Barbara Graziosi
Princeton University
An Annotated Dataset of Errors in Premodern Greek and Baselines for Detecting Them
Oct 14, 2024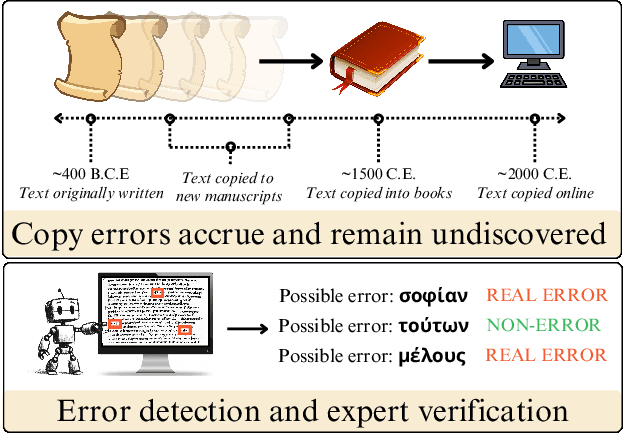
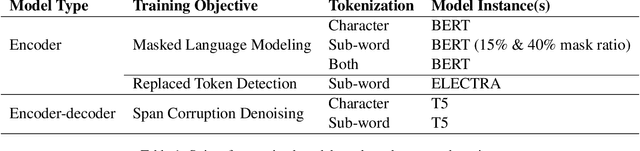
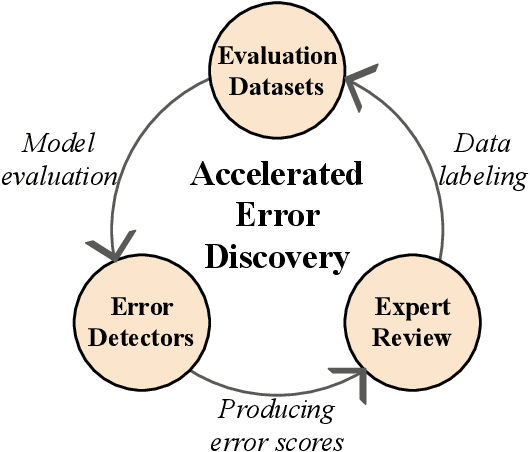
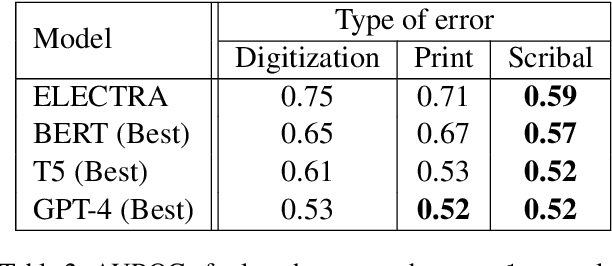
Abstract:As premodern texts are passed down over centuries, errors inevitably accrue. These errors can be challenging to identify, as some have survived undetected for so long precisely because they are so elusive. While prior work has evaluated error detection methods on artificially-generated errors, we introduce the first dataset of real errors in premodern Greek, enabling the evaluation of error detection methods on errors that genuinely accumulated at some stage in the centuries-long copying process. To create this dataset, we use metrics derived from BERT conditionals to sample 1,000 words more likely to contain errors, which are then annotated and labeled by a domain expert as errors or not. We then propose and evaluate new error detection methods and find that our discriminator-based detector outperforms all other methods, improving the true positive rate for classifying real errors by 5%. We additionally observe that scribal errors are more difficult to detect than print or digitization errors. Our dataset enables the evaluation of error detection methods on real errors in premodern texts for the first time, providing a benchmark for developing more effective error detection algorithms to assist scholars in restoring premodern works.
Logion: Machine Learning for Greek Philology
May 01, 2023Abstract:This paper presents machine-learning methods to address various problems in Greek philology. After training a BERT model on the largest premodern Greek dataset used for this purpose to date, we identify and correct previously undetected errors made by scribes in the process of textual transmission, in what is, to our knowledge, the first successful identification of such errors via machine learning. Additionally, we demonstrate the model's capacity to fill gaps caused by material deterioration of premodern manuscripts and compare the model's performance to that of a domain expert. We find that best performance is achieved when the domain expert is provided with model suggestions for inspiration. With such human-computer collaborations in mind, we explore the model's interpretability and find that certain attention heads appear to encode select grammatical features of premodern Greek.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge