Benjamin Bustos
Bridging Vision and Language from the Video-to-Text Perspective: A Comprehensive Review
Mar 27, 2021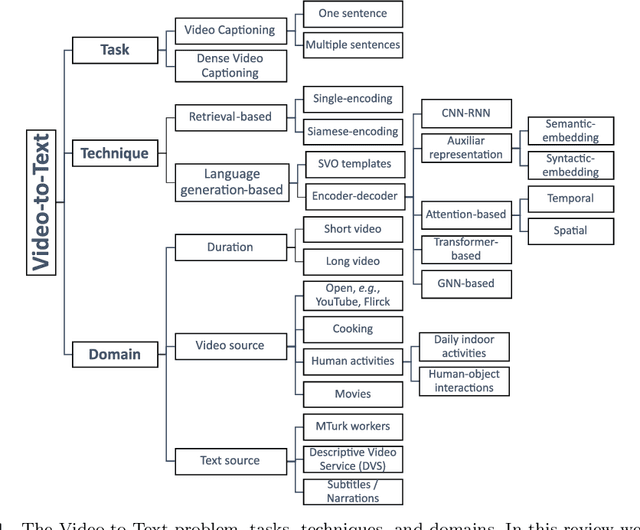
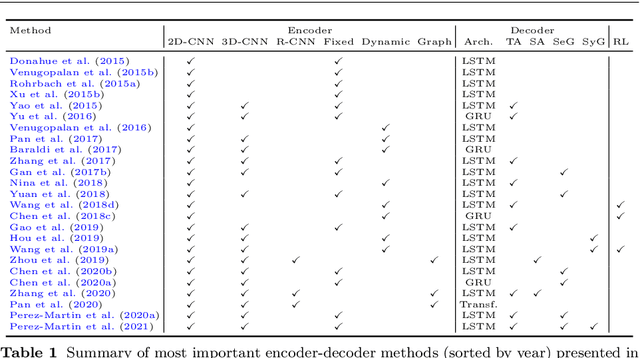
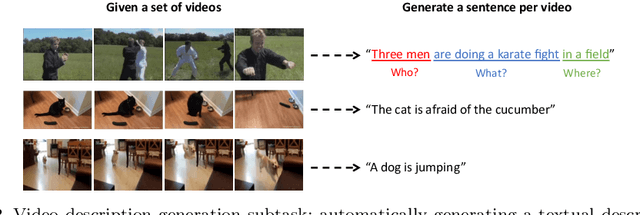
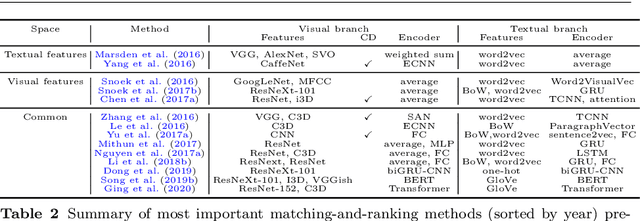
Abstract:Research in the area of Vision and Language encompasses challenging topics that seek to connect visual and textual information. The video-to-text problem is one of these topics, in which the goal is to connect an input video with its textual description. This connection can be mainly made by retrieving the most significant descriptions from a corpus or generating a new one given a context video. These two ways represent essential tasks for Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing communities, called text retrieval from video task and video captioning/description task. These two tasks are substantially more complex than predicting or retrieving a single sentence from an image. The spatiotemporal information present in videos introduces diversity and complexity regarding the visual content and the structure of associated language descriptions. This review categorizes and describes the state-of-the-art techniques for the video-to-text problem. It covers the main video-to-text methods and the ways to evaluate their performance. We analyze how the most reported benchmark datasets have been created, showing their drawbacks and strengths for the problem requirements. We also show the impressive progress that researchers have made on each dataset, and we analyze why, despite this progress, the video-to-text conversion is still unsolved. State-of-the-art techniques are still a long way from achieving human-like performance in generating or retrieving video descriptions. We cover several significant challenges in the field and discuss future research directions.
A Convolutional Architecture for 3D Model Embedding
Mar 05, 2021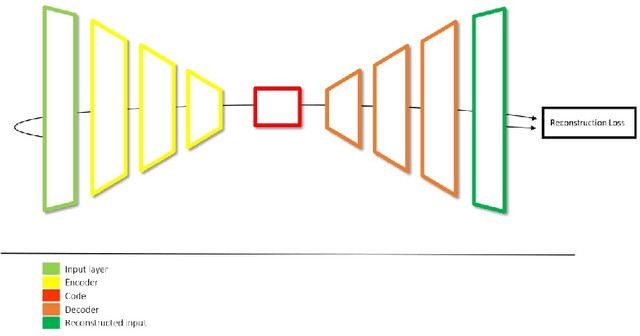
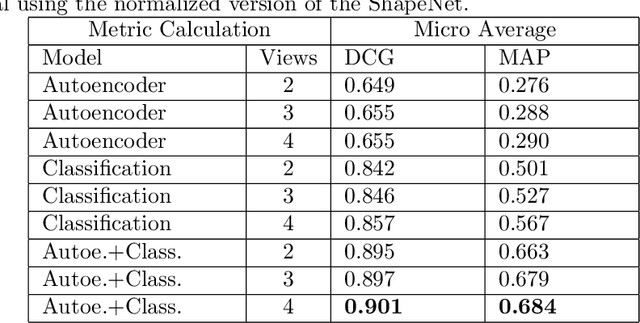
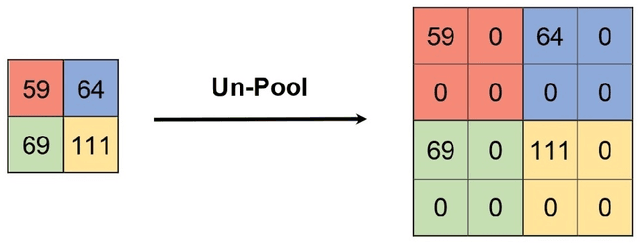
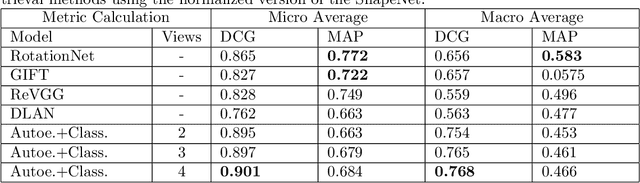
Abstract:During the last years, many advances have been made in tasks like3D model retrieval, 3D model classification, and 3D model segmentation.The typical 3D representations such as point clouds, voxels, and poly-gon meshes are mostly suitable for rendering purposes, while their use forcognitive processes (retrieval, classification, segmentation) is limited dueto their high redundancy and complexity. We propose a deep learningarchitecture to handle 3D models as an input. We combine this architec-ture with other standard architectures like Convolutional Neural Networksand autoencoders for computing 3D model embeddings. Our goal is torepresent a 3D model as a vector with enough information to substitutethe 3D model for high-level tasks. Since this vector is a learned repre-sentation which tries to capture the relevant information of a 3D model,we show that the embedding representation conveys semantic informationthat helps to deal with the similarity assessment of 3D objects. Our ex-periments show the benefit of computing the embeddings of a 3D modeldata set and use them for effective 3D Model Retrieval.
Semantic Search of Memes on Twitter
Feb 09, 2020



Abstract:Memes are becoming a useful source of data for analyzing behavior on social media. However, a problem to tackle is how to correctly identify a meme. As the number of memes published every day on social media is huge, there is a need for automatic methods for classifying and searching in large meme datasets. This paper proposes and compares several methods for automatically classifying images as memes. Also, we propose a method that allows us to implement a system for retrieving memes from a dataset using a textual query. We experimentally evaluate the methods using a large dataset of memes collected from Twitter users in Chile, which was annotated by a group of experts. Though some of the evaluated methods are effective, there is still room for improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge