Bibo Wu
Optimizing Value of Learning in Task-Oriented Federated Meta-Learning Systems
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has gained significant attention in recent years due to its distributed nature and privacy preserving benefits. However, a key limitation of conventional FL is that it learns and distributes a common global model to all participants, which fails to provide customized solutions for diverse task requirements. Federated meta-learning (FML) offers a promising solution to this issue by enabling devices to finetune local models after receiving a shared meta-model from the server. In this paper, we propose a task-oriented FML framework over non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) networks. A novel metric, termed value of learning (VoL), is introduced to assess the individual training needs across devices. Moreover, a task-level weight (TLW) metric is defined based on task requirements and fairness considerations, guiding the prioritization of edge devices during FML training. The formulated problem, to maximize the sum of TLW-based VoL across devices, forms a non-convex mixed-integer non-linear programming (MINLP) challenge, addressed here using a parameterized deep Q-network (PDQN) algorithm to handle both discrete and continuous variables. Simulation results demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms baseline schemes, underscoring the advantages of the proposed framework.
Stackelberg Game Based Performance Optimization in Digital Twin Assisted Federated Learning over NOMA Networks
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:Despite the advantage of preserving data privacy, federated learning (FL) still suffers from the straggler issue due to the limited computing resources of distributed clients and the unreliable wireless communication environment. By effectively imitating the distributed resources, digital twin (DT) shows great potential in alleviating this issue. In this paper, we leverage DT in the FL framework over non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) network to assist FL training process, considering malicious attacks on model updates from clients. A reputationbased client selection scheme is proposed, which accounts for client heterogeneity in multiple aspects and effectively mitigates the risks of poisoning attacks in FL systems. To minimize the total latency and energy consumption in the proposed system, we then formulate a Stackelberg game by considering clients and the server as the leader and the follower, respectively. Specifically, the leader aims to minimize the energy consumption while the objective of the follower is to minimize the total latency during FL training. The Stackelberg equilibrium is achieved to obtain the optimal solutions. We first derive the strategies for the followerlevel problem and include them in the leader-level problem which is then solved via problem decomposition. Simulation results verify the superior performance of the proposed scheme.
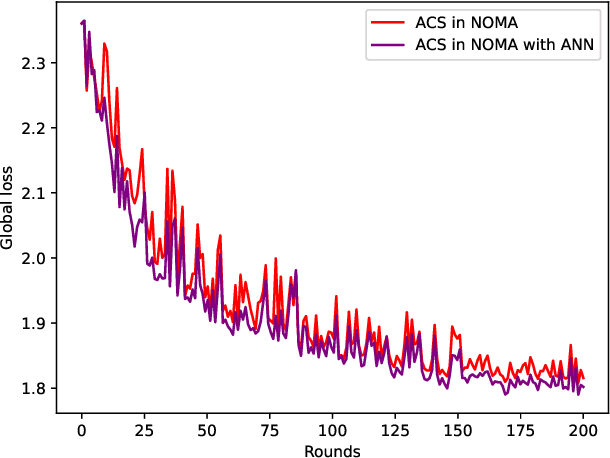
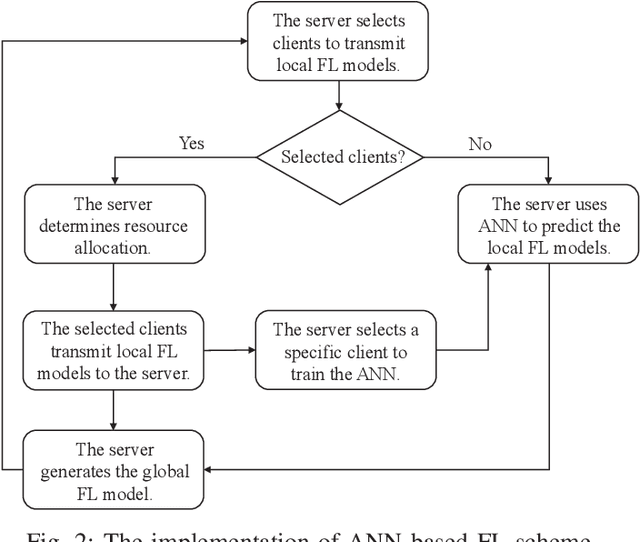
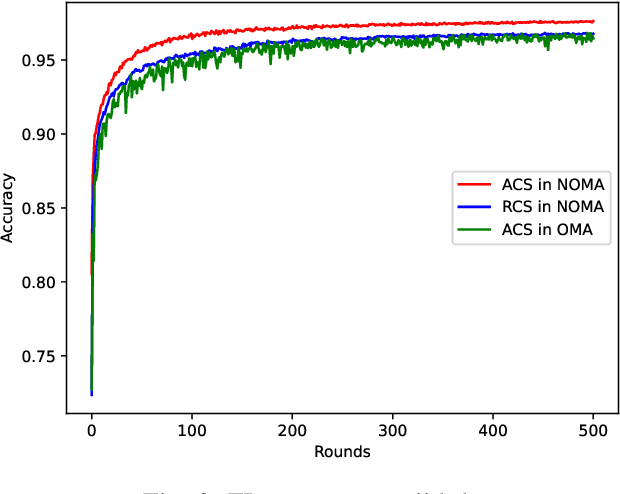
Client Orchestration and Cost-Efficient Joint Optimization for NOMA-Enabled Hierarchical Federated Learning
Nov 03, 2023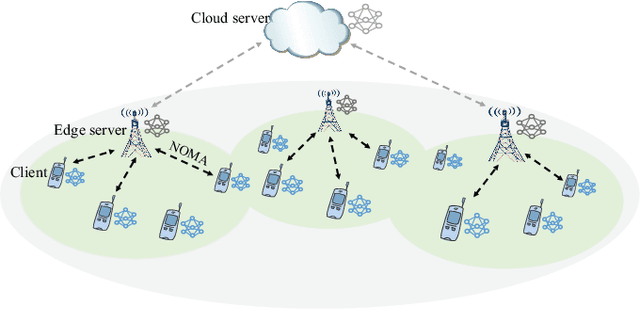
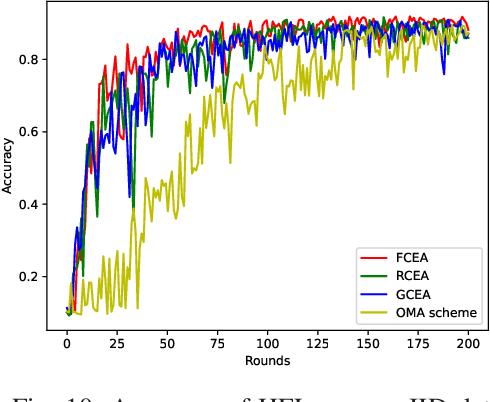
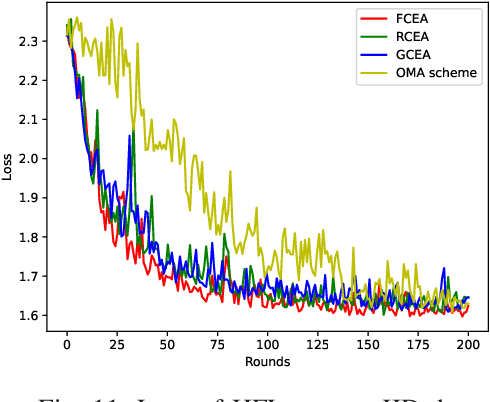
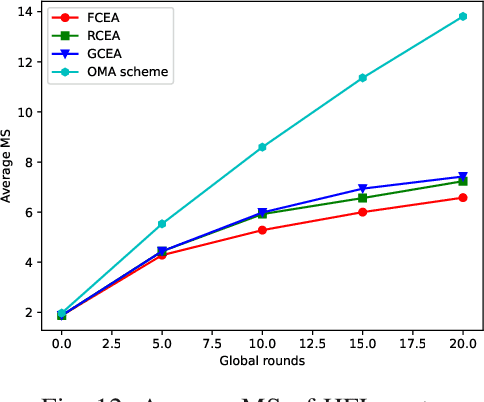
Abstract:Hierarchical federated learning (HFL) shows great advantages over conventional two-layer federated learning (FL) in reducing network overhead and interaction latency while still retaining the data privacy of distributed FL clients. However, the communication and energy overhead still pose a bottleneck for HFL performance, especially as the number of clients raises dramatically. To tackle this issue, we propose a non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) enabled HFL system under semi-synchronous cloud model aggregation in this paper, aiming to minimize the total cost of time and energy at each HFL global round. Specifically, we first propose a novel fuzzy logic based client orchestration policy considering client heterogenerity in multiple aspects, including channel quality, data quantity and model staleness. Subsequently, given the fuzzy based client-edge association, a joint edge server scheduling and resource allocation problem is formulated. Utilizing problem decomposition, we firstly derive the closed-form solution for the edge server scheduling subproblem via the penalty dual decomposition (PDD) method. Next, a deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) based algorithm is proposed to tackle the resource allocation subproblem considering time-varying environments. Finally, extensive simulations demonstrate that the proposed scheme outperforms the considered benchmarks regarding HFL performance improvement and total cost reduction.
Energy-Efficient Design of STAR-RIS Aided MIMO-NOMA Networks
Apr 19, 2023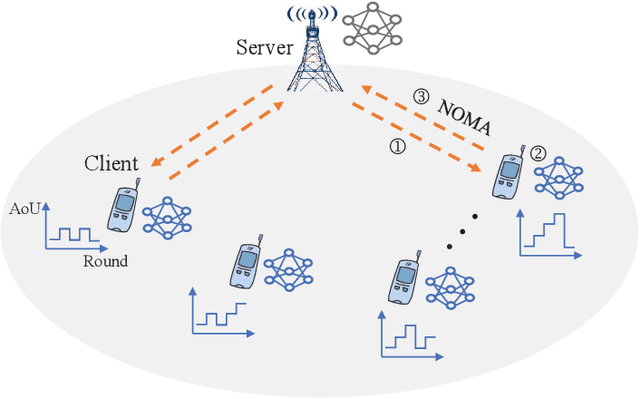
Abstract:Simultaneous transmission and reflection-reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) can provide expanded coverage compared with the conventional reflection-only RIS. This paper exploits the energy efficient potential of STAR-RIS in a multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) enabled non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) system. Specifically, we mainly focus on energy-efficient resource allocation with MIMO technology in the STAR-RIS assisted NOMA network. To maximize the system energy efficiency, we propose an algorithm to optimize the transmit beamforming and the phases of the low-cost passive elements on the STAR-RIS alternatively until the convergence. Specifically, we first decompose the formulated energy efficiency problem into beamforming and phase shift optimization problems. To efficiently address the non-convex beamforming optimization problem, we exploit signal alignment and zero-forcing precoding methods in each user pair to decompose MIMO-NOMA channels into single-antenna NOMA channels. Then, the Dinkelbach approach and dual decomposition are utilized to optimize the beamforming vectors. In order to solve non-convex phase shift optimization problem, we propose a successive convex approximation (SCA) based method to efficiently obtain the optimized phase shift of STAR-RIS. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm with NOMA technology can yield superior energy efficiency performance over the orthogonal multiple access (OMA) scheme and the random phase shift scheme.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge