Arnaud A. A. Setio
Robust Classification from Noisy Labels: Integrating Additional Knowledge for Chest Radiography Abnormality Assessment
Apr 21, 2021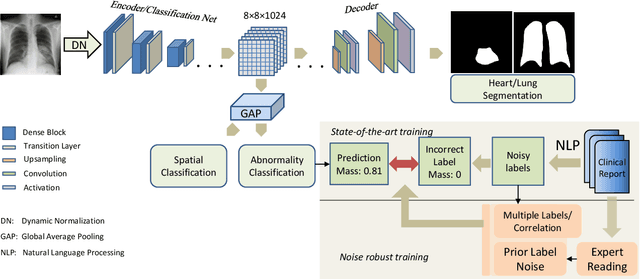
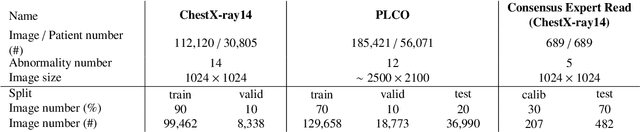
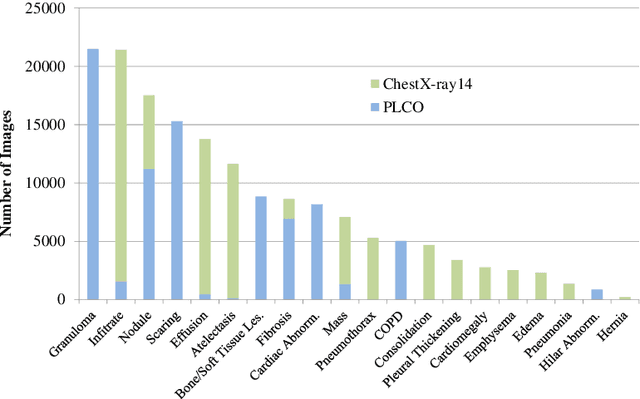
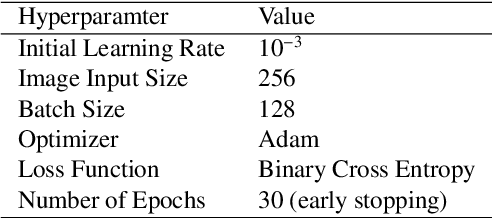
Abstract:Chest radiography is the most common radiographic examination performed in daily clinical practice for the detection of various heart and lung abnormalities. The large amount of data to be read and reported, with more than 100 studies per day for a single radiologist, poses a challenge in consistently maintaining high interpretation accuracy. The introduction of large-scale public datasets has led to a series of novel systems for automated abnormality classification. However, the labels of these datasets were obtained using natural language processed medical reports, yielding a large degree of label noise that can impact the performance. In this study, we propose novel training strategies that handle label noise from such suboptimal data. Prior label probabilities were measured on a subset of training data re-read by 4 board-certified radiologists and were used during training to increase the robustness of the training model to the label noise. Furthermore, we exploit the high comorbidity of abnormalities observed in chest radiography and incorporate this information to further reduce the impact of label noise. Additionally, anatomical knowledge is incorporated by training the system to predict lung and heart segmentation, as well as spatial knowledge labels. To deal with multiple datasets and images derived from various scanners that apply different post-processing techniques, we introduce a novel image normalization strategy. Experiments were performed on an extensive collection of 297,541 chest radiographs from 86,876 patients, leading to a state-of-the-art performance level for 17 abnormalities from 2 datasets. With an average AUC score of 0.880 across all abnormalities, our proposed training strategies can be used to significantly improve performance scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge