Extracting Structured Data from Physician-Patient Conversations By Predicting Noteworthy Utterances
Paper and Code
Jul 14, 2020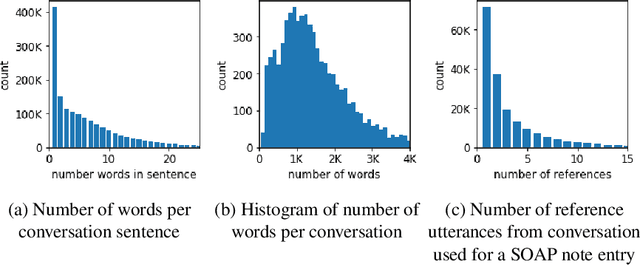
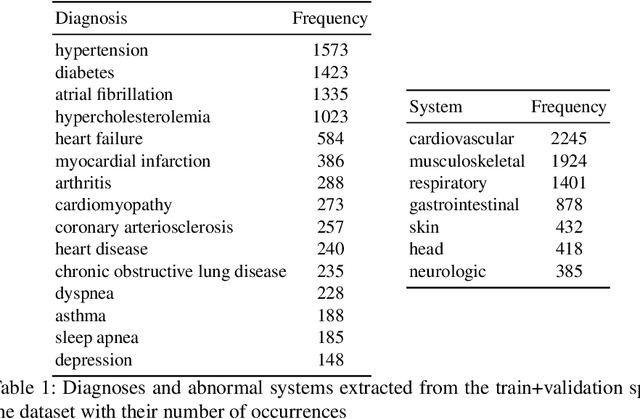
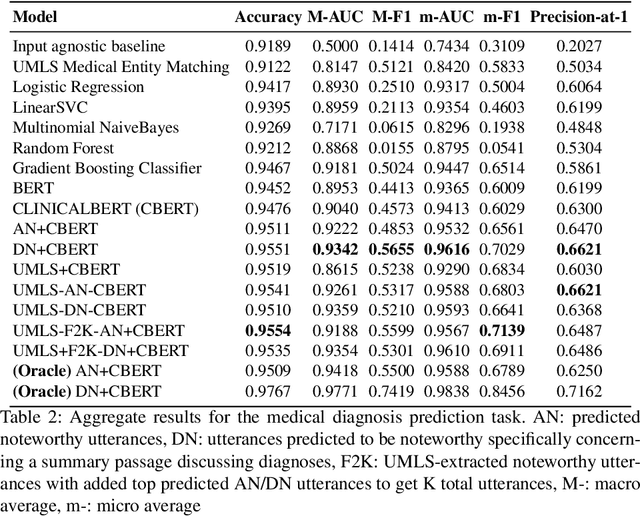
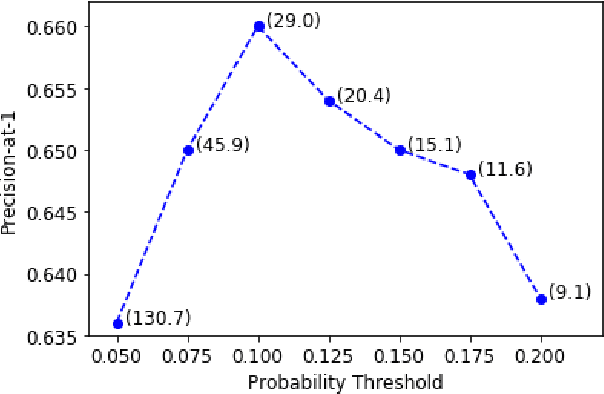
Despite diverse efforts to mine various modalities of medical data, the conversations between physicians and patients at the time of care remain an untapped source of insights. In this paper, we leverage this data to extract structured information that might assist physicians with post-visit documentation in electronic health records, potentially lightening the clerical burden. In this exploratory study, we describe a new dataset consisting of conversation transcripts, post-visit summaries, corresponding supporting evidence (in the transcript), and structured labels. We focus on the tasks of recognizing relevant diagnoses and abnormalities in the review of organ systems (RoS). One methodological challenge is that the conversations are long (around 1500 words), making it difficult for modern deep-learning models to use them as input. To address this challenge, we extract noteworthy utterances---parts of the conversation likely to be cited as evidence supporting some summary sentence. We find that by first filtering for (predicted) noteworthy utterances, we can significantly boost predictive performance for recognizing both diagnoses and RoS abnormalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge