Binbin Cao
ReaSeq: Unleashing World Knowledge via Reasoning for Sequential Modeling
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Industrial recommender systems face two fundamental limitations under the log-driven paradigm: (1) knowledge poverty in ID-based item representations that causes brittle interest modeling under data sparsity, and (2) systemic blindness to beyond-log user interests that constrains model performance within platform boundaries. These limitations stem from an over-reliance on shallow interaction statistics and close-looped feedback while neglecting the rich world knowledge about product semantics and cross-domain behavioral patterns that Large Language Models have learned from vast corpora. To address these challenges, we introduce ReaSeq, a reasoning-enhanced framework that leverages world knowledge in Large Language Models to address both limitations through explicit and implicit reasoning. Specifically, ReaSeq employs explicit Chain-of-Thought reasoning via multi-agent collaboration to distill structured product knowledge into semantically enriched item representations, and latent reasoning via Diffusion Large Language Models to infer plausible beyond-log behaviors. Deployed on Taobao's ranking system serving hundreds of millions of users, ReaSeq achieves substantial gains: >6.0% in IPV and CTR, >2.9% in Orders, and >2.5% in GMV, validating the effectiveness of world-knowledge-enhanced reasoning over purely log-driven approaches.
RecGPT-V2 Technical Report
Dec 16, 2025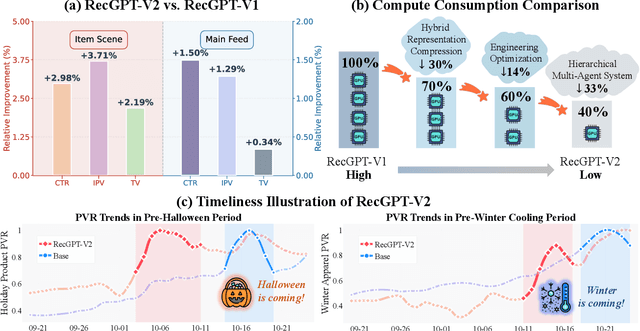
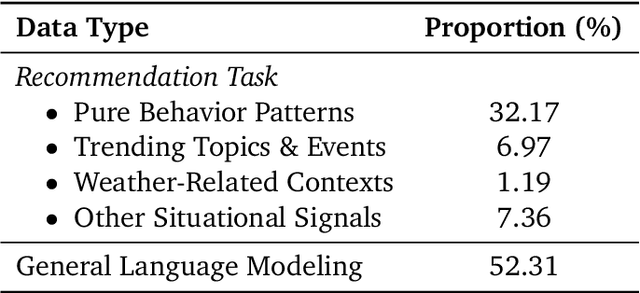
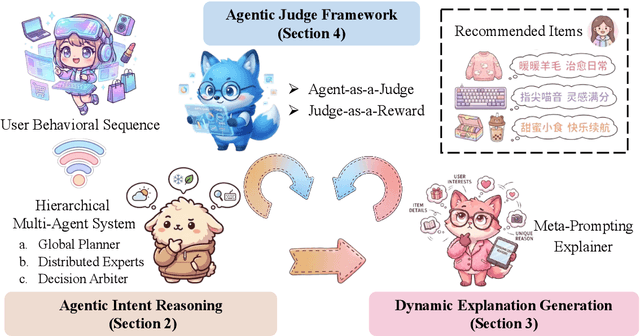
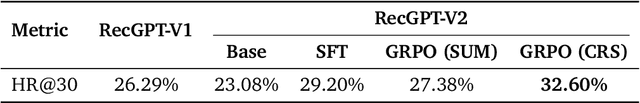
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in transforming recommender systems from implicit behavioral pattern matching to explicit intent reasoning. While RecGPT-V1 successfully pioneered this paradigm by integrating LLM-based reasoning into user interest mining and item tag prediction, it suffers from four fundamental limitations: (1) computational inefficiency and cognitive redundancy across multiple reasoning routes; (2) insufficient explanation diversity in fixed-template generation; (3) limited generalization under supervised learning paradigms; and (4) simplistic outcome-focused evaluation that fails to match human standards. To address these challenges, we present RecGPT-V2 with four key innovations. First, a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System restructures intent reasoning through coordinated collaboration, eliminating cognitive duplication while enabling diverse intent coverage. Combined with Hybrid Representation Inference that compresses user-behavior contexts, our framework reduces GPU consumption by 60% and improves exclusive recall from 9.39% to 10.99%. Second, a Meta-Prompting framework dynamically generates contextually adaptive prompts, improving explanation diversity by +7.3%. Third, constrained reinforcement learning mitigates multi-reward conflicts, achieving +24.1% improvement in tag prediction and +13.0% in explanation acceptance. Fourth, an Agent-as-a-Judge framework decomposes assessment into multi-step reasoning, improving human preference alignment. Online A/B tests on Taobao demonstrate significant improvements: +2.98% CTR, +3.71% IPV, +2.19% TV, and +11.46% NER. RecGPT-V2 establishes both the technical feasibility and commercial viability of deploying LLM-powered intent reasoning at scale, bridging the gap between cognitive exploration and industrial utility.
DeLS-3D: Deep Localization and Segmentation with a 3D Semantic Map
May 13, 2018



Abstract:For applications such as autonomous driving, self-localization/camera pose estimation and scene parsing are crucial technologies. In this paper, we propose a unified framework to tackle these two problems simultaneously. The uniqueness of our design is a sensor fusion scheme which integrates camera videos, motion sensors (GPS/IMU), and a 3D semantic map in order to achieve robustness and efficiency of the system. Specifically, we first have an initial coarse camera pose obtained from consumer-grade GPS/IMU, based on which a label map can be rendered from the 3D semantic map. Then, the rendered label map and the RGB image are jointly fed into a pose CNN, yielding a corrected camera pose. In addition, to incorporate temporal information, a multi-layer recurrent neural network (RNN) is further deployed improve the pose accuracy. Finally, based on the pose from RNN, we render a new label map, which is fed together with the RGB image into a segment CNN which produces per-pixel semantic label. In order to validate our approach, we build a dataset with registered 3D point clouds and video camera images. Both the point clouds and the images are semantically-labeled. Each video frame has ground truth pose from highly accurate motion sensors. We show that practically, pose estimation solely relying on images like PoseNet may fail due to street view confusion, and it is important to fuse multiple sensors. Finally, various ablation studies are performed, which demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed system. In particular, we show that scene parsing and pose estimation are mutually beneficial to achieve a more robust and accurate system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge