Bekir Sait Ciftler
Hierarchical Multi-Agent DRL-Based Framework for Joint Multi-RAT Assignment and Dynamic Resource Allocation in Next-Generation HetNets
Feb 28, 2022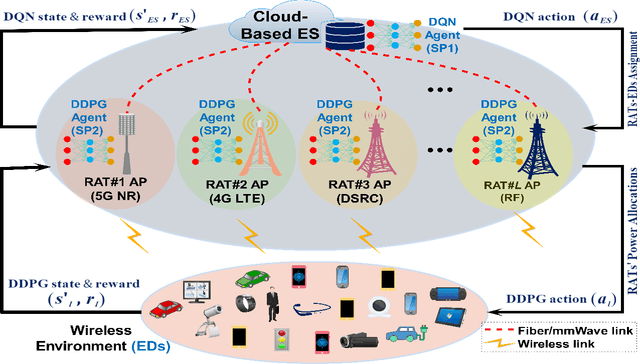
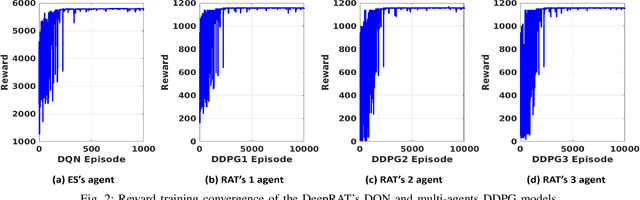
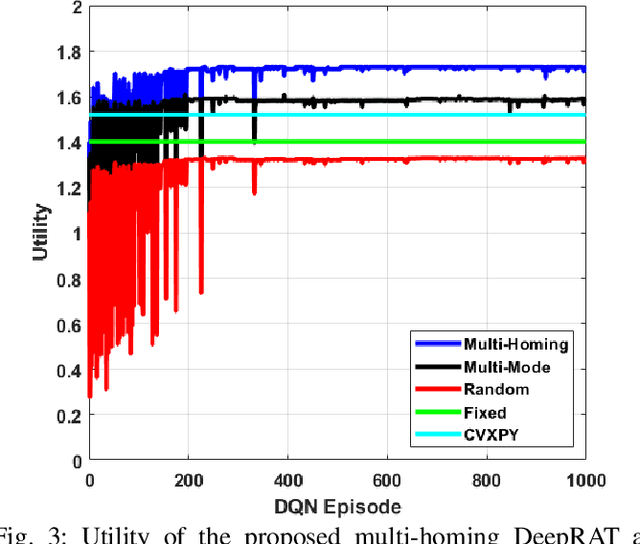
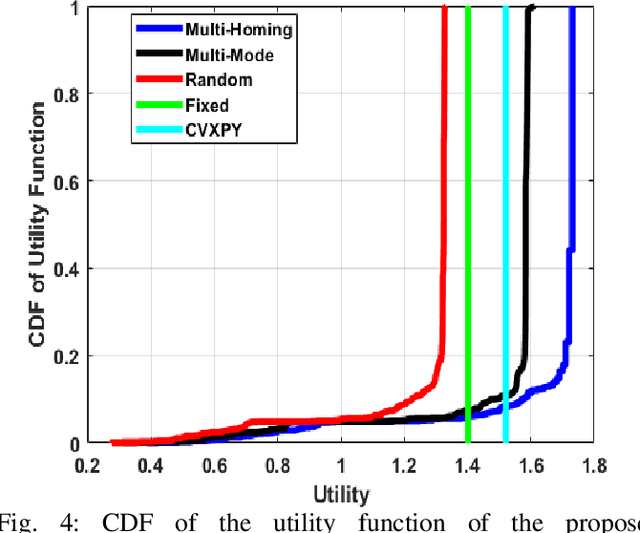
Abstract:This paper considers the problem of cost-aware downlink sum-rate maximization via joint optimal radio access technologies (RATs) assignment and power allocation in next-generation heterogeneous wireless networks (HetNets). We consider a future HetNet comprised of multi-RATs and serving multi-connectivity edge devices (EDs), and we formulate the problem as mixed-integer non-linear programming (MINP) problem. Due to the high complexity and combinatorial nature of this problem and the difficulty to solve it using conventional methods, we propose a hierarchical multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based framework, called DeepRAT, to solve it efficiently and learn system dynamics. In particular, the DeepRAT framework decomposes the problem into two main stages; the RATs-EDs assignment stage, which implements a single-agent Deep Q Network (DQN) algorithm, and the power allocation stage, which utilizes a multi-agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm. Using simulations, we demonstrate how the various DRL agents efficiently interact to learn system dynamics and derive the global optimal policy. Furthermore, our simulation results show that the proposed DeepRAT algorithm outperforms existing state-of-the-art heuristic approaches in terms of network utility. Finally, we quantitatively show the ability of the DeepRAT model to quickly and dynamically adapt to abrupt changes in network dynamics, such as EDs mobility.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Radio Resource Allocation and Management in Next Generation Heterogeneous Wireless Networks: A Survey
May 25, 2021Abstract:Next generation wireless networks are expected to be extremely complex due to their massive heterogeneity in terms of the types of network architectures they incorporate, the types and numbers of smart IoT devices they serve, and the types of emerging applications they support. In such large-scale and heterogeneous networks (HetNets), radio resource allocation and management (RRAM) becomes one of the major challenges encountered during system design and deployment. In this context, emerging Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) techniques are expected to be one of the main enabling technologies to address the RRAM in future wireless HetNets. In this paper, we conduct a systematic in-depth, and comprehensive survey of the applications of DRL techniques in RRAM for next generation wireless networks. Towards this, we first overview the existing traditional RRAM methods and identify their limitations that motivate the use of DRL techniques in RRAM. Then, we provide a comprehensive review of the most widely used DRL algorithms to address RRAM problems, including the value- and policy-based algorithms. The advantages, limitations, and use-cases for each algorithm are provided. We then conduct a comprehensive and in-depth literature review and classify existing related works based on both the radio resources they are addressing and the type of wireless networks they are investigating. To this end, we carefully identify the types of DRL algorithms utilized in each related work, the elements of these algorithms, and the main findings of each related work. Finally, we highlight important open challenges and provide insights into several future research directions in the context of DRL-based RRAM. This survey is intentionally designed to guide and stimulate more research endeavors towards building efficient and fine-grained DRL-based RRAM schemes for future wireless networks.
Federated Learning for Localization: A Privacy-Preserving Crowdsourcing Method
Feb 04, 2020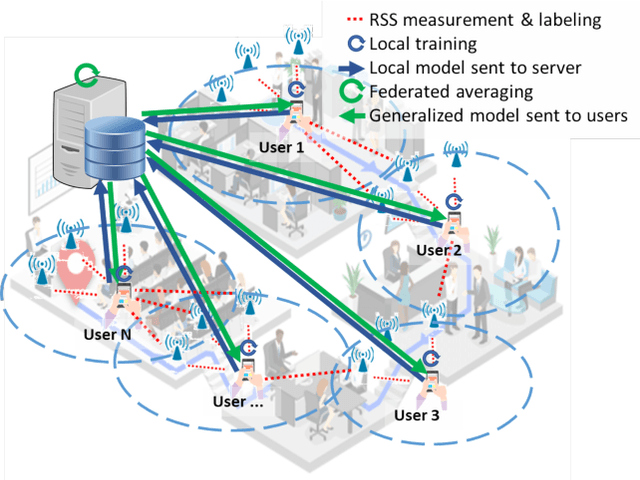
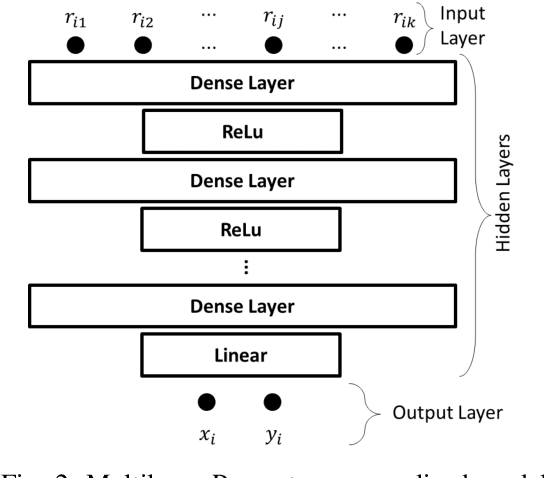
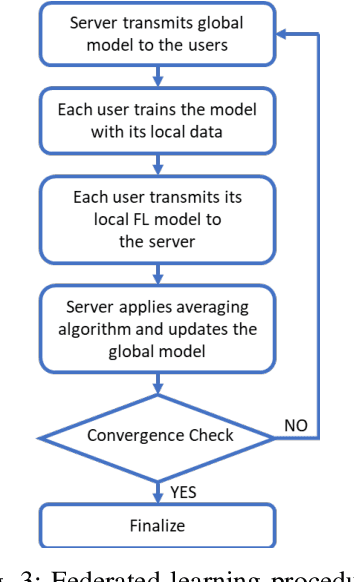
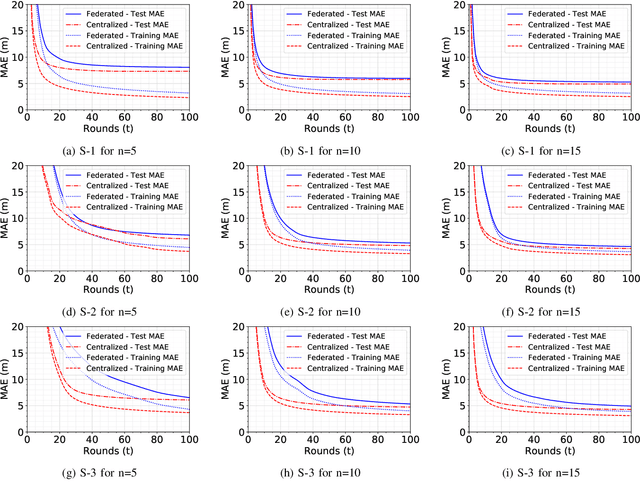
Abstract:Received Signal Strength (RSS) fingerprint-based localization has attracted a lot of research effort and cultivated many commercial applications of location-based services due to its low cost and ease of implementation. Many studies are exploring the use of deep learning (DL) algorithms for localization. DL's ability to extract features and to classify autonomously makes it an attractive solution for fingerprint-based localization. These solutions require frequent retraining of DL models with vast amounts of measurements. Although crowdsourcing is an excellent way to gather immense amounts of data, it jeopardizes the privacy of participants, as it requires to collect labeled data at a centralized server. Recently, federated learning has emerged as a practical concept in solving the privacy preservation issue of crowdsourcing participants by performing model training at the edge devices in a decentralized manner; the participants do not expose their data anymore to a centralized server. This paper presents a novel method utilizing federated learning to improve the accuracy of RSS fingerprint-based localization while preserving the privacy of the crowdsourcing participants. Employing federated learning allows ensuring \emph{preserving the privacy of user data} while enabling an adequate localization performance with experimental data captured in real-world settings. The proposed method improved localization accuracy by 1.8 meters when used as a booster for centralized learning and achieved satisfactory localization accuracy when used standalone.
Exploiting Unlabeled Data in Smart Cities using Federated Learning
Jan 10, 2020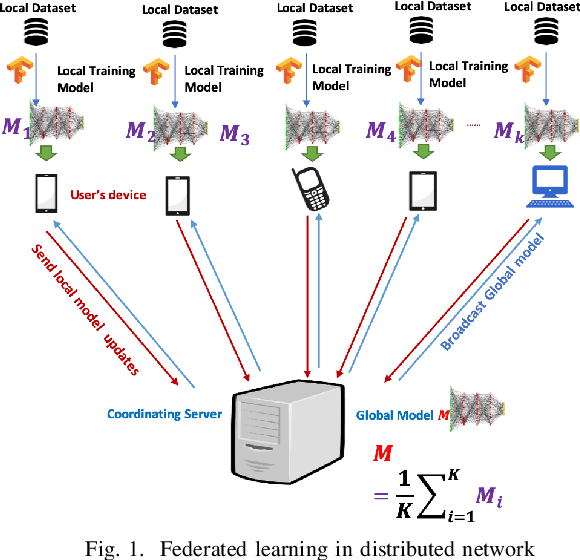
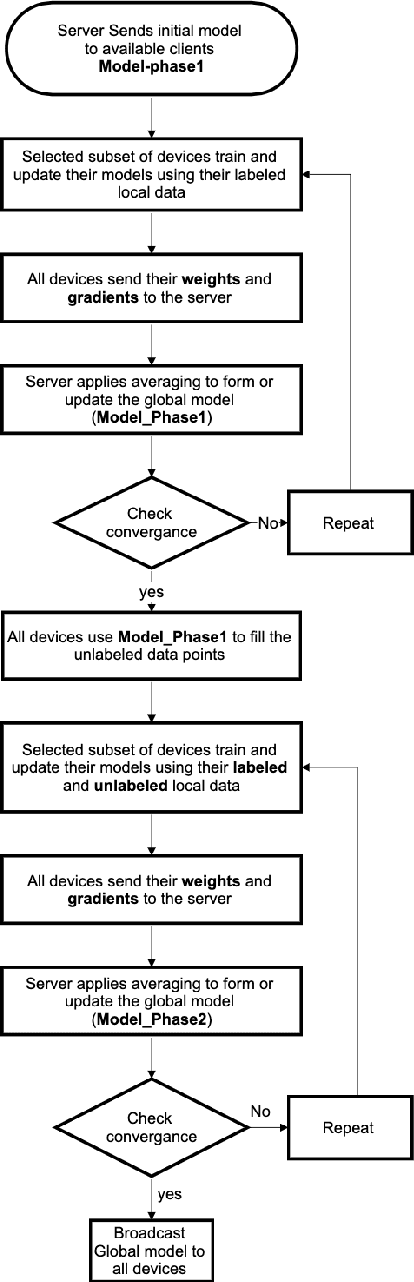
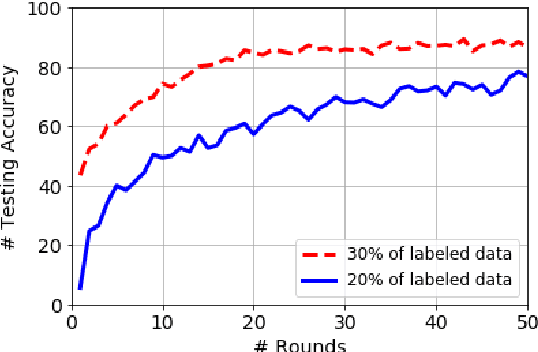
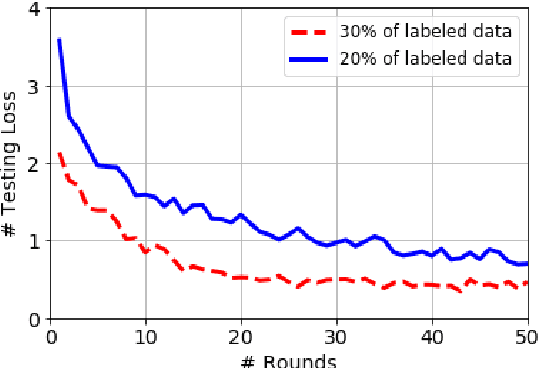
Abstract:Privacy concerns are considered one of the main challenges in smart cities as sharing sensitive data brings threatening problems to people's lives. Federated learning has emerged as an effective technique to avoid privacy infringement as well as increase the utilization of the data. However, there is a scarcity in the amount of labeled data and an abundance of unlabeled data collected in smart cities, hence there is a need to use semi-supervised learning. We propose a semi-supervised federated learning method called FedSem that exploits unlabeled data. The algorithm is divided into two phases where the first phase trains a global model based on the labeled data. In the second phase, we use semi-supervised learning based on the pseudo labeling technique to improve the model. We conducted several experiments using traffic signs dataset to show that FedSem can improve accuracy up to 8% by utilizing the unlabeled data in the learning process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge