Aritra Kundu
Intramuscular High-Density Micro-Electrode Arrays Enable High-Precision Decoding and Mapping of Spinal Motor Neurons to Reveal Hand Control
Oct 14, 2024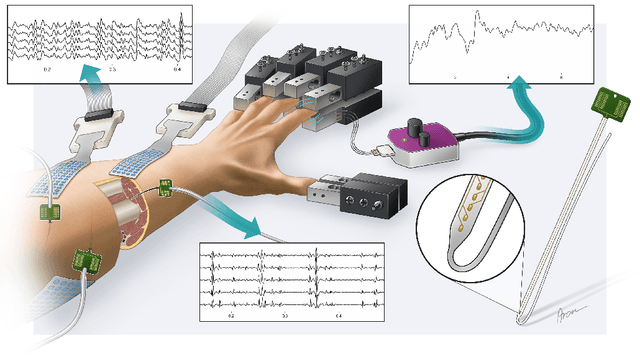
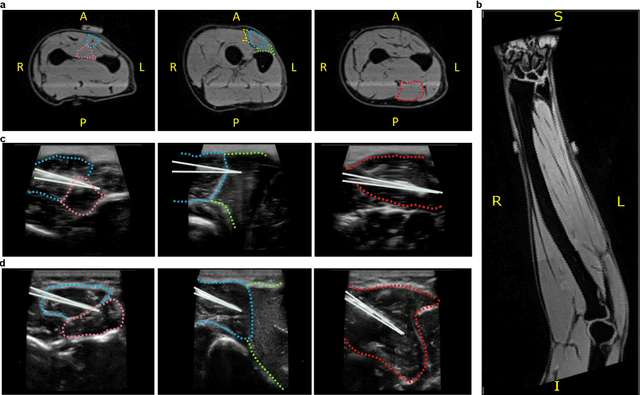
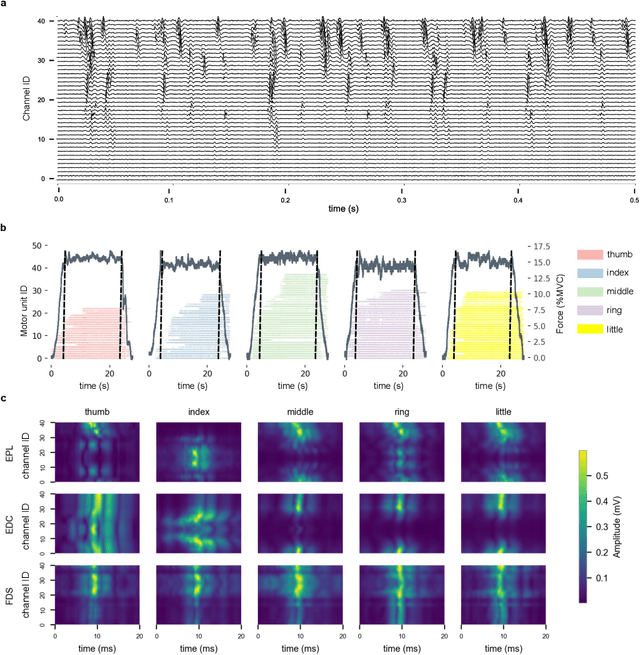
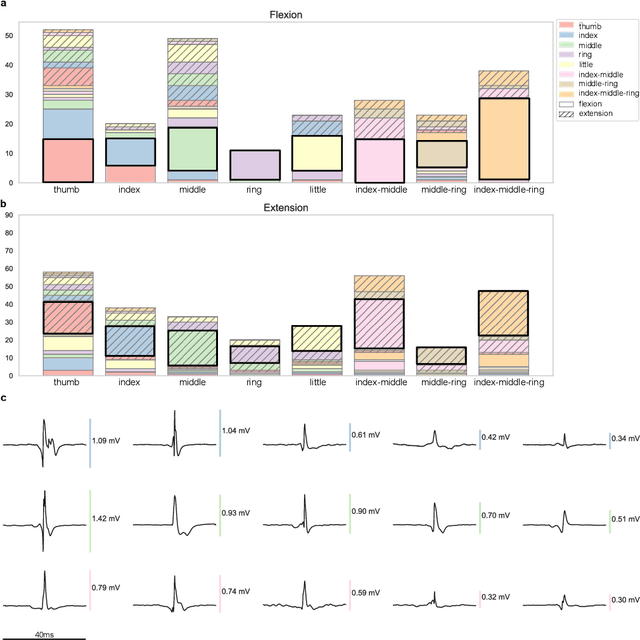
Abstract:Decoding nervous system activity is a key challenge in neuroscience and neural interfacing. In this study, we propose a novel neural decoding system that enables unprecedented large-scale sampling of muscle activity. Using micro-electrode arrays with more than 100 channels embedded within the forearm muscles, we recorded high-density signals that captured multi-unit motor neuron activity. This extensive sampling was complemented by advanced methods for neural decomposition, analysis, and classification, allowing us to accurately detect and interpret the spiking activity of spinal motor neurons that innervate hand muscles. We evaluated this system in two healthy participants, each implanted with three electromyogram (EMG) micro-electrode arrays (comprising 40 electrodes each) in the forearm. These arrays recorded muscle activity during both single- and multi-digit isometric contractions. For the first time under controlled conditions, we demonstrate that multi-digit tasks elicit unique patterns of motor neuron recruitment specific to each task, rather than employing combinations of recruitment patterns from single-digit tasks. This observation led us to hypothesize that hand tasks could be classified with high precision based on the decoded neural activity. We achieved perfect classification accuracy (100%) across 12 distinct single- and multi-digit tasks, and consistently high accuracy (>96\%) across all conditions and subjects, for up to 16 task classes. These results significantly outperformed conventional EMG classification methods. The exceptional performance of this system paves the way for developing advanced neural interfaces based on invasive high-density EMG technology. This innovation could greatly enhance human-computer interaction and lead to substantial improvements in assistive technologies, offering new possibilities for restoring motor function in clinical applications.
Design, Fabrication and Evaluation of a Stretchable High-Density Electromyography Array
Mar 29, 2024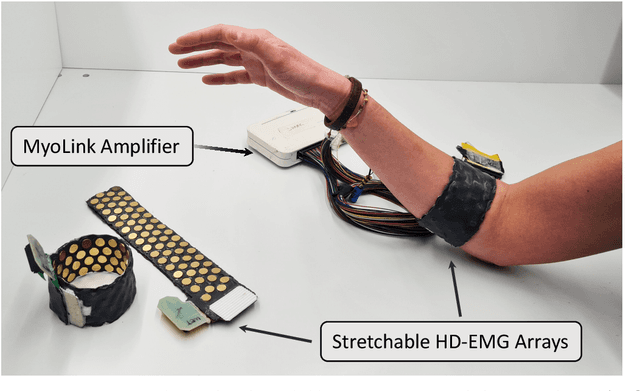
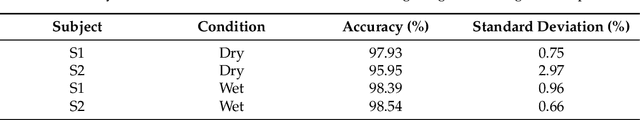
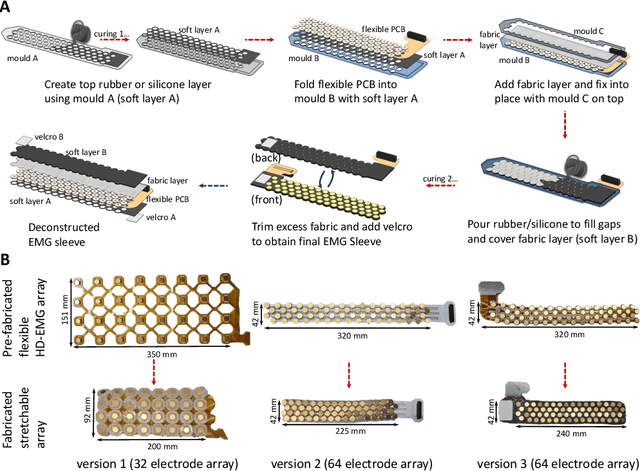
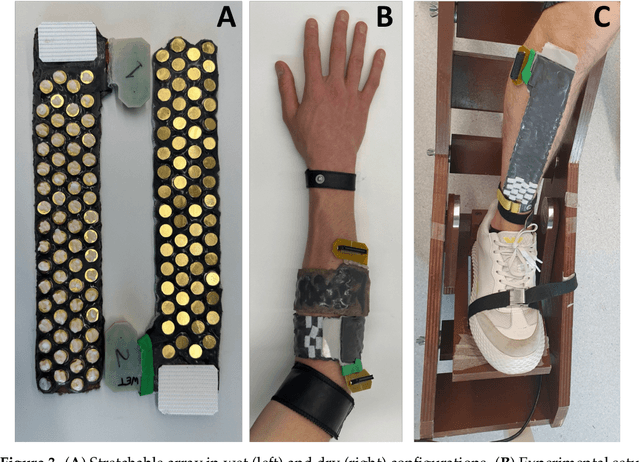
Abstract:The adoption of high-density electrode systems for human-machine interfaces in real-life applications has been impeded by practical and technical challenges, including noise interference, motion artifacts and the lack of compact electrode interfaces. To overcome some of these challenges, we introduce a wearable and stretchable electromyography (EMG) array, and present its design, fabrication methodology, characterisation, and comprehensive evaluation. Our proposed solution comprises dry-electrodes on flexible printed circuit board (PCB) substrates, eliminating the need for time-consuming skin preparation. The proposed fabrication method allows the manufacturing of stretchable sleeves, with consistent and standardised coverage across subjects. We thoroughly tested our developed prototype, evaluating its potential for application in both research and real-world environments. The results of our study showed that the developed stretchable array matches or outperforms traditional EMG grids and holds promise in furthering the real-world translation of high-density EMG for human-machine interfaces.
* This is the author's version of the manuscript published in MDPI Sensors journal - https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/24/6/1810 , This manuscript is in IEEE format - 8 pages, 5 figures, 1 table
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge