Aya Watanabe
Who Finds This Voice Attractive? A Large-Scale Experiment Using In-the-Wild Data
Jul 05, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces CocoNut-Humoresque, an open-source large-scale speech likability corpus that includes speech segments and their per-listener likability scores. Evaluating voice likability is essential to designing preferable voices for speech systems, such as dialogue or announcement systems. In this study, we let 885 listeners rate 1800 speech segments of a wide range of speakers regarding their likability. When constructing the corpus, we also collected the multiple speaker attributes: genders, ages, and favorite YouTube videos. Therefore, the corpus enables the large-scale statistical analysis of voice likability regarding both speaker and listener factors. This paper describes the construction methodology and preliminary data analysis to reveal the gender and age biases in voice likability. In addition, the relationship between the likability and two acoustic features, the fundamental frequencies and the x-vectors of given utterances, is also investigated.
Building speech corpus with diverse voice characteristics for its prompt-based representation
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:In text-to-speech synthesis, the ability to control voice characteristics is vital for various applications. By leveraging thriving text prompt-based generation techniques, it should be possible to enhance the nuanced control of voice characteristics. While previous research has explored the prompt-based manipulation of voice characteristics, most studies have used pre-recorded speech, which limits the diversity of voice characteristics available. Thus, we aim to address this gap by creating a novel corpus and developing a model for prompt-based manipulation of voice characteristics in text-to-speech synthesis, facilitating a broader range of voice characteristics. Specifically, we propose a method to build a sizable corpus pairing voice characteristics descriptions with corresponding speech samples. This involves automatically gathering voice-related speech data from the Internet, ensuring its quality, and manually annotating it using crowdsourcing. We implement this method with Japanese language data and analyze the results to validate its effectiveness. Subsequently, we propose a construction method of the model to retrieve speech from voice characteristics descriptions based on a contrastive learning method. We train the model using not only conservative contrastive learning but also feature prediction learning to predict quantitative speech features corresponding to voice characteristics. We evaluate the model performance via experiments with the corpus we constructed above.
Coco-Nut: Corpus of Japanese Utterance and Voice Characteristics Description for Prompt-based Control
Sep 24, 2023



Abstract:In text-to-speech, controlling voice characteristics is important in achieving various-purpose speech synthesis. Considering the success of text-conditioned generation, such as text-to-image, free-form text instruction should be useful for intuitive and complicated control of voice characteristics. A sufficiently large corpus of high-quality and diverse voice samples with corresponding free-form descriptions can advance such control research. However, neither an open corpus nor a scalable method is currently available. To this end, we develop Coco-Nut, a new corpus including diverse Japanese utterances, along with text transcriptions and free-form voice characteristics descriptions. Our methodology to construct this corpus consists of 1) automatic collection of voice-related audio data from the Internet, 2) quality assurance, and 3) manual annotation using crowdsourcing. Additionally, we benchmark our corpus on the prompt embedding model trained by contrastive speech-text learning.
Mid-attribute speaker generation using optimal-transport-based interpolation of Gaussian mixture models
Oct 18, 2022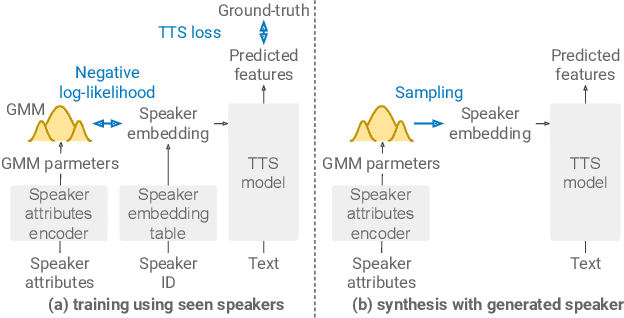
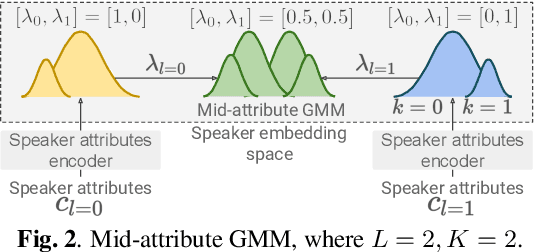
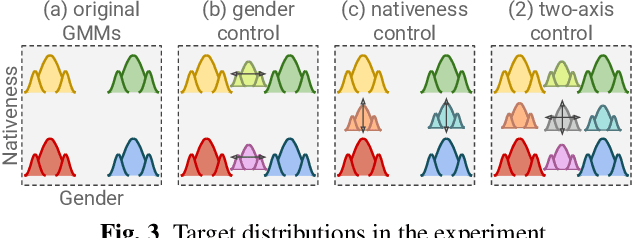
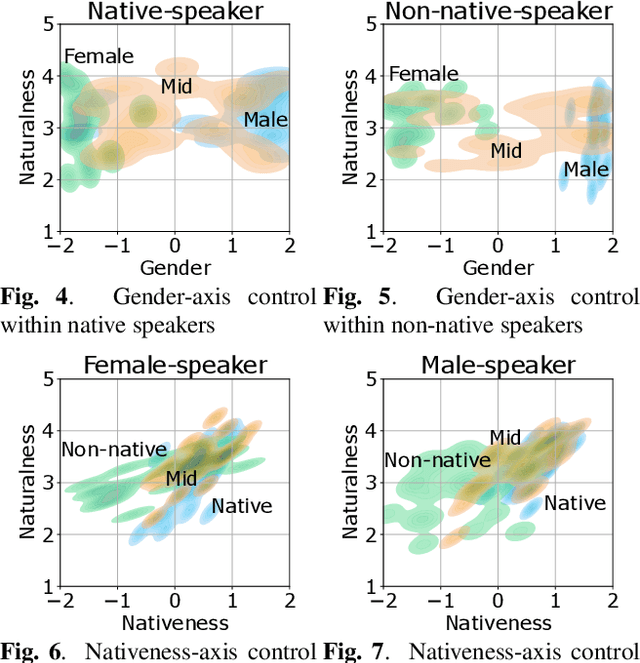
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a method for intermediating multiple speakers' attributes and diversifying their voice characteristics in ``speaker generation,'' an emerging task that aims to synthesize a nonexistent speaker's naturally sounding voice. The conventional TacoSpawn-based speaker generation method represents the distributions of speaker embeddings by Gaussian mixture models (GMMs) conditioned with speaker attributes. Although this method enables the sampling of various speakers from the speaker-attribute-aware GMMs, it is not yet clear whether the learned distributions can represent speakers with an intermediate attribute (i.e., mid-attribute). To this end, we propose an optimal-transport-based method that interpolates the learned GMMs to generate nonexistent speakers with mid-attribute (e.g., gender-neutral) voices. We empirically validate our method and evaluate the naturalness of synthetic speech and the controllability of two speaker attributes: gender and language fluency. The evaluation results show that our method can control the generated speakers' attributes by a continuous scalar value without statistically significant degradation of speech naturalness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge