Austin Lee
The Design of an LLM-powered Unstructured Analytics System
Sep 04, 2024
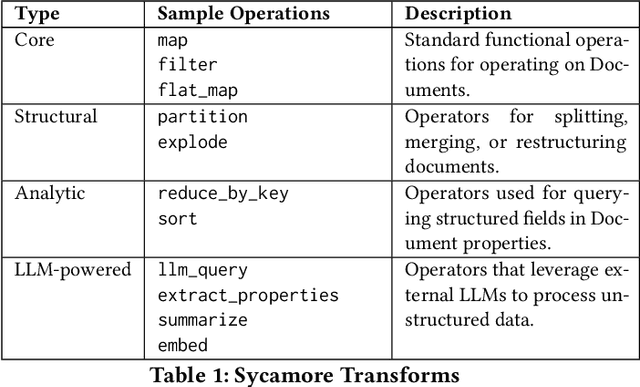


Abstract:LLMs demonstrate an uncanny ability to process unstructured data, and as such, have the potential to go beyond search and run complex, semantic analyses at scale. We describe the design of an unstructured analytics system, Aryn, and the tenets and use cases that motivate its design. With Aryn, users can specify queries in natural language and the system automatically determines a semantic plan and executes it to compute an answer from a large collection of unstructured documents using LLMs. At the core of Aryn is Sycamore, a declarative document processing engine, built using Ray, that provides a reliable distributed abstraction called DocSets. Sycamore allows users to analyze, enrich, and transform complex documents at scale. Aryn also comprises Luna, a query planner that translates natural language queries to Sycamore scripts, and the Aryn Partitioner, which takes raw PDFs and document images, and converts them to DocSets for downstream processing. Using Aryn, we demonstrate a real world use case for analyzing accident reports from the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), and discuss some of the major challenges we encountered in deploying Aryn in the wild.
Leveraging Subjective Human Annotation for Clustering Historic Newspaper Articles
Aug 17, 2012
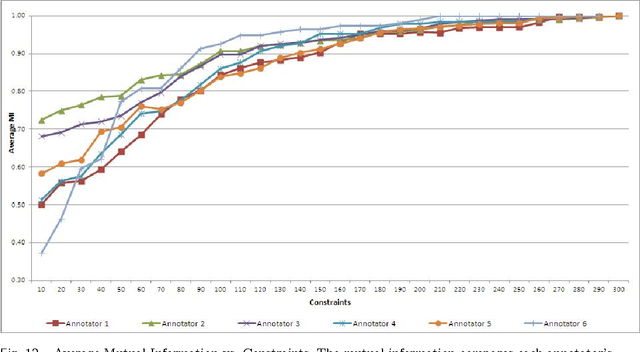
Abstract:The New York Public Library is participating in the Chronicling America initiative to develop an online searchable database of historically significant newspaper articles. Microfilm copies of the newspapers are scanned and high resolution Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software is run on them. The text from the OCR provides a wealth of data and opinion for researchers and historians. However, categorization of articles provided by the OCR engine is rudimentary and a large number of the articles are labeled editorial without further grouping. Manually sorting articles into fine-grained categories is time consuming if not impossible given the size of the corpus. This paper studies techniques for automatic categorization of newspaper articles so as to enhance search and retrieval on the archive. We explore unsupervised (e.g. KMeans) and semi-supervised (e.g. constrained clustering) learning algorithms to develop article categorization schemes geared towards the needs of end-users. A pilot study was designed to understand whether there was unanimous agreement amongst patrons regarding how articles can be categorized. It was found that the task was very subjective and consequently automated algorithms that could deal with subjective labels were used. While the small scale pilot study was extremely helpful in designing machine learning algorithms, a much larger system needs to be developed to collect annotations from users of the archive. The "BODHI" system currently being developed is a step in that direction, allowing users to correct wrongly scanned OCR and providing keywords and tags for newspaper articles used frequently. On successful implementation of the beta version of this system, we hope that it can be integrated with existing software being developed for the Chronicling America project.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge