Bhawani Selvaretnam
Document-Level Zero-Shot Relation Extraction with Entity Side Information
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Document-Level Zero-Shot Relation Extraction (DocZSRE) aims to predict unseen relation labels in text documents without prior training on specific relations. Existing approaches rely on Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate synthetic data for unseen labels, which poses challenges for low-resource languages like Malaysian English. These challenges include the incorporation of local linguistic nuances and the risk of factual inaccuracies in LLM-generated data. This paper introduces Document-Level Zero-Shot Relation Extraction with Entity Side Information (DocZSRE-SI) to address limitations in the existing DocZSRE approach. The DocZSRE-SI framework leverages Entity Side Information, such as Entity Mention Descriptions and Entity Mention Hypernyms, to perform ZSRE without depending on LLM-generated synthetic data. The proposed low-complexity model achieves an average improvement of 11.6% in the macro F1-Score compared to baseline models and existing benchmarks. By utilizing Entity Side Information, DocZSRE-SI offers a robust and efficient alternative to error-prone, LLM-based methods, demonstrating significant advancements in handling low-resource languages and linguistic diversity in relation extraction tasks. This research provides a scalable and reliable solution for ZSRE, particularly in contexts like Malaysian English news articles, where traditional LLM-based approaches fall short.
Bridging the Gap: Transfer Learning from English PLMs to Malaysian English
Jul 01, 2024Abstract:Malaysian English is a low resource creole language, where it carries the elements of Malay, Chinese, and Tamil languages, in addition to Standard English. Named Entity Recognition (NER) models underperform when capturing entities from Malaysian English text due to its distinctive morphosyntactic adaptations, semantic features and code-switching (mixing English and Malay). Considering these gaps, we introduce MENmBERT and MENBERT, a pre-trained language model with contextual understanding, specifically tailored for Malaysian English. We have fine-tuned MENmBERT and MENBERT using manually annotated entities and relations from the Malaysian English News Article (MEN) Dataset. This fine-tuning process allows the PLM to learn representations that capture the nuances of Malaysian English relevant for NER and RE tasks. MENmBERT achieved a 1.52\% and 26.27\% improvement on NER and RE tasks respectively compared to the bert-base-multilingual-cased model. Although the overall performance of NER does not have a significant improvement, our further analysis shows that there is a significant improvement when evaluated by the 12 entity labels. These findings suggest that pre-training language models on language-specific and geographically-focused corpora can be a promising approach for improving NER performance in low-resource settings. The dataset and code published in this paper provide valuable resources for NLP research work focusing on Malaysian English.
Malaysian English News Decoded: A Linguistic Resource for Named Entity and Relation Extraction
Feb 22, 2024Abstract:Standard English and Malaysian English exhibit notable differences, posing challenges for natural language processing (NLP) tasks on Malaysian English. Unfortunately, most of the existing datasets are mainly based on standard English and therefore inadequate for improving NLP tasks in Malaysian English. An experiment using state-of-the-art Named Entity Recognition (NER) solutions on Malaysian English news articles highlights that they cannot handle morphosyntactic variations in Malaysian English. To the best of our knowledge, there is no annotated dataset available to improvise the model. To address these issues, we constructed a Malaysian English News (MEN) dataset, which contains 200 news articles that are manually annotated with entities and relations. We then fine-tuned the spaCy NER tool and validated that having a dataset tailor-made for Malaysian English could improve the performance of NER in Malaysian English significantly. This paper presents our effort in the data acquisition, annotation methodology, and thorough analysis of the annotated dataset. To validate the quality of the annotation, inter-annotator agreement was used, followed by adjudication of disagreements by a subject matter expert. Upon completion of these tasks, we managed to develop a dataset with 6,061 entities and 3,268 relation instances. Finally, we discuss on spaCy fine-tuning setup and analysis on the NER performance. This unique dataset will contribute significantly to the advancement of NLP research in Malaysian English, allowing researchers to accelerate their progress, particularly in NER and relation extraction. The dataset and annotation guideline has been published on Github.
How well ChatGPT understand Malaysian English? An Evaluation on Named Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:Recently, ChatGPT has attracted a lot of interest from both researchers and the general public. While the performance of ChatGPT in named entity recognition and relation extraction from Standard English texts is satisfactory, it remains to be seen if it can perform similarly for Malaysian English. Malaysian English is unique as it exhibits morphosyntactic and semantical adaptation from local contexts. In this study, we assess ChatGPT's capability in extracting entities and relations from the Malaysian English News (MEN) dataset. We propose a three-step methodology referred to as \textbf{\textit{educate-predict-evaluate}}. The performance of ChatGPT is assessed using F1-Score across 18 unique prompt settings, which were carefully engineered for a comprehensive review. From our evaluation, we found that ChatGPT does not perform well in extracting entities from Malaysian English news articles, with the highest F1-Score of 0.497. Further analysis shows that the morphosyntactic adaptation in Malaysian English caused the limitation. However, interestingly, this morphosyntactic adaptation does not impact the performance of ChatGPT for relation extraction.
A Linguistically Driven Framework for Query Expansion via Grammatical Constituent Highlighting and Role-Based Concept Weighting
Apr 25, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a linguistically-motivated query expansion framework that recognizes and en-codes significant query constituents that characterize query intent in order to improve retrieval performance. Concepts-of-Interest are recognized as the core concepts that represent the gist of the search goal whilst the remaining query constituents which serve to specify the search goal and complete the query structure are classified as descriptive, relational or structural. Acknowledging the need to form semantically-associated base pairs for the purpose of extracting related potential expansion concepts, an algorithm which capitalizes on syntactical dependencies to capture relationships between adjacent and non-adjacent query concepts is proposed. Lastly, a robust weighting scheme that duly emphasizes the importance of query constituents based on their linguistic role within the expanded query is presented. We demonstrate improvements in retrieval effectiveness in terms of increased mean average precision (MAP) garnered by the proposed linguistic-based query expansion framework through experimentation on the TREC ad hoc test collections.
Natural language technology and query expansion: issues, state-of-the-art and perspectives
Apr 23, 2020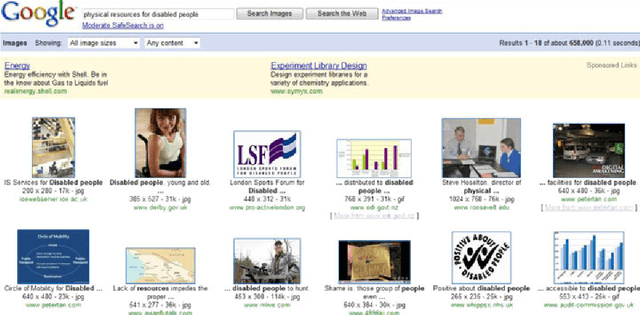
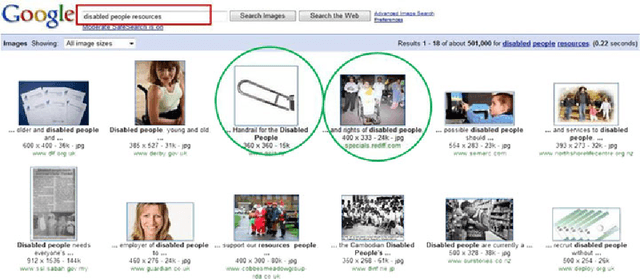
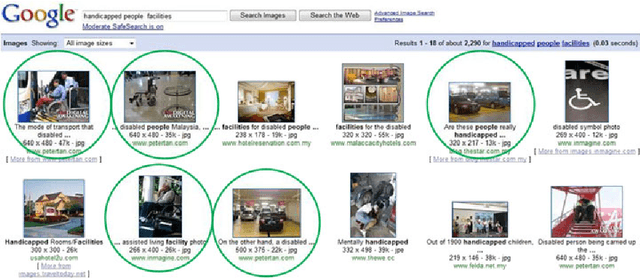
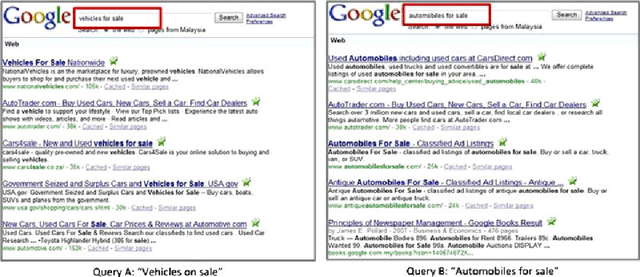
Abstract:The availability of an abundance of knowledge sources has spurred a large amount of effort in the development and enhancement of Information Retrieval techniques. Users information needs are expressed in natural language and successful retrieval is very much dependent on the effective communication of the intended purpose. Natural language queries consist of multiple linguistic features which serve to represent the intended search goal. Linguistic characteristics that cause semantic ambiguity and misinterpretation of queries as well as additional factors such as the lack of familiarity with the search environment affect the users ability to accurately represent their information needs, coined by the concept intention gap. The latter directly affects the relevance of the returned search results which may not be to the users satisfaction and therefore is a major issue impacting the effectiveness of information retrieval systems. Central to our discussion is the identification of the significant constituents that characterize the query intent and their enrichment through the addition of meaningful terms, phrases or even latent representations, either manually or automatically to capture their intended meaning. Specifically, we discuss techniques to achieve the enrichment and in particular those utilizing the information gathered from statistical processing of term dependencies within a document corpus or from external knowledge sources such as ontologies. We lay down the anatomy of a generic linguistic based query expansion framework and propose its module-based decomposition, covering topical issues from query processing, information retrieval, computational linguistics and ontology engineering. For each of the modules we review state-of-the-art solutions in the literature categorized and analyzed under the light of the techniques used.
Coupled intrinsic and extrinsic human language resource-based query expansion
Apr 23, 2020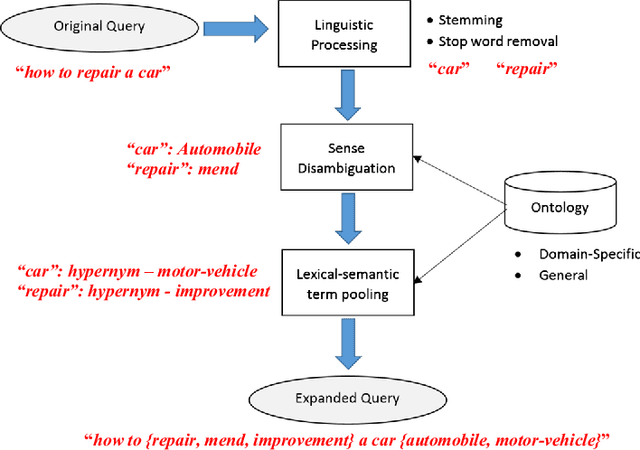
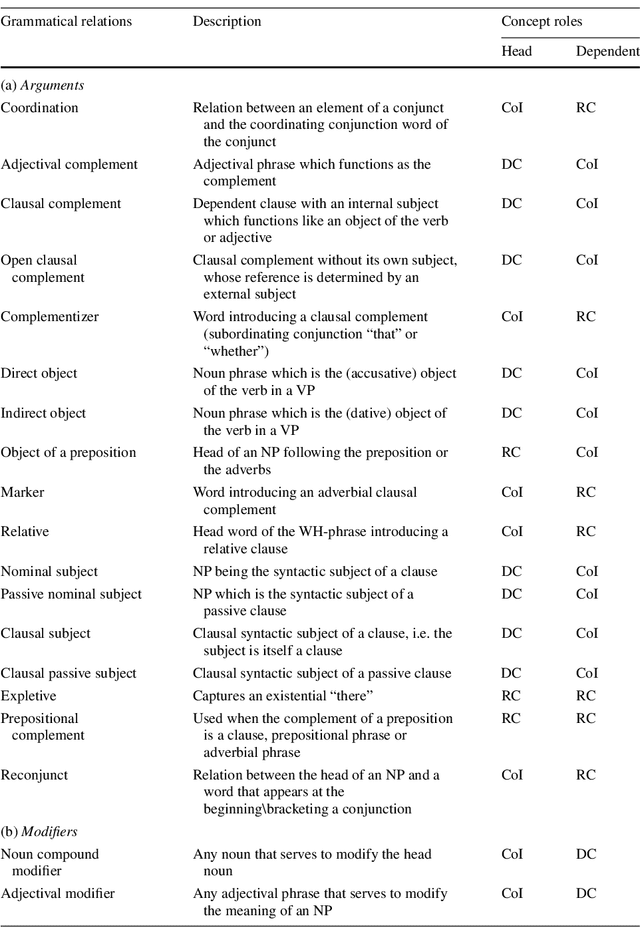
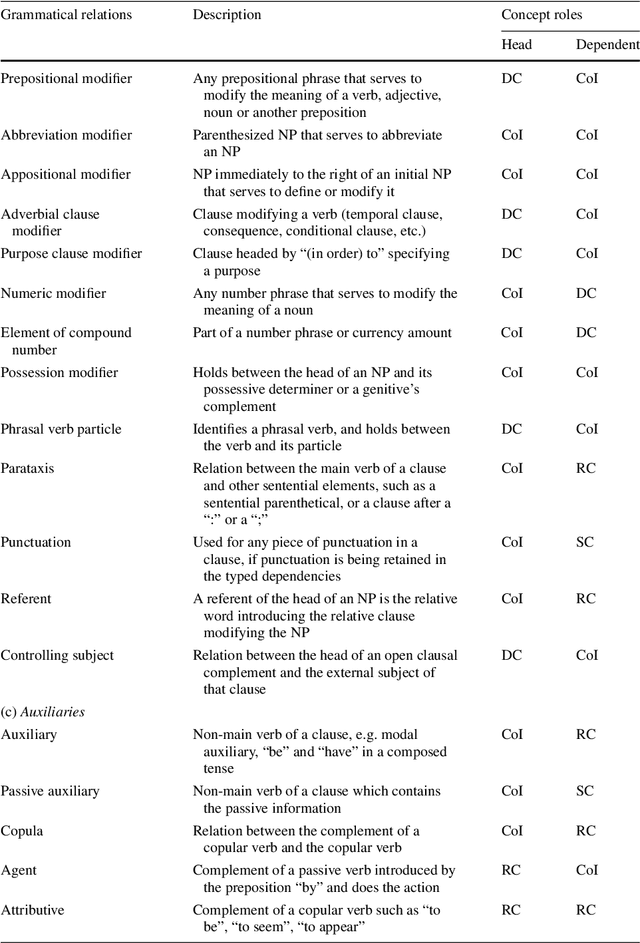

Abstract:Poor information retrieval performance has often been attributed to the query-document vocabulary mismatch problem which is defined as the difficulty for human users to formulate precise natural language queries that are in line with the vocabulary of the documents deemed relevant to a specific search goal. To alleviate this problem, query expansion processes are applied in order to spawn and integrate additional terms to an initial query. This requires accurate identification of main query concepts to ensure the intended search goal is duly emphasized and relevant expansion concepts are extracted and included in the enriched query. Natural language queries have intrinsic linguistic properties such as parts-of-speech labels and grammatical relations which can be utilized in determining the intended search goal. Additionally, extrinsic language-based resources such as ontologies are needed to suggest expansion concepts semantically coherent with the query content. We present here a query expansion framework which capitalizes on both linguistic characteristics of user queries and ontology resources for query constituent encoding, expansion concept extraction and concept weighting. A thorough empirical evaluation on real-world datasets validates our approach against unigram language model, relevance model and a sequential dependence based technique.
Leveraging Cognitive Search Patterns to Enhance Automated Natural Language Retrieval Performance
Apr 21, 2020



Abstract:The search of information in large text repositories has been plagued by the so-called document-query vocabulary gap, i.e. the semantic discordance between the contents in the stored document entities on the one hand and the human query on the other hand. Over the past two decades, a significant body of works has advanced technical retrieval prowess while several studies have shed light on issues pertaining to human search behavior. We believe that these efforts should be conjoined, in the sense that automated retrieval systems have to fully emulate human search behavior and thus consider the procedure according to which users incrementally enhance their initial query. To this end, cognitive reformulation patterns that mimic user search behaviour are highlighted and enhancement terms which are statistically collocated with or lexical-semantically related to the original terms adopted in the retrieval process. We formalize the application of these patterns by considering a query conceptual representation and introducing a set of operations allowing to operate modifications on the initial query. A genetic algorithm-based weighting process allows placing emphasis on terms according to their conceptual role-type. An experimental evaluation on real-world datasets against relevance, language, conceptual and knowledge-based models is conducted. We also show, when compared to language and relevance models, a better performance in terms of mean average precision than a word embedding-based model instantiation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge