Benjamin C. Warner
Autoregressive Language Models For Estimating the Entropy of Epic EHR Audit Logs
Nov 26, 2023



Abstract:EHR audit logs are a highly granular stream of events that capture clinician activities, and is a significant area of interest for research in characterizing clinician workflow on the electronic health record (EHR). Existing techniques to measure the complexity of workflow through EHR audit logs (audit logs) involve time- or frequency-based cross-sectional aggregations that are unable to capture the full complexity of a EHR session. We briefly evaluate the usage of transformer-based tabular language model (tabular LM) in measuring the entropy or disorderedness of action sequences within workflow and release the evaluated models publicly.
Utilizing Semantic Textual Similarity for Clinical Survey Data Feature Selection
Aug 19, 2023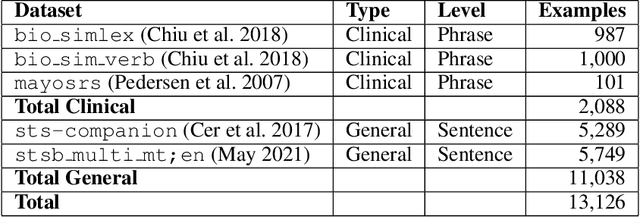
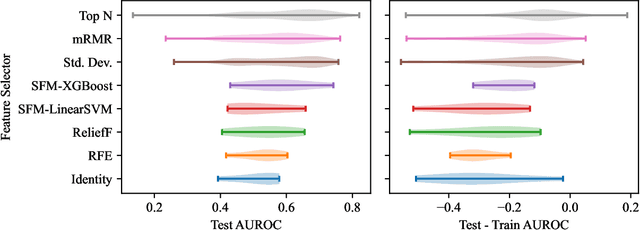
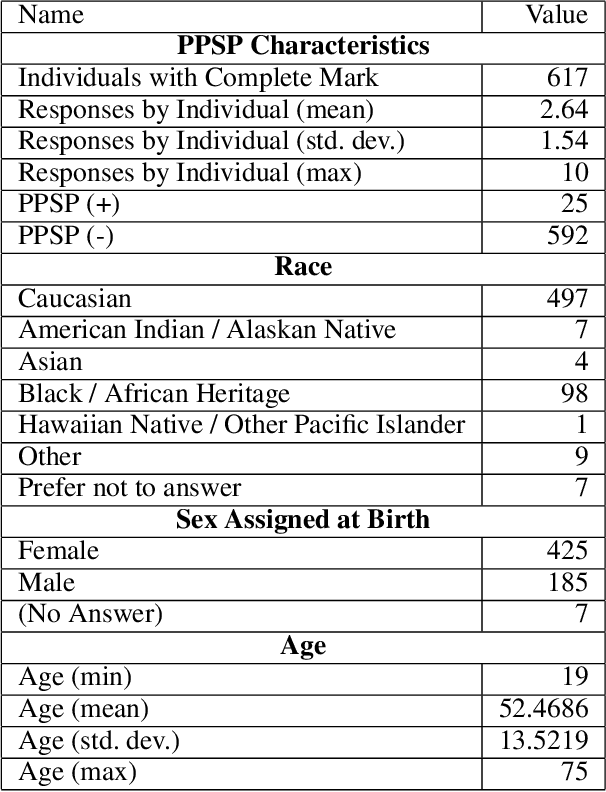
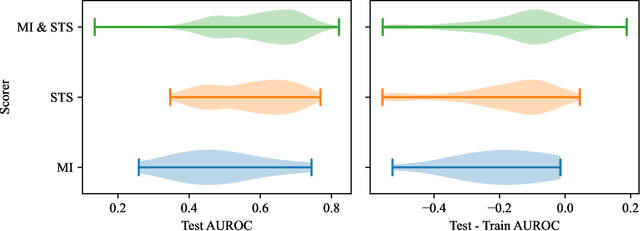
Abstract:Survey data can contain a high number of features while having a comparatively low quantity of examples. Machine learning models that attempt to predict outcomes from survey data under these conditions can overfit and result in poor generalizability. One remedy to this issue is feature selection, which attempts to select an optimal subset of features to learn upon. A relatively unexplored source of information in the feature selection process is the usage of textual names of features, which may be semantically indicative of which features are relevant to a target outcome. The relationships between feature names and target names can be evaluated using language models (LMs) to produce semantic textual similarity (STS) scores, which can then be used to select features. We examine the performance using STS to select features directly and in the minimal-redundancy-maximal-relevance (mRMR) algorithm. The performance of STS as a feature selection metric is evaluated against preliminary survey data collected as a part of a clinical study on persistent post-surgical pain (PPSP). The results suggest that features selected with STS can result in higher performance models compared to traditional feature selection algorithms.
HiPAL: A Deep Framework for Physician Burnout Prediction Using Activity Logs in Electronic Health Records
May 24, 2022



Abstract:Burnout is a significant public health concern affecting nearly half of the healthcare workforce. This paper presents the first end-to-end deep learning framework for predicting physician burnout based on clinician activity logs, digital traces of their work activities, available in any electronic health record (EHR) system. In contrast to prior approaches that exclusively relied on surveys for burnout measurement, our framework directly learns deep workload representations from large-scale clinician activity logs to predict burnout. We propose the Hierarchical burnout Prediction based on Activity Logs (HiPAL), featuring a pre-trained time-dependent activity embedding mechanism tailored for activity logs and a hierarchical predictive model, which mirrors the natural hierarchical structure of clinician activity logs and captures physician's evolving workload patterns at both short-term and long-term levels. To utilize the large amount of unlabeled activity logs, we propose a semi-supervised framework that learns to transfer knowledge extracted from unlabeled clinician activities to the HiPAL-based prediction model. The experiment on over 15 million clinician activity logs collected from the EHR at a large academic medical center demonstrates the advantages of our proposed framework in predictive performance of physician burnout and training efficiency over state of the art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge