Bastian Bischoff
Exploiting Sparsity in Automotive Radar Object Detection Networks
Aug 15, 2023Abstract:Having precise perception of the environment is crucial for ensuring the secure and reliable functioning of autonomous driving systems. Radar object detection networks are one fundamental part of such systems. CNN-based object detectors showed good performance in this context, but they require large compute resources. This paper investigates sparse convolutional object detection networks, which combine powerful grid-based detection with low compute resources. We investigate radar specific challenges and propose sparse kernel point pillars (SKPP) and dual voxel point convolutions (DVPC) as remedies for the grid rendering and sparse backbone architectures. We evaluate our SKPP-DPVCN architecture on nuScenes, which outperforms the baseline by 5.89% and the previous state of the art by 4.19% in Car AP4.0. Moreover, SKPP-DPVCN reduces the average scale error (ASE) by 21.41% over the baseline.
Improved Multi-Scale Grid Rendering of Point Clouds for Radar Object Detection Networks
May 25, 2023



Abstract:Architectures that first convert point clouds to a grid representation and then apply convolutional neural networks achieve good performance for radar-based object detection. However, the transfer from irregular point cloud data to a dense grid structure is often associated with a loss of information, due to the discretization and aggregation of points. In this paper, we propose a novel architecture, multi-scale KPPillarsBEV, that aims to mitigate the negative effects of grid rendering. Specifically, we propose a novel grid rendering method, KPBEV, which leverages the descriptive power of kernel point convolutions to improve the encoding of local point cloud contexts during grid rendering. In addition, we propose a general multi-scale grid rendering formulation to incorporate multi-scale feature maps into convolutional backbones of detection networks with arbitrary grid rendering methods. We perform extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset and evaluate the methods in terms of detection performance and computational complexity. The proposed multi-scale KPPillarsBEV architecture outperforms the baseline by 5.37% and the previous state of the art by 2.88% in Car AP4.0 (average precision for a matching threshold of 4 meters) on the nuScenes validation set. Moreover, the proposed single-scale KPBEV grid rendering improves the Car AP4.0 by 2.90% over the baseline while maintaining the same inference speed.
On Detecting Adversarial Perturbations
Feb 21, 2017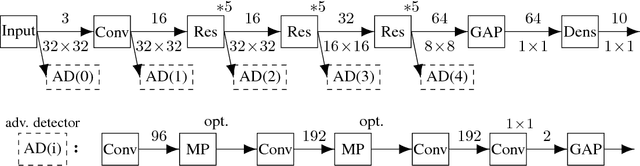

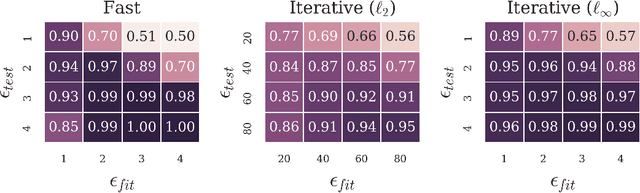
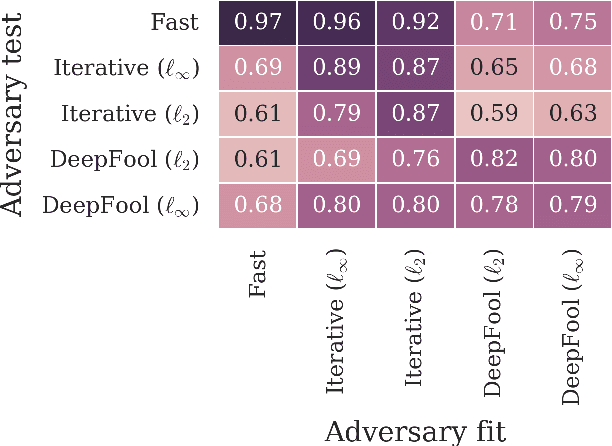
Abstract:Machine learning and deep learning in particular has advanced tremendously on perceptual tasks in recent years. However, it remains vulnerable against adversarial perturbations of the input that have been crafted specifically to fool the system while being quasi-imperceptible to a human. In this work, we propose to augment deep neural networks with a small "detector" subnetwork which is trained on the binary classification task of distinguishing genuine data from data containing adversarial perturbations. Our method is orthogonal to prior work on addressing adversarial perturbations, which has mostly focused on making the classification network itself more robust. We show empirically that adversarial perturbations can be detected surprisingly well even though they are quasi-imperceptible to humans. Moreover, while the detectors have been trained to detect only a specific adversary, they generalize to similar and weaker adversaries. In addition, we propose an adversarial attack that fools both the classifier and the detector and a novel training procedure for the detector that counteracts this attack.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge