Benjamin Schloss
Towards an Automated SOAP Note: Classifying Utterances from Medical Conversations
Jul 27, 2020


Abstract:Summaries generated from medical conversations can improve recall and understanding of care plans for patients and reduce documentation burden for doctors. Recent advancements in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and natural language understanding (NLU) offer potential solutions to generate these summaries automatically, but rigorous quantitative baselines for benchmarking research in this domain are lacking. In this paper, we bridge this gap for two tasks: classifying utterances from medical conversations according to (i) the SOAP section and (ii) the speaker role. Both are fundamental building blocks along the path towards an end-to-end, automated SOAP note for medical conversations. We provide details on a dataset that contains human and ASR transcriptions of medical conversations and corresponding machine learning optimized SOAP notes. We then present a systematic analysis in which we adapt an existing deep learning architecture to the two aforementioned tasks. The results suggest that modelling context in a hierarchical manner, which captures both word and utterance level context, yields substantial improvements on both classification tasks. Additionally, we develop and analyze a modular method for adapting our model to ASR output.
Extracting Structured Data from Physician-Patient Conversations By Predicting Noteworthy Utterances
Jul 14, 2020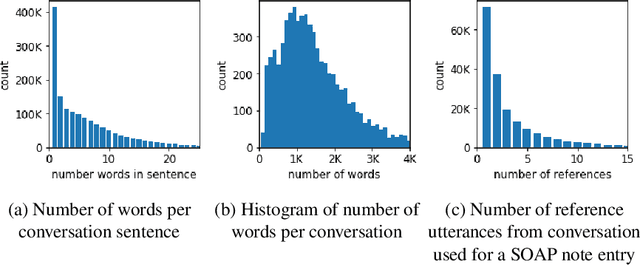
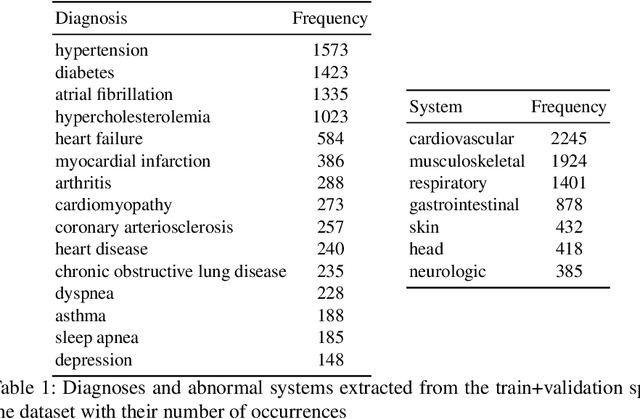
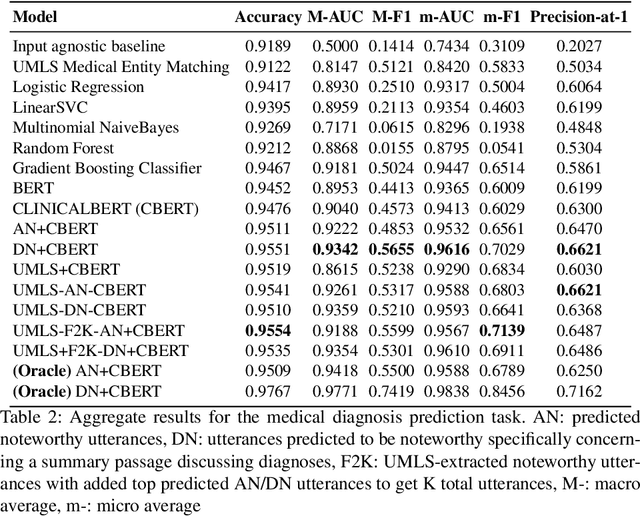
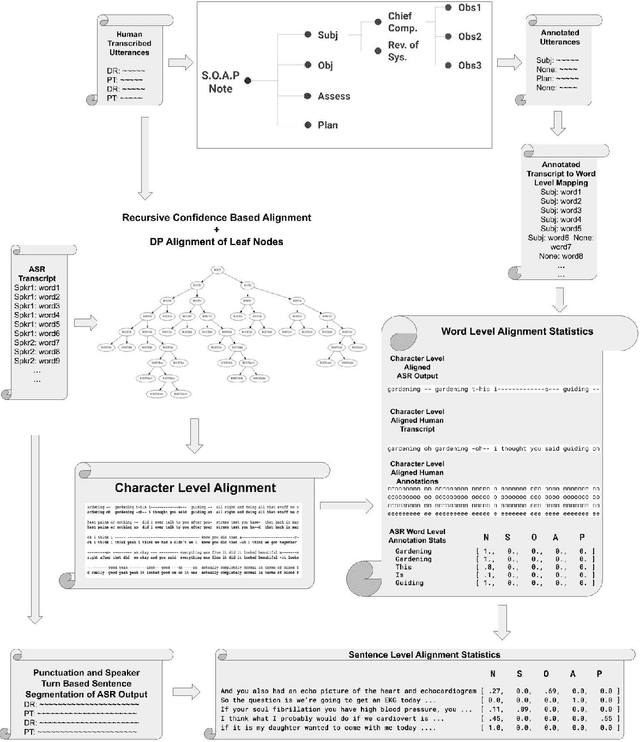
Abstract:Despite diverse efforts to mine various modalities of medical data, the conversations between physicians and patients at the time of care remain an untapped source of insights. In this paper, we leverage this data to extract structured information that might assist physicians with post-visit documentation in electronic health records, potentially lightening the clerical burden. In this exploratory study, we describe a new dataset consisting of conversation transcripts, post-visit summaries, corresponding supporting evidence (in the transcript), and structured labels. We focus on the tasks of recognizing relevant diagnoses and abnormalities in the review of organ systems (RoS). One methodological challenge is that the conversations are long (around 1500 words), making it difficult for modern deep-learning models to use them as input. To address this challenge, we extract noteworthy utterances---parts of the conversation likely to be cited as evidence supporting some summary sentence. We find that by first filtering for (predicted) noteworthy utterances, we can significantly boost predictive performance for recognizing both diagnoses and RoS abnormalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge