Benjamin K. Ng
On the Impact of Phase Errors in Phase-Dependent Amplitudes of Near-Field RISs
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates mutual coupling between phase-dependent amplitudes (PDAs) and designed phase shifts within pixels of near-field (NF) reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) in the presence of phase errors (PEs). In contrast to existing research that treats phase shifts with errors (PSEs) and the PDAs separately, we introduce a remaining power (RP) metric to quantify the proportion of power preserved in the signals reflected by the RIS, and we prove its asymptotic convergence to theoretical values by leveraging extended Glivenko-Cantelli theorem. Then, the RP of signals passing through RIS pixels is jointly examined under combined phase and amplitude uncertainties. In addition, we propose four pixel reflection models to capture practical conditions, and we derive approximate polynomial upper bounds for the RP with error terms by applying Taylor expansion. Furthermore, based on Friis transmission formula and projected aperture, we propose a general NF channel model that incorporates the coupling between the PSEs and the PDAs. By using Cauchy-Bunyakovsky-Schwarz inequality and Riemann sums, we derive a closed-form upper bound on spectral efficiency, and the bound becomes tighter as the pixel area decreases. We reveal that as the RIS phase shifts approach the ends of their range, the RP under independent and identically distributed PEs is smaller than that under fully correlated PEs, whereas this relationship reverses when the phase shifts are near the middle of their range. Neglecting the PEs in the PDAs leads to an overestimation of the RIS performance gain, explaining the discrepancies between theoretical and measured results.
RIS-Empowered OTFS Modulation With Faster-than-Nyquist Signaling in High-Mobility Wireless Communications
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:High-mobility wireless communication systems suffer from severe Doppler spread and multi-path delay, which degrade the reliability and spectral efficiency of conventional modulation schemes. Orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation offers strong robustness in such environments by representing symbols in the delay-Doppler (DD) domain, while faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) signaling can further enhance spectral efficiency through intentional symbol packing. Meanwhile, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) provide a promising means to improve link quality via passive beamforming. Motivated by these advantages, we propose a novel RIS-empowered OTFS modulation with FTN signaling (RIS-OTFS-FTN) scheme. First, we establish a unified DD-domain input-output relationship that jointly accounts for RIS passive beamforming, FTN-induced inter-symbol interference, and DD-domain channel characteristics. Based on this model, we provide comprehensive analytical performance for the frame error rate, spectral efficiency, and peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR), etc. Furthermore, a practical RIS phase adjustment strategy with quantized phase selection is designed to maximize the effective channel gain. Extensive Monte Carlo simulations under a standardized extended vehicular A (EVA) channel model validate the theoretical results and provide key insights into the trade-offs among spectral efficiency, PAPR, input back-off (IBO), and error performance, with some interesting insights.The proposed RIS-OTFS-FTN scheme demonstrates notable performance gains in both reliability and spectral efficiency, offering a viable solution for future high-mobility and spectrum-constrained wireless systems.
What Roles can Spatial Modulation and Space Shift Keying Play in LEO Satellite-Assisted Communication?
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, the rapid evolution of satellite communications play a pivotal role in addressing the ever-increasing demand for global connectivity, among which the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites attract a great amount of attention due to their low latency and high data throughput capabilities. Based on this, we explore spatial modulation (SM) and space shift keying (SSK) designs as pivotal techniques to enhance spectral efficiency (SE) and bit-error rate (BER) performance in the LEO satellite-assisted multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. The various performance analysis of these designs are presented in this paper, revealing insightful findings and conclusions through analytical methods and Monte Carlo simulations with perfect and imperfect channel state information (CSI) estimation. The results provide a comprehensive analysis of the merits and trade-offs associated with the investigated schemes, particularly in terms of BER, computational complexity, and SE. This analysis underscores the potential of both schemes as viable candidates for future 6G LEO satellite-assisted wireless communication systems.
Maximum Channel Coding Rate of Finite Block Length MIMO Faster-Than-Nyquist Signaling
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:The pursuit of higher data rates and efficient spectrum utilization in modern communication technologies necessitates novel solutions. In order to provide insights into improving spectral efficiency and reducing latency, this study investigates the maximum channel coding rate (MCCR) of finite block length (FBL) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) channels. By optimizing power allocation, we derive the system's MCCR expression. Simulation results are compared with the existing literature to reveal the benefits of FTN in FBL transmission.
MIMO Asynchronous MAC with Faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) Signaling
May 20, 2023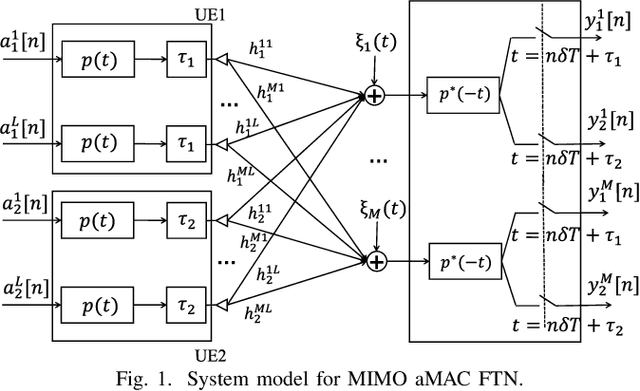
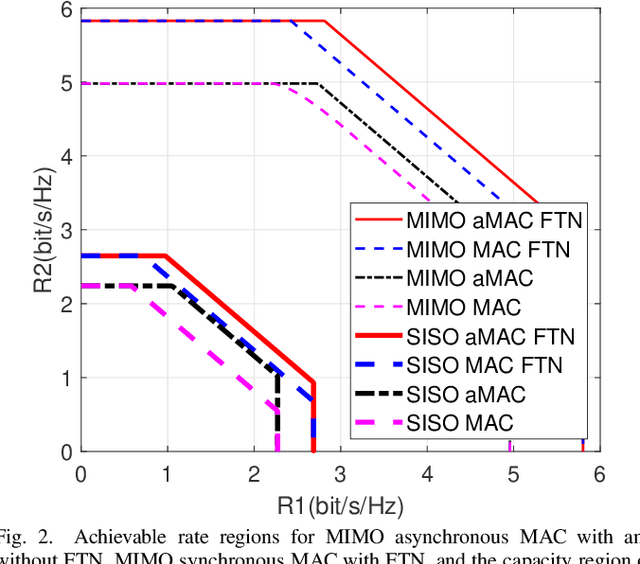
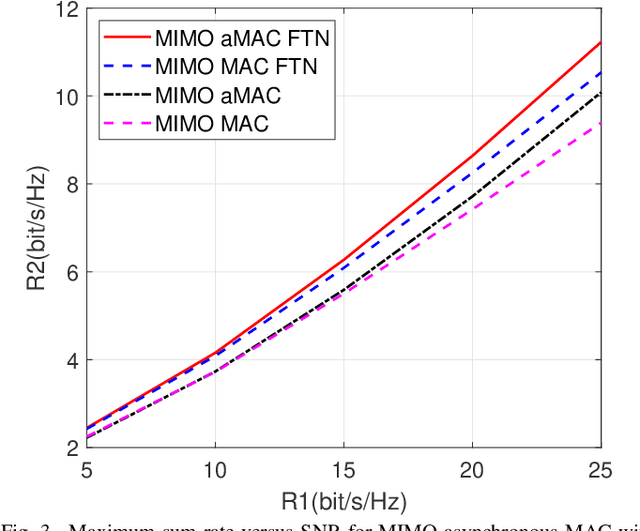

Abstract:Faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) signaling is a nonorthogonal transmission technique, which brings in intentional inter-symbol interference. This way it can significantly enhance spectral efficiency for practical pulse shapes such as the root raised cosine pulses. This paper proposes an achievable rate region for the multiple antenna (MIMO) asynchronous multiple access channel (aMAC) with FTN signaling. The scheme applies waterfilling in the spatial domain and precoding in time. Waterfilling in space provides better power allocation and precoding helps mitigate inter-symbol interference due to asynchronous transmission and FTN. The results show that the gains due to asynchronous transmission and FTN are more emphasized in MIMO aMAC than in single antenna aMAC. Moreover, FTN improves single-user rates, and asynchronous transmission improves the sum-rate, due to better inter-user interference management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge