Aradhana M. Venkatesan
Two Stage Segmentation of Cervical Tumors using PocketNet
Sep 17, 2024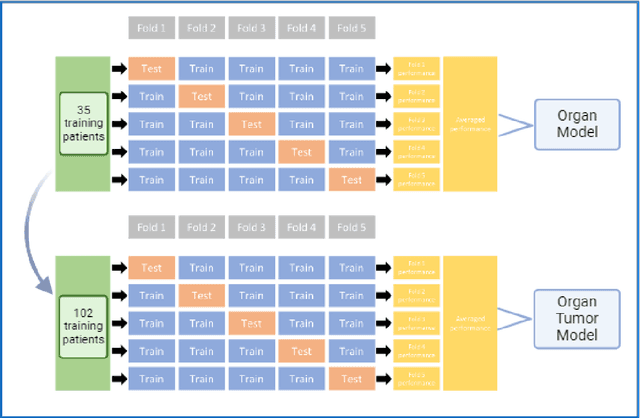

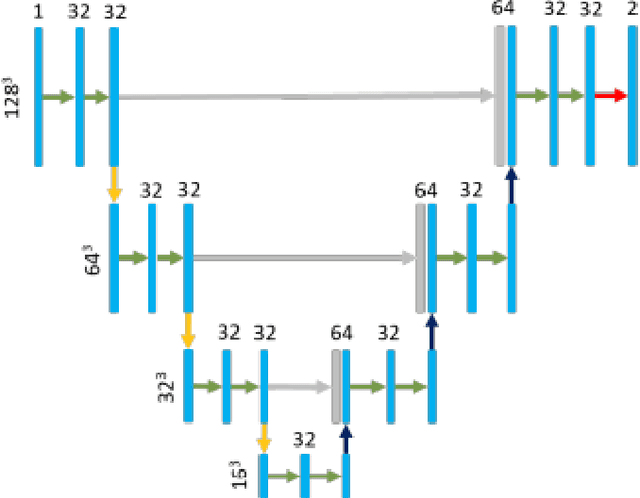
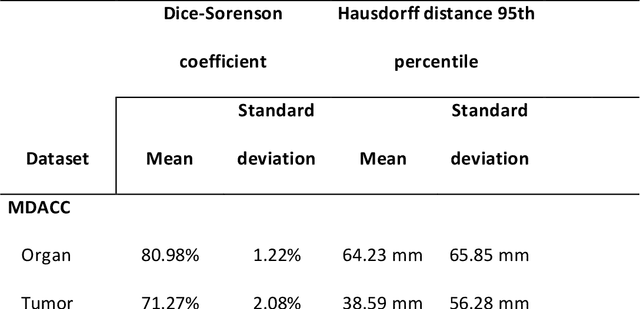
Abstract:Cervical cancer remains the fourth most common malignancy amongst women worldwide.1 Concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) serves as the mainstay definitive treatment regimen for locally advanced cervical cancers and includes external beam radiation followed by brachytherapy.2 Integral to radiotherapy treatment planning is the routine contouring of both the target tumor at the level of the cervix, associated gynecologic anatomy and the adjacent organs at risk (OARs). However, manual contouring of these structures is both time and labor intensive and associated with known interobserver variability that can impact treatment outcomes. While multiple tools have been developed to automatically segment OARs and the high-risk clinical tumor volume (HR-CTV) using computed tomography (CT) images,3,4,5,6 the development of deep learning-based tumor segmentation tools using routine T2-weighted (T2w) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) addresses an unmet clinical need to improve the routine contouring of both anatomical structures and cervical cancers, thereby increasing quality and consistency of radiotherapy planning. This work applied a novel deep-learning model (PocketNet) to segment the cervix, vagina, uterus, and tumor(s) on T2w MRI. The performance of the PocketNet architecture was evaluated, when trained on data via 5-fold cross validation. PocketNet achieved a mean Dice-Sorensen similarity coefficient (DSC) exceeding 70% for tumor segmentation and 80% for organ segmentation. These results suggest that PocketNet is robust to variations in contrast protocols, providing reliable segmentation of the ROIs.
Evaluating the Performance of StyleGAN2-ADA on Medical Images
Oct 07, 2022Abstract:Although generative adversarial networks (GANs) have shown promise in medical imaging, they have four main limitations that impeded their utility: computational cost, data requirements, reliable evaluation measures, and training complexity. Our work investigates each of these obstacles in a novel application of StyleGAN2-ADA to high-resolution medical imaging datasets. Our dataset is comprised of liver-containing axial slices from non-contrast and contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scans. Additionally, we utilized four public datasets composed of various imaging modalities. We trained a StyleGAN2 network with transfer learning (from the Flickr-Faces-HQ dataset) and data augmentation (horizontal flipping and adaptive discriminator augmentation). The network's generative quality was measured quantitatively with the Fr\'echet Inception Distance (FID) and qualitatively with a visual Turing test given to seven radiologists and radiation oncologists. The StyleGAN2-ADA network achieved a FID of 5.22 ($\pm$ 0.17) on our liver CT dataset. It also set new record FIDs of 10.78, 3.52, 21.17, and 5.39 on the publicly available SLIVER07, ChestX-ray14, ACDC, and Medical Segmentation Decathlon (brain tumors) datasets. In the visual Turing test, the clinicians rated generated images as real 42% of the time, approaching random guessing. Our computational ablation study revealed that transfer learning and data augmentation stabilize training and improve the perceptual quality of the generated images. We observed the FID to be consistent with human perceptual evaluation of medical images. Finally, our work found that StyleGAN2-ADA consistently produces high-quality results without hyperparameter searches or retraining.
* This preprint has not undergone post-submission improvements or corrections. The Version of Record of this contribution is published in LNCS, volume 13570, and is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16980-9_14
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge