Bartomeu Coll
Accurate Motion Estimation through Random Sample Aggregated Consensus
Jan 19, 2017
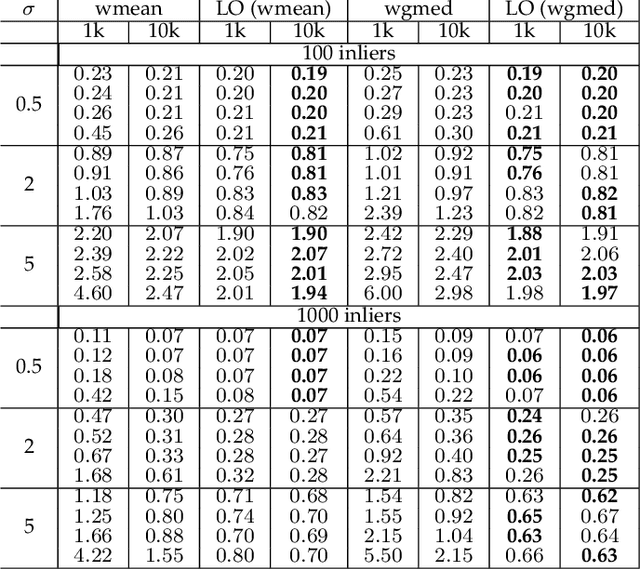
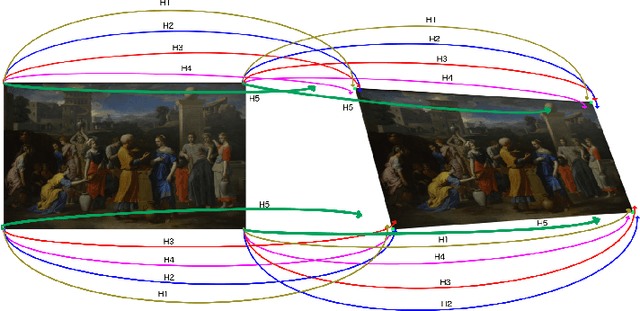
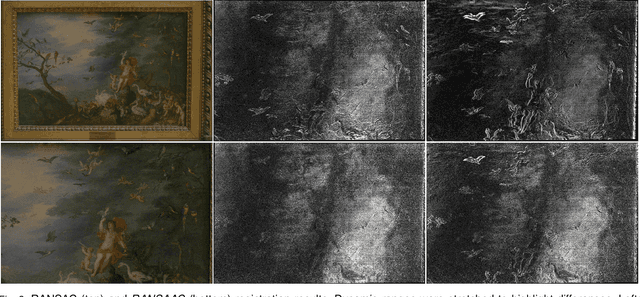
Abstract:We reconsider the classic problem of estimating accurately a 2D transformation from point matches between images containing outliers. RANSAC discriminates outliers by randomly generating minimalistic sampled hypotheses and verifying their consensus over the input data. Its response is based on the single hypothesis that obtained the largest inlier support. In this article we show that the resulting accuracy can be improved by aggregating all generated hypotheses. This yields RANSAAC, a framework that improves systematically over RANSAC and its state-of-the-art variants by statistically aggregating hypotheses. To this end, we introduce a simple strategy that allows to rapidly average 2D transformations, leading to an almost negligible extra computational cost. We give practical applications on projective transforms and homography+distortion models and demonstrate a significant performance gain in both cases.
A Survey of Pansharpening Methods with A New Band-Decoupled Variational Model
Jun 17, 2016
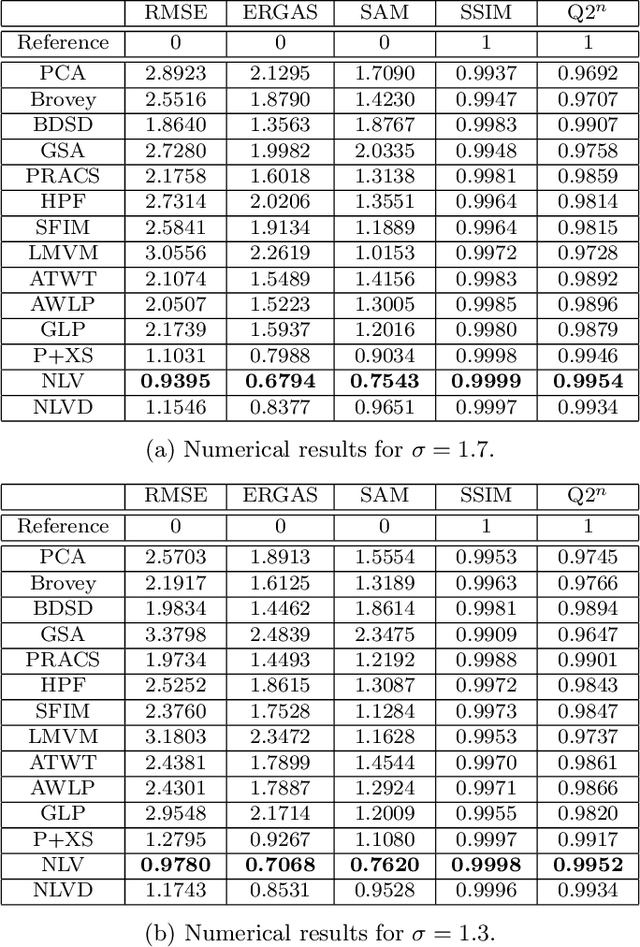


Abstract:Most satellites decouple the acquisition of a panchromatic image at high spatial resolution from the acquisition of a multispectral image at lower spatial resolution. Pansharpening is a fusion technique used to increase the spatial resolution of the multispectral data while simultaneously preserving its spectral information. In this paper, we consider pansharpening as an optimization problem minimizing a cost function with a nonlocal regularization term. The energy functional which is to be minimized decouples for each band, thus permitting the application to misregistered spectral components. This requirement is achieved by dropping the, commonly used, assumption that relates the spectral and panchromatic modalities by a linear transformation. Instead, a new constraint that preserves the radiometric ratio between the panchromatic and each spectral component is introduced. An exhaustive performance comparison of the proposed fusion method with several classical and state-of-the-art pansharpening techniques illustrates its superiority in preserving spatial details, reducing color distortions, and avoiding the creation of aliasing artifacts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge