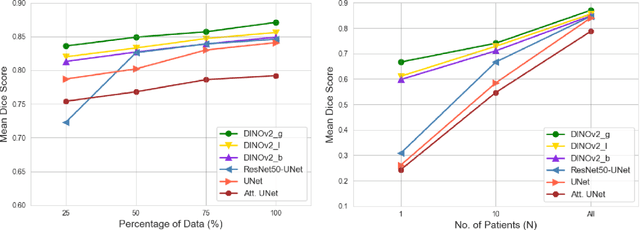
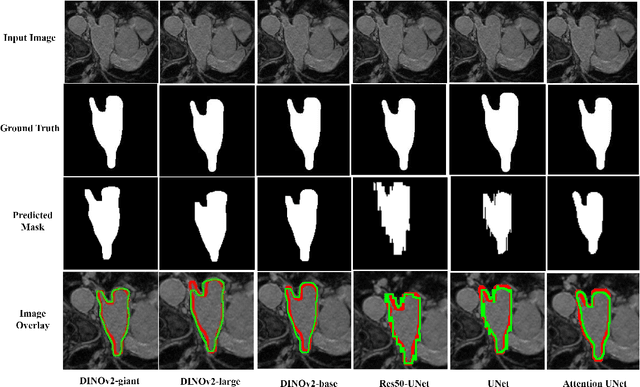
Abstract:Accurate left atrium (LA) segmentation from pre-operative scans is crucial for diagnosing atrial fibrillation, treatment planning, and supporting surgical interventions. While deep learning models are key in medical image segmentation, they often require extensive manually annotated data. Foundation models trained on larger datasets have reduced this dependency, enhancing generalizability and robustness through transfer learning. We explore DINOv2, a self-supervised learning vision transformer trained on natural images, for LA segmentation using MRI. The challenges for LA's complex anatomy, thin boundaries, and limited annotated data make accurate segmentation difficult before & during the image-guided intervention. We demonstrate DINOv2's ability to provide accurate & consistent segmentation, achieving a mean Dice score of .871 & a Jaccard Index of .792 for end-to-end fine-tuning. Through few-shot learning across various data sizes & patient counts, DINOv2 consistently outperforms baseline models. These results suggest that DINOv2 effectively adapts to MRI with limited data, highlighting its potential as a competitive tool for segmentation & encouraging broader use in medical imaging.
Temperature Detection from Images Using Smartphones
Apr 07, 2023
Abstract:Since late 2019, the global spread of COVID-19 has affected people's daily life. Temperature is an early and common symptom of Covid. Therefore, a convenient and remote temperature detection method is needed. In this paper, a non-contact method for detecting body temperature is proposed. Our developed algorithm based on blackbody radiation calculates the body temperature of a user-selected area from an obtained image. The findings were confirmed using a FLIR Thermal Camera with an accuracy of 97%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge