Ayesha Tasnim
Authorship Attribution in Bangla Literature (AABL) via Transfer Learning using ULMFiT
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:Authorship Attribution is the task of creating an appropriate characterization of text that captures the authors' writing style to identify the original author of a given piece of text. With increased anonymity on the internet, this task has become increasingly crucial in various security and plagiarism detection fields. Despite significant advancements in other languages such as English, Spanish, and Chinese, Bangla lacks comprehensive research in this field due to its complex linguistic feature and sentence structure. Moreover, existing systems are not scalable when the number of author increases, and the performance drops for small number of samples per author. In this paper, we propose the use of Average-Stochastic Gradient Descent Weight-Dropped Long Short-Term Memory (AWD-LSTM) architecture and an effective transfer learning approach that addresses the problem of complex linguistic features extraction and scalability for authorship attribution in Bangla Literature (AABL). We analyze the effect of different tokenization, such as word, sub-word, and character level tokenization, and demonstrate the effectiveness of these tokenizations in the proposed model. Moreover, we introduce the publicly available Bangla Authorship Attribution Dataset of 16 authors (BAAD16) containing 17,966 sample texts and 13.4+ million words to solve the standard dataset scarcity problem and release six variations of pre-trained language models for use in any Bangla NLP downstream task. For evaluation, we used our developed BAAD16 dataset as well as other publicly available datasets. Empirically, our proposed model outperformed state-of-the-art models and achieved 99.8% accuracy in the BAAD16 dataset. Furthermore, we showed that the proposed system scales much better even with an increasing number of authors, and performance remains steady despite few training samples.
BAN-ABSA: An Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis dataset for Bengali and it's baseline evaluation
Dec 01, 2020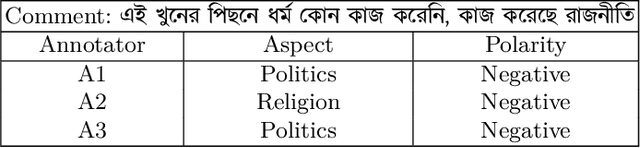
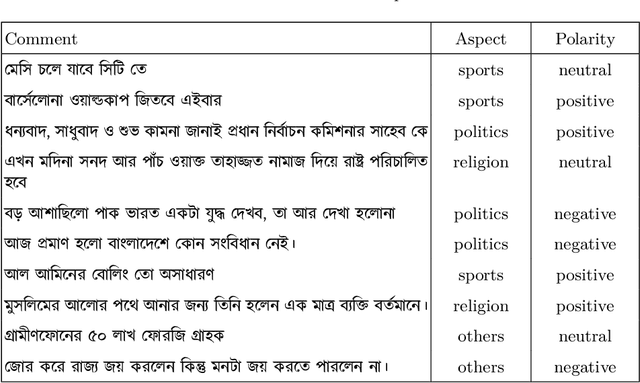
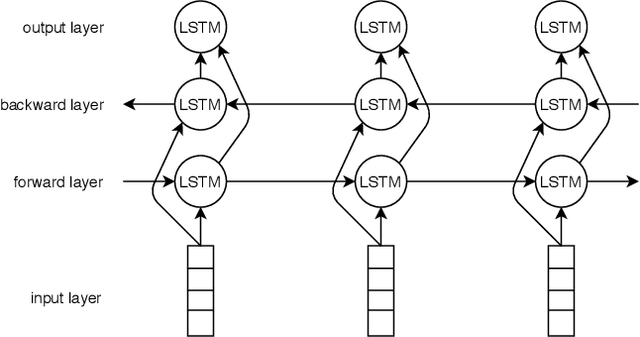
Abstract:Due to the breathtaking growth of social media or newspaper user comments, online product reviews comments, sentiment analysis (SA) has captured substantial interest from the researchers. With the fast increase of domain, SA work aims not only to predict the sentiment of a sentence or document but also to give the necessary detail on different aspects of the sentence or document (i.e. aspect-based sentiment analysis). A considerable number of datasets for SA and aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) have been made available for English and other well-known European languages. In this paper, we present a manually annotated Bengali dataset of high quality, BAN-ABSA, which is annotated with aspect and its associated sentiment by 3 native Bengali speakers. The dataset consists of 2,619 positive, 4,721 negative and 1,669 neutral data samples from 9,009 unique comments gathered from some famous Bengali news portals. In addition, we conducted a baseline evaluation with a focus on deep learning model, achieved an accuracy of 78.75% for aspect term extraction and accuracy of 71.08% for sentiment classification. Experiments on the BAN-ABSA dataset show that the CNN model is better in terms of accuracy though Bi-LSTM significantly outperforms CNN model in terms of average F1-score.
A Subword Level Language Model for Bangla Language
Nov 15, 2019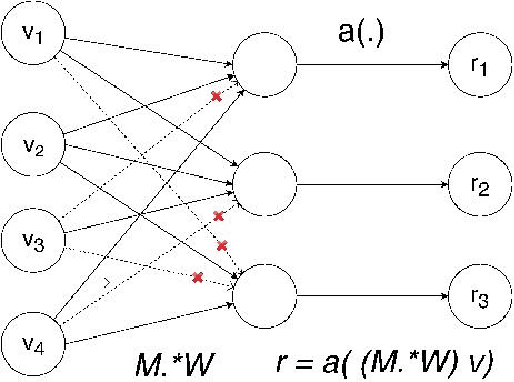
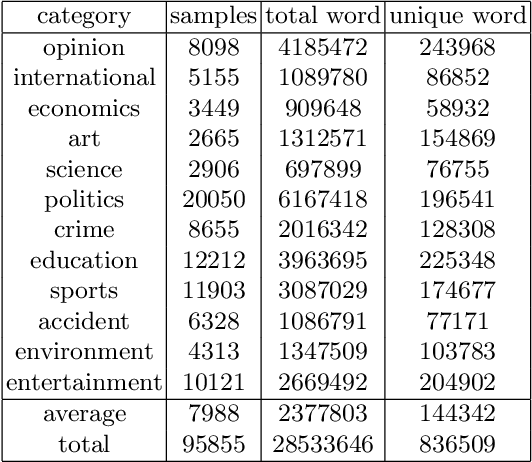
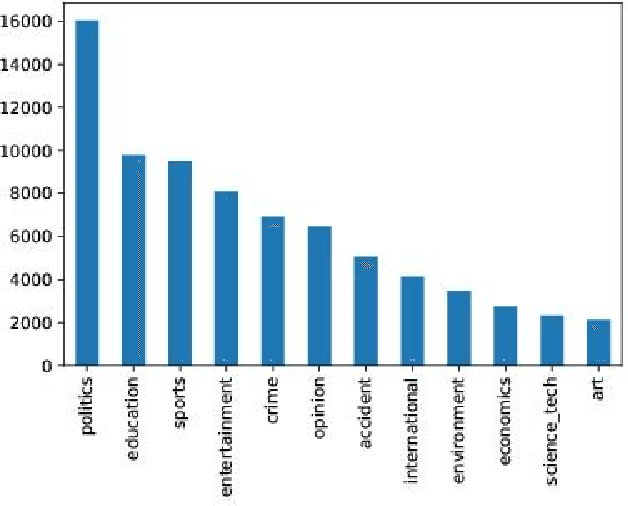
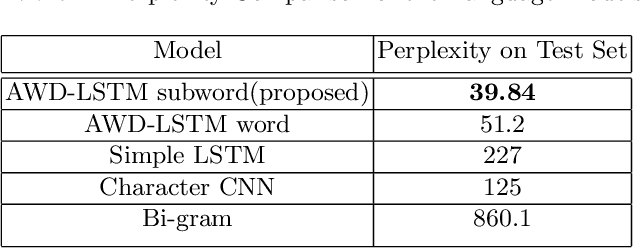
Abstract:Language models are at the core of natural language processing. The ability to represent natural language gives rise to its applications in numerous NLP tasks including text classification, summarization, and translation. Research in this area is very limited in Bangla due to the scarcity of resources, except for some count-based models and very recent neural language models being proposed, which are all based on words and limited in practical tasks due to their high perplexity. This paper attempts to approach this issue of perplexity and proposes a subword level neural language model with the AWD-LSTM architecture and various other techniques suitable for training in Bangla language. The model is trained on a corpus of Bangla newspaper articles of an appreciable size consisting of more than 28.5 million word tokens. The performance comparison with various other models depicts the significant reduction in perplexity the proposed model provides, reaching as low as 39.84, in just 20 epochs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge