Ayumu Sasagawa
A New Autoregressive Neural Network Model with Command Compensation for Imitation Learning Based on Bilateral Control
Mar 16, 2021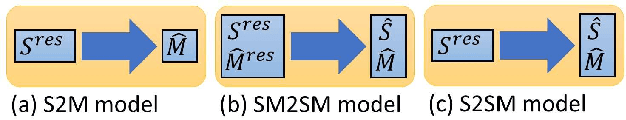
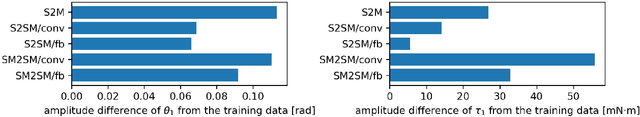
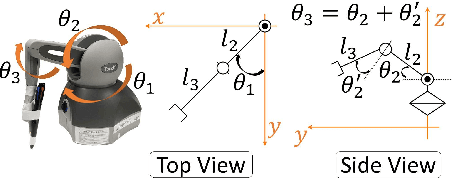
Abstract:In the near future, robots are expected to work with humans or operate alone and may replace human workers in various fields such as homes and factories. In a previous study, we proposed bilateral control-based imitation learning that enables robots to utilize force information and operate almost simultaneously with an expert's demonstration. In addition, we recently proposed an autoregressive neural network model (SM2SM) for bilateral control-based imitation learning to obtain long-term inferences. In the SM2SM model, both master and slave states must be input, but the master states are obtained from the previous outputs of the SM2SM model, resulting in destabilized estimation under large environmental variations. Hence, a new autoregressive neural network model (S2SM) is proposed in this study. This model requires only the slave state as input and its outputs are the next slave and master states, thereby improving the task success rates. In addition, a new feedback controller that utilizes the error between the responses and estimates of the slave is proposed, which shows better reproducibility.
Imitation learning for variable speed motion generation over multiple actions
Mar 11, 2021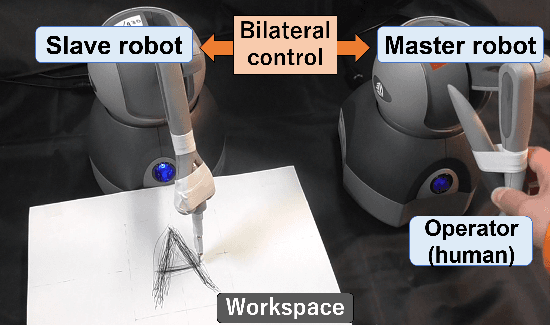
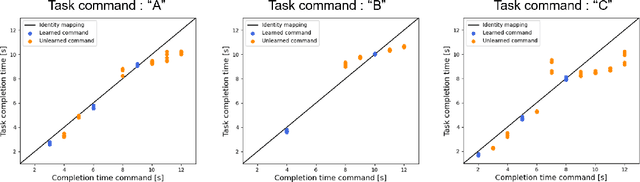
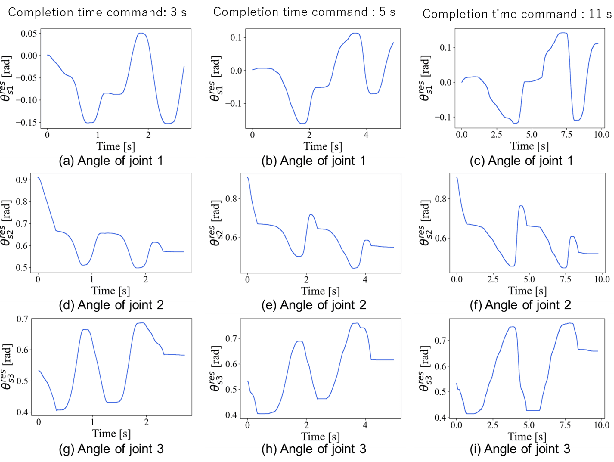
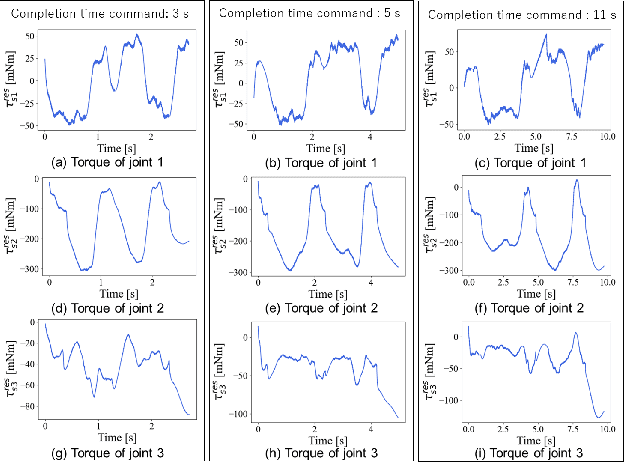
Abstract:Robot motion generation methods using machine learning have been studied in recent years. Bilateral controlbased imitation learning can imitate human motions using force information. By means of this method, variable speed motion generation that considers physical phenomena such as the inertial force and friction can be achieved. Previous research demonstrated that the complex relationship between the force and speed can be learned by using a neural network model. However, the previous study only focused on a simple reciprocating motion. To learn the complex relationship between the force and speed more accurately, it is necessary to learn multiple actions using many joints. In this paper, we propose a variable speed motion generation method for multiple motions. We considered four types of neural network models for the motion generation and determined the best model for multiple motions at variable speeds. Subsequently, we used the best model to evaluate the reproducibility of the task completion time for the input completion time command. The results revealed that the proposed method could change the task completion time according to the specified completion time command in multiple motions.
Motion Generation Using Bilateral Control-Based Imitation Learning with Autoregressive Learning
Nov 13, 2020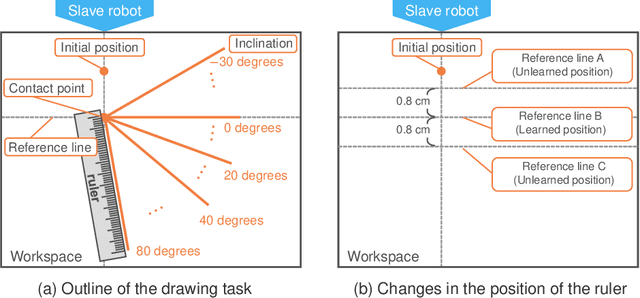
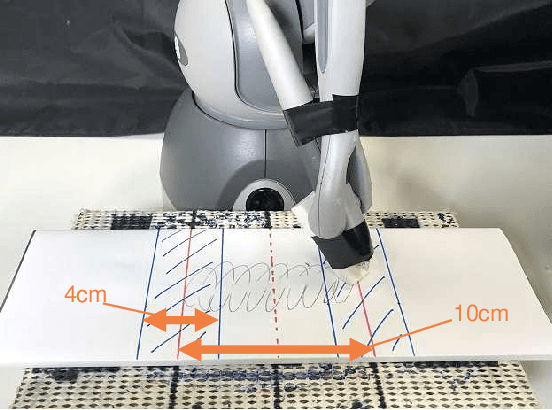
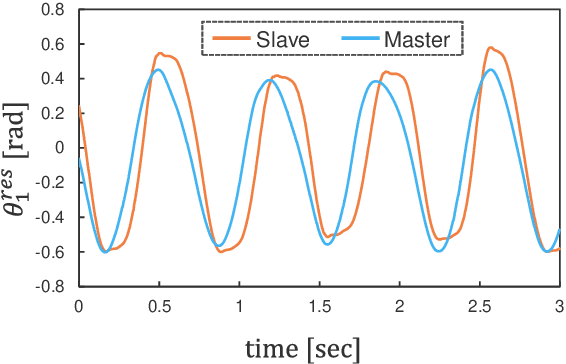
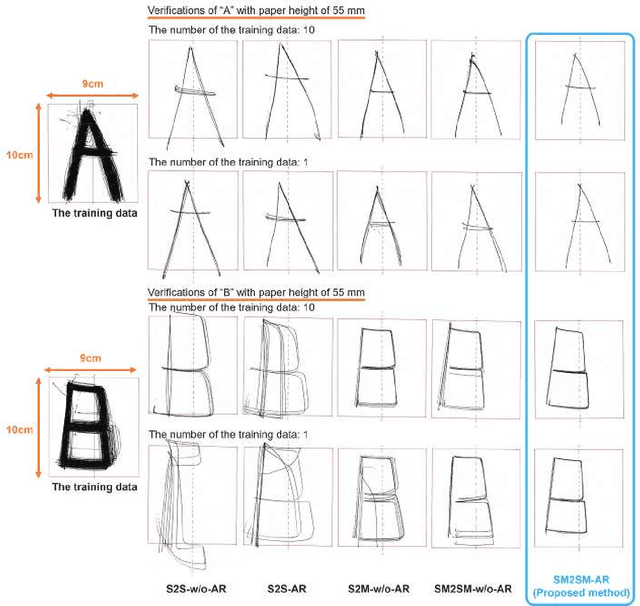
Abstract:Robots that can execute various tasks automatically on behalf of humans are becoming an increasingly important focus of research in the field of robotics. Imitation learning has been studied as an efficient and high-performance method, and imitation learning based on bilateral control has been proposed as a method that can realize fast motion. However, because this method cannot implement autoregressive learning, this method may not generate desirable long-term behavior. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a method of autoregressive learning for bilateral control-based imitation learning. A new neural network model for implementing autoregressive learning is proposed. In this study, three types of experiments are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. The performance is improved compared to conventional approaches; the proposed method has the highest rate of success. Owing to the structure and autoregressive learning of the proposed model, the proposed method can generate the desirable motion for successful tasks and have a high generalization ability for environmental changes.
Imitation Learning for Human-robot Cooperation Using Bilateral Control
Sep 28, 2019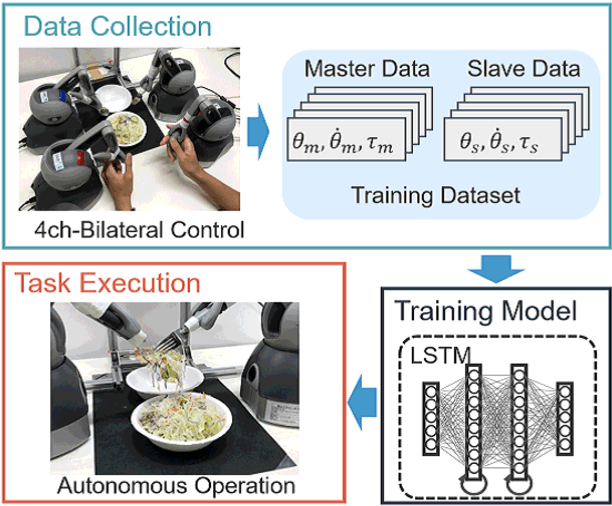
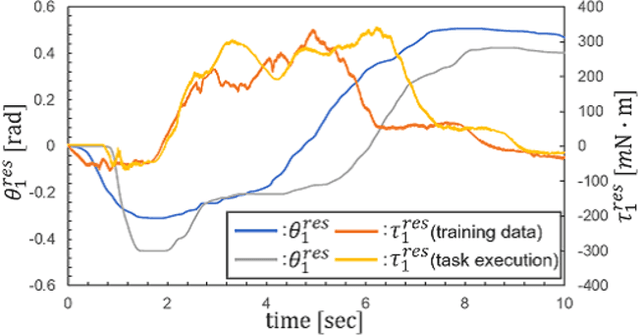
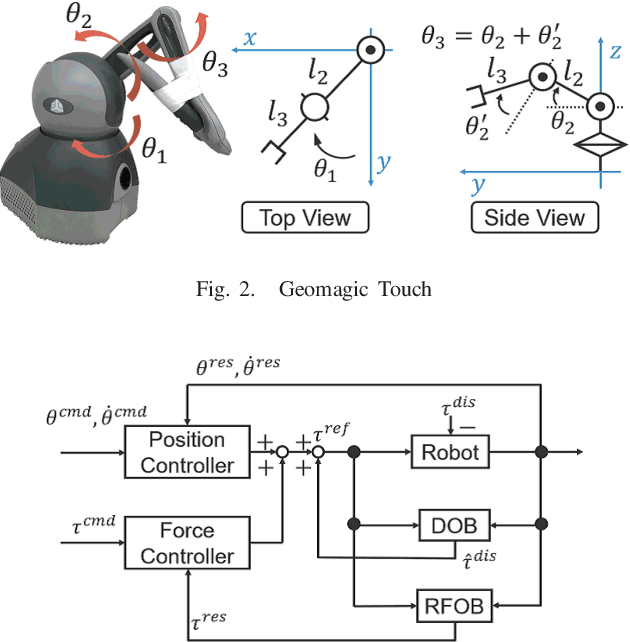
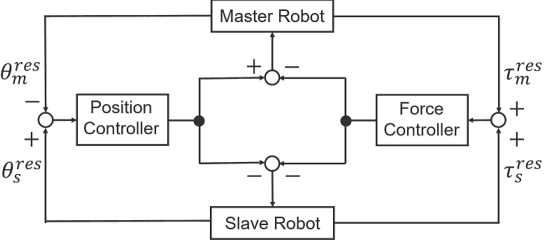
Abstract:Robots are required to operate autonomously in response to changing situations. Previously, imitation learning using 4ch-bilateral control was demonstrated to be suitable for imitation of object manipulation. However, cooperative work between humans and robots has not yet been verified in these studies. In this study, the task was expanded by cooperative work between a human and a robot. 4ch-bilateral control was used to collect training data for training robot motion. We focused on serving salad as a task in the home. The task was executed with a spoon and a fork fixed to robots. Adjustment of force was indispensable in manipulating indefinitely shaped objects such as salad. Results confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed method as demonstrated by the success of the task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge