Bill Wang
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
A Simulation Study of Passing Drivers' Responses to the Automated Truck-Mounted Attenuator System in Road Maintenance
Aug 01, 2022

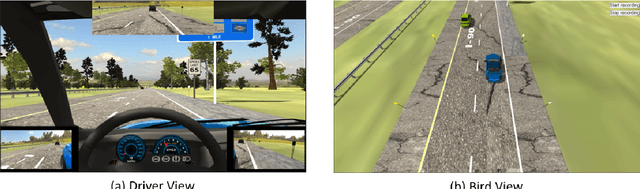
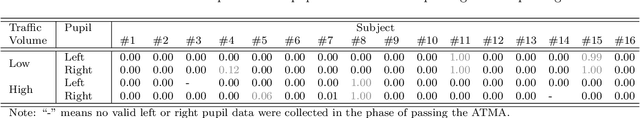
Abstract:The Autonomous Truck-Mounted Attenuator (ATMA) system is a lead-follower vehicle system based on autonomous driving and connected vehicle technologies. The lead truck performs maintenance tasks on the road, and the unmanned follower truck is designed to improve the visibility of the moving work zone to passing vehicles and to protect workers and equipment. While the ATMA has been under testing by transportation maintenance and operations agencies in recent years, a simulator-based testing capability is a supplement, especially if human subjects are involved. This paper aims to discover how passing drivers perceive, understand, and react to the ATMA system in road maintenance accordingly. A driving simulator for ATMA studies is developed for collecting the driving data. Then, driving simulation experiments were performed, wherein a screen-based eye tracker collected sixteen subjects' gaze points and pupil diameters. Data analysis has evidenced the changes in the visual attention pattern of subjects when they were passing the ATMA. On average, the ATMA starts to attract subjects' attention from 500 ft behind the follower truck. Most (87.50%) understood the follower truck's protection purpose, and the majority (86.67%) reasoned the association between the two trucks. But still, many (43.75%) did not recognize that ATMA is a connected autonomous vehicle system. While all subjects safely changed lanes and attempted to pass the slow-moving ATMA, their inadequate understanding of ATMA is a potential risk, like cutting into the ATAM. Results implied that transportation maintenance and operations agencies should take this into consideration in establishing the deployment guidance.
A Multi-tasking Model of Speaker-Keyword Classification for Keeping Human in the Loop of Drone-assisted Inspection
Jul 08, 2022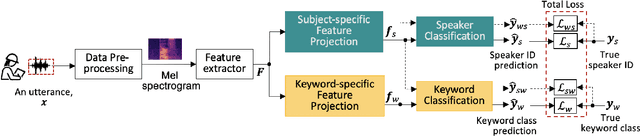

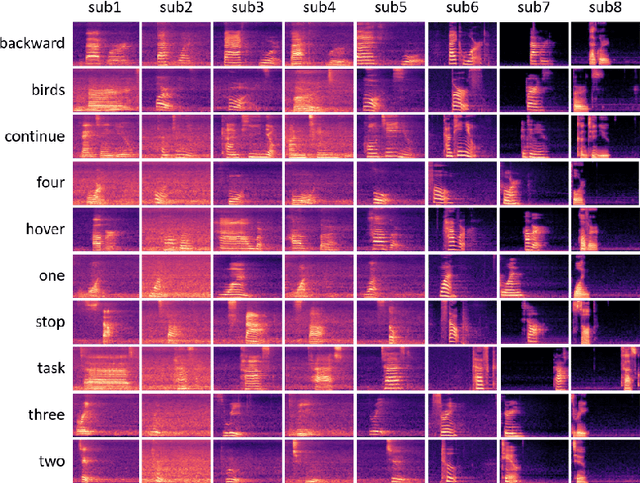
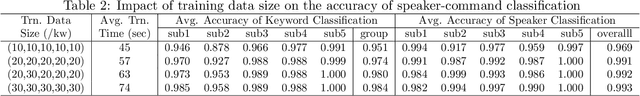
Abstract:Audio commands are a preferred communication medium to keep inspectors in the loop of civil infrastructure inspection performed by a semi-autonomous drone. To understand job-specific commands from a group of heterogeneous and dynamic inspectors, a model needs to be developed cost-effectively for the group and easily adapted when the group changes. This paper is motivated to build a multi-tasking deep learning model that possesses a Share-Split-Collaborate architecture. This architecture allows the two classification tasks to share the feature extractor and then split subject-specific and keyword-specific features intertwined in the extracted features through feature projection and collaborative training. A base model for a group of five authorized subjects is trained and tested on the inspection keyword dataset collected by this study. The model achieved a 95.3% or higher mean accuracy in classifying the keywords of any authorized inspectors. Its mean accuracy in speaker classification is 99.2%. Due to the richer keyword representations that the model learns from the pooled training data, adapting the base model to a new inspector requires only a little training data from that inspector, like five utterances per keyword. Using the speaker classification scores for inspector verification can achieve a success rate of at least 93.9% in verifying authorized inspectors and 76.1\% in detecting unauthorized ones. Further, the paper demonstrates the applicability of the proposed model to larger-size groups on a public dataset. This paper provides a solution to addressing challenges facing AI-assisted human-robot interaction, including worker heterogeneity, worker dynamics, and job heterogeneity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge