Apratim Mishra
Revisiting gender bias research in bibliometrics: Standardizing methodological variability using Scholarly Data Analysis (SoDA) Cards
Jan 30, 2025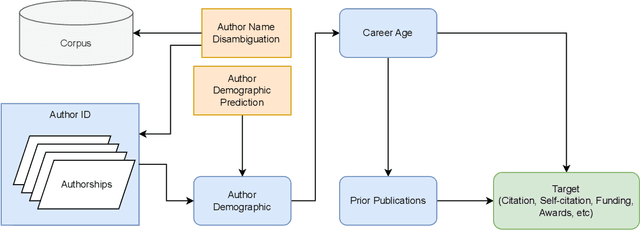

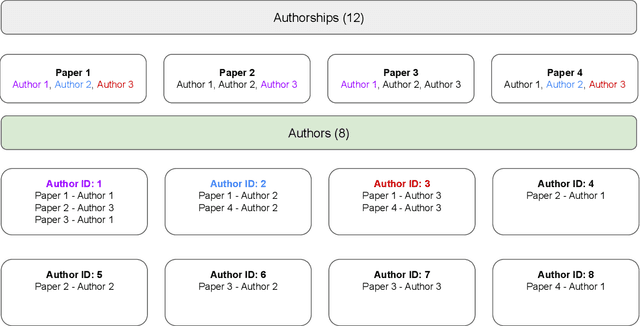

Abstract:Gender biases in scholarly metrics remain a persistent concern, despite numerous bibliometric studies exploring their presence and absence across productivity, impact, acknowledgment, and self-citations. However, methodological inconsistencies, particularly in author name disambiguation and gender identification, limit the reliability and comparability of these studies, potentially perpetuating misperceptions and hindering effective interventions. A review of 70 relevant publications over the past 12 years reveals a wide range of approaches, from name-based and manual searches to more algorithmic and gold-standard methods, with no clear consensus on best practices. This variability, compounded by challenges such as accurately disambiguating Asian names and managing unassigned gender labels, underscores the urgent need for standardized and robust methodologies. To address this critical gap, we propose the development and implementation of ``Scholarly Data Analysis (SoDA) Cards." These cards will provide a structured framework for documenting and reporting key methodological choices in scholarly data analysis, including author name disambiguation and gender identification procedures. By promoting transparency and reproducibility, SoDA Cards will facilitate more accurate comparisons and aggregations of research findings, ultimately supporting evidence-informed policymaking and enabling the longitudinal tracking of analytical approaches in the study of gender and other social biases in academia.
Beyond Binary Gender Labels: Revealing Gender Biases in LLMs through Gender-Neutral Name Predictions
Jul 07, 2024Abstract:Name-based gender prediction has traditionally categorized individuals as either female or male based on their names, using a binary classification system. That binary approach can be problematic in the cases of gender-neutral names that do not align with any one gender, among other reasons. Relying solely on binary gender categories without recognizing gender-neutral names can reduce the inclusiveness of gender prediction tasks. We introduce an additional gender category, i.e., "neutral", to study and address potential gender biases in Large Language Models (LLMs). We evaluate the performance of several foundational and large language models in predicting gender based on first names only. Additionally, we investigate the impact of adding birth years to enhance the accuracy of gender prediction, accounting for shifting associations between names and genders over time. Our findings indicate that most LLMs identify male and female names with high accuracy (over 80%) but struggle with gender-neutral names (under 40%), and the accuracy of gender prediction is higher for English-based first names than non-English names. The experimental results show that incorporating the birth year does not improve the overall accuracy of gender prediction, especially for names with evolving gender associations. We recommend using caution when applying LLMs for gender identification in downstream tasks, particularly when dealing with non-binary gender labels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge