Benoit Massé
Extended Gaze Following: Detecting Objects in Videos Beyond the Camera Field of View
Feb 28, 2019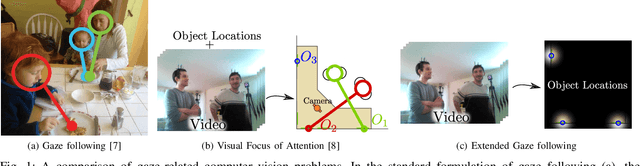
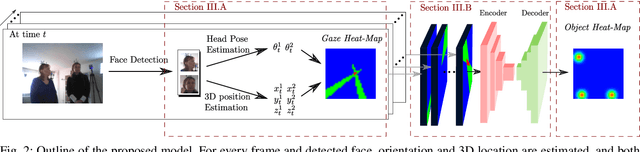
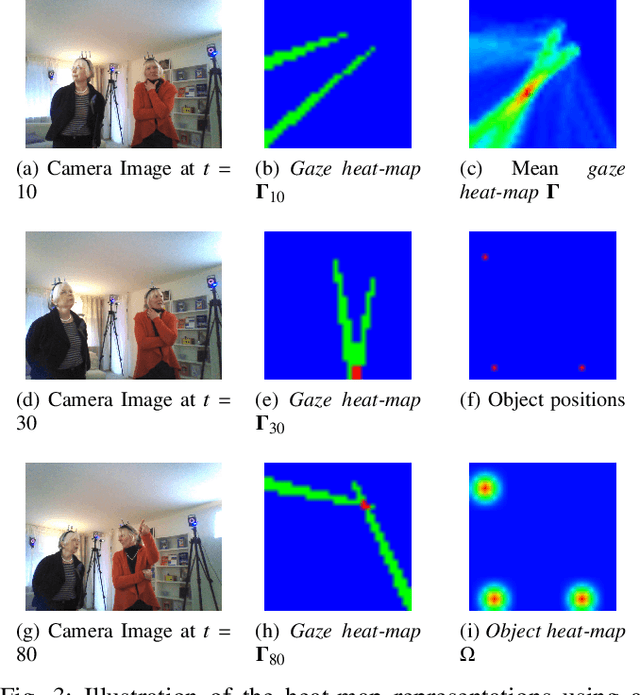
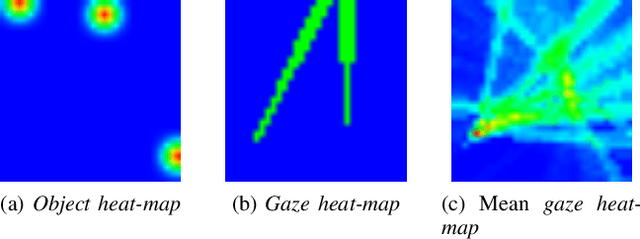
Abstract:In this paper we address the problems of detecting objects of interest in a video and of estimating their locations, solely from the gaze directions of people present in the video. Objects can be indistinctly located inside or outside the camera field of view. We refer to this problem as extended gaze following. The contributions of the paper are the followings. First, we propose a novel spatial representation of the gaze directions adopting a top-view perspective. Second, we develop several convolutional encoder/decoder networks to predict object locations and compare them with heuristics and with classical learning-based approaches. Third, in order to train the proposed models, we generate a very large number of synthetic scenarios employing a probabilistic formulation. Finally, our methodology is empirically validated using a publicly available dataset.
Neural Network Based Reinforcement Learning for Audio-Visual Gaze Control in Human-Robot Interaction
Apr 23, 2018



Abstract:This paper introduces a novel neural network-based reinforcement learning approach for robot gaze control. Our approach enables a robot to learn and to adapt its gaze control strategy for human-robot interaction neither with the use of external sensors nor with human supervision. The robot learns to focus its attention onto groups of people from its own audio-visual experiences, independently of the number of people, of their positions and of their physical appearances. In particular, we use a recurrent neural network architecture in combination with Q-learning to find an optimal action-selection policy; we pre-train the network using a simulated environment that mimics realistic scenarios that involve speaking/silent participants, thus avoiding the need of tedious sessions of a robot interacting with people. Our experimental evaluation suggests that the proposed method is robust against parameter estimation, i.e. the parameter values yielded by the method do not have a decisive impact on the performance. The best results are obtained when both audio and visual information is jointly used. Experiments with the Nao robot indicate that our framework is a step forward towards the autonomous learning of socially acceptable gaze behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge