Ashirbad Mishra
Batch Speculative Decoding Done Right
Oct 26, 2025



Abstract:Speculative decoding speeds up LLM inference by using a small draft model to propose multiple tokens that a target model verifies in parallel. Extending this idea to batches is essential for production serving, but it introduces the ragged tensor problem: sequences in the same batch accept different numbers of draft tokens, breaking right-alignment and corrupting position IDs, attention masks, and KV-cache state. We show that several existing batch implementations violate output equivalence-the fundamental requirement that speculative decoding must produce identical token sequences to standard autoregressive generation. These violations occur precisely due to improper handling of the ragged tensor problem. In response, we (1) characterize the synchronization requirements that guarantee correctness, (2) present a correctness-first batch speculative decoding EQSPEC that exposes realignment as consuming 40% of overhead, and (3) introduce EXSPEC, which maintains a sliding pool of sequences and dynamically forms same-length groups, to reduce the realignment overhead while preserving per-sequence speculative speedups. On the SpecBench dataset, across Vicuna-7B/68M, Qwen3-8B/0.6B, and GLM-4-9B/0.6B target/draft pairs, our approach achieves up to 3$\times$ throughput improvement at batch size 8 compared to batch size 1, with efficient scaling through batch size 8, while maintaining 95% output equivalence. Our method requires no custom kernels and integrates cleanly with existing inference stacks. Our code is available at https://github.com/eBay/spec_dec.
BroadGen: A Framework for Generating Effective and Efficient Advertiser Broad Match Keyphrase Recommendations
May 25, 2025Abstract:In the domain of sponsored search advertising, the focus of Keyphrase recommendation has largely been on exact match types, which pose issues such as high management expenses, limited targeting scope, and evolving search query patterns. Alternatives like Broad match types can alleviate certain drawbacks of exact matches but present challenges like poor targeting accuracy and minimal supervisory signals owing to limited advertiser usage. This research defines the criteria for an ideal broad match, emphasizing on both efficiency and effectiveness, ensuring that a significant portion of matched queries are relevant. We propose BroadGen, an innovative framework that recommends efficient and effective broad match keyphrases by utilizing historical search query data. Additionally, we demonstrate that BroadGen, through token correspondence modeling, maintains better query stability over time. BroadGen's capabilities allow it to serve daily, millions of sellers at eBay with over 2.3 billion items.
GraphEx: A Graph-based Extraction Method for Advertiser Keyphrase Recommendation
Sep 05, 2024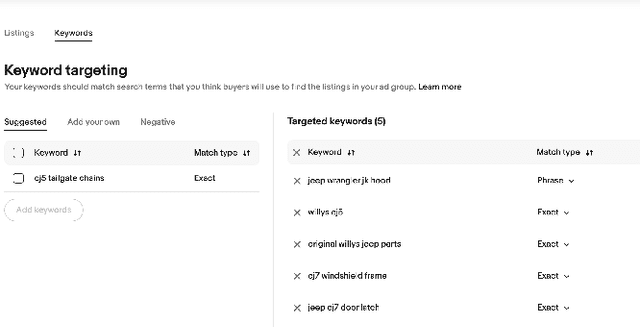
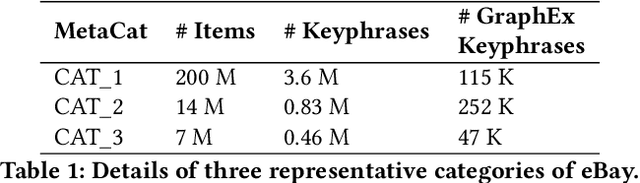
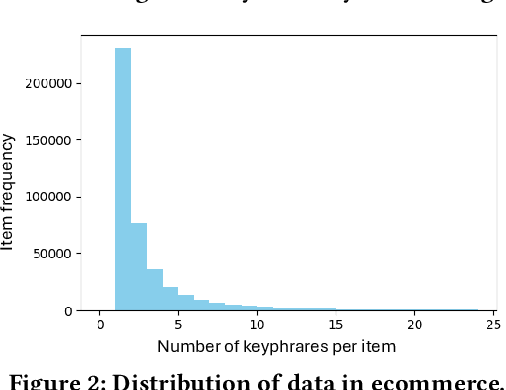
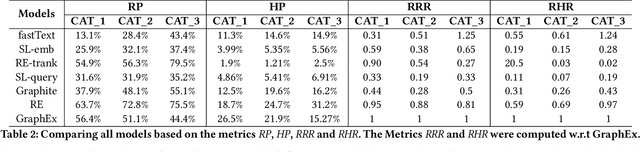
Abstract:Online sellers and advertisers are recommended keyphrases for their listed products, which they bid on to enhance their sales. One popular paradigm that generates such recommendations is Extreme Multi-Label Classification (XMC), which involves tagging/mapping keyphrases to items. We outline the limitations of using traditional item-query based tagging or mapping techniques for keyphrase recommendations on E-Commerce platforms. We introduce GraphEx, an innovative graph-based approach that recommends keyphrases to sellers using extraction of token permutations from item titles. Additionally, we demonstrate that relying on traditional metrics such as precision/recall can be misleading in practical applications, thereby necessitating a combination of metrics to evaluate performance in real-world scenarios. These metrics are designed to assess the relevance of keyphrases to items and the potential for buyer outreach. GraphEx outperforms production models at eBay, achieving the objectives mentioned above. It supports near real-time inferencing in resource-constrained production environments and scales effectively for billions of items.
Graphite: A Graph-based Extreme Multi-Label Short Text Classifier for Keyphrase Recommendation
Jul 29, 2024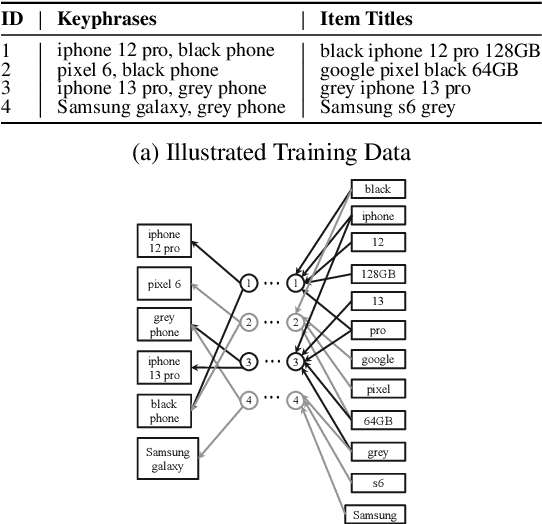
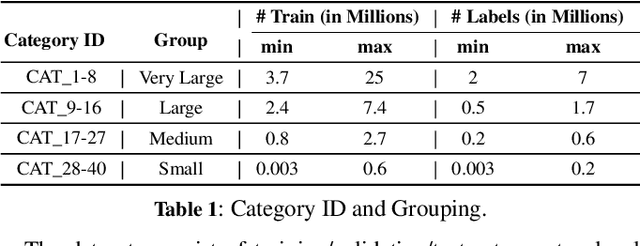
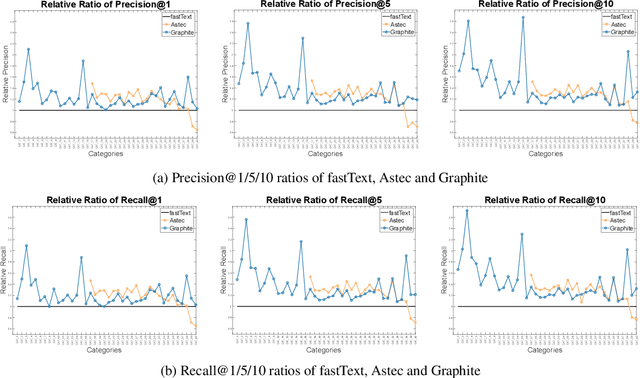
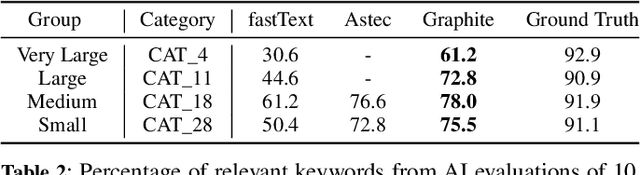
Abstract:Keyphrase Recommendation has been a pivotal problem in advertising and e-commerce where advertisers/sellers are recommended keyphrases (search queries) to bid on to increase their sales. It is a challenging task due to the plethora of items shown on online platforms and various possible queries that users search while showing varying interest in the displayed items. Moreover, query/keyphrase recommendations need to be made in real-time and in a resource-constrained environment. This problem can be framed as an Extreme Multi-label (XML) Short text classification by tagging the input text with keywords as labels. Traditional neural network models are either infeasible or have slower inference latency due to large label spaces. We present Graphite, a graph-based classifier model that provides real-time keyphrase recommendations that are on par with standard text classification models. Furthermore, it doesn't utilize GPU resources, which can be limited in production environments. Due to its lightweight nature and smaller footprint, it can train on very large datasets, where state-of-the-art XML models fail due to extreme resource requirements. Graphite is deterministic, transparent, and intrinsically more interpretable than neural network-based models. We present a comprehensive analysis of our model's performance across forty categories spanning eBay's English-speaking sites.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge