Anupam Golder
Leveraging ASIC AI Chips for Homomorphic Encryption
Jan 13, 2025
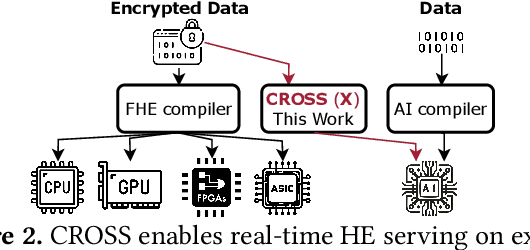
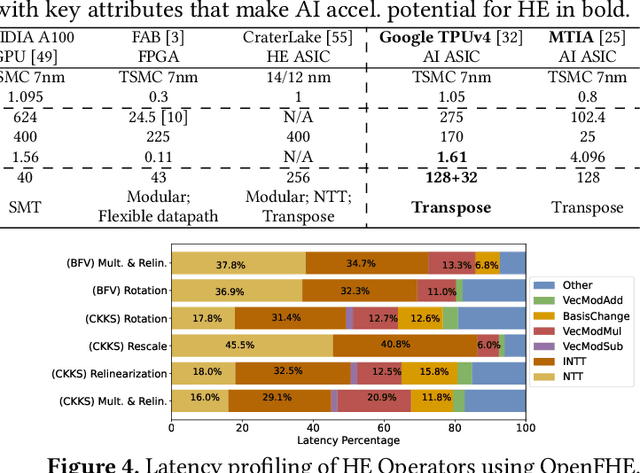
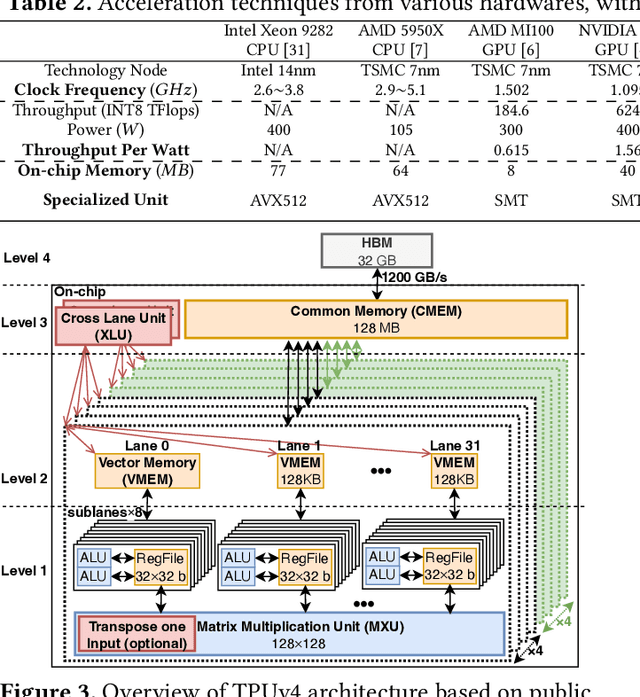
Abstract:Cloud-based services are making the outsourcing of sensitive client data increasingly common. Although homomorphic encryption (HE) offers strong privacy guarantee, it requires substantially more resources than computing on plaintext, often leading to unacceptably large latencies in getting the results. HE accelerators have emerged to mitigate this latency issue, but with the high cost of ASICs. In this paper we show that HE primitives can be converted to AI operators and accelerated on existing ASIC AI accelerators, like TPUs, which are already widely deployed in the cloud. Adapting such accelerators for HE requires (1) supporting modular multiplication, (2) high-precision arithmetic in software, and (3) efficient mapping on matrix engines. We introduce the CROSS compiler (1) to adopt Barrett reduction to provide modular reduction support using multiplier and adder, (2) Basis Aligned Transformation (BAT) to convert high-precision multiplication as low-precision matrix-vector multiplication, (3) Matrix Aligned Transformation (MAT) to covert vectorized modular operation with reduction into matrix multiplication that can be efficiently processed on 2D spatial matrix engine. Our evaluation of CROSS on a Google TPUv4 demonstrates significant performance improvements, with up to 161x and 5x speedup compared to the previous work on many-core CPUs and V100. The kernel-level codes are open-sourced at https://github.com/google/jaxite.git.
SNOW-SCA: ML-assisted Side-Channel Attack on SNOW-V
Mar 13, 2024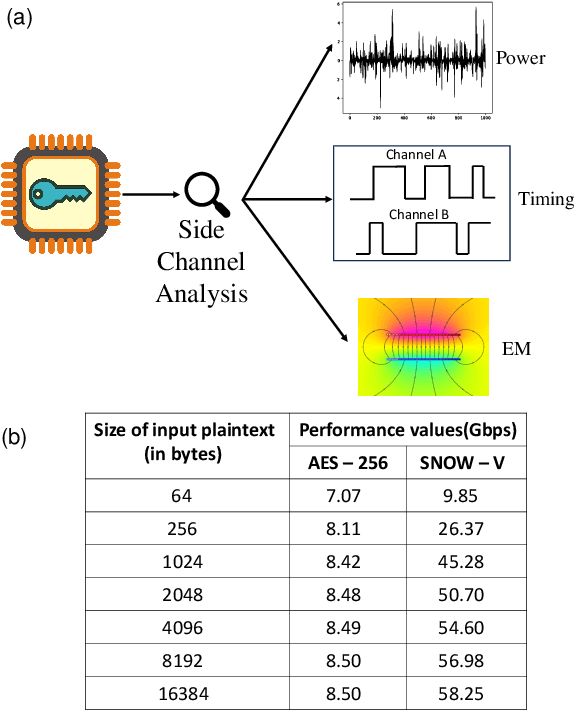
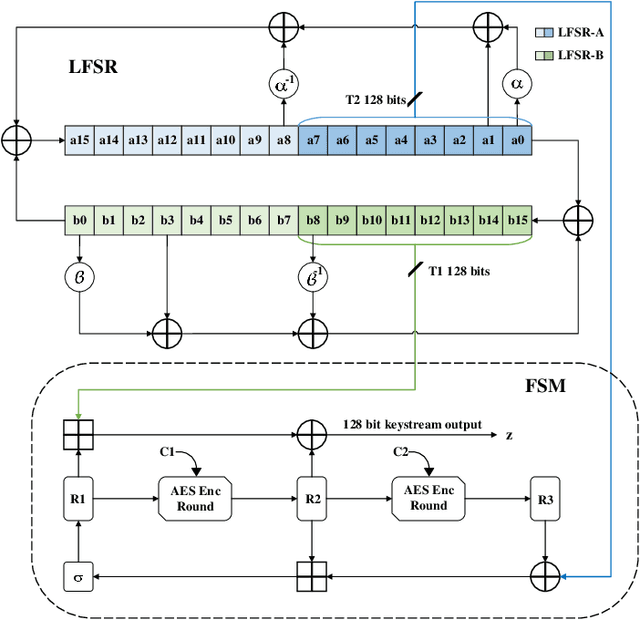
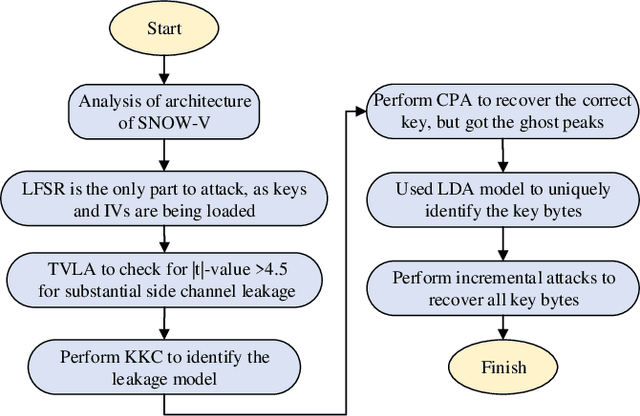
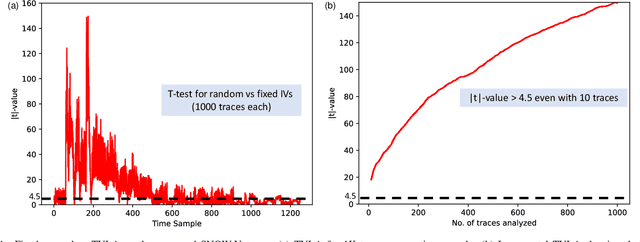
Abstract:This paper presents SNOW-SCA, the first power side-channel analysis (SCA) attack of a 5G mobile communication security standard candidate, SNOW-V, running on a 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4 microcontroller. First, we perform a generic known-key correlation (KKC) analysis to identify the leakage points. Next, a correlation power analysis (CPA) attack is performed, which reduces the attack complexity to two key guesses for each key byte. The correct secret key is then uniquely identified utilizing linear discriminant analysis (LDA). The profiled SCA attack with LDA achieves 100% accuracy after training with $<200$ traces, which means the attack succeeds with just a single trace. Overall, using the \textit{combined CPA and LDA attack} model, the correct secret key byte is recovered with <50 traces collected using the ChipWhisperer platform. The entire 256-bit secret key of SNOW-V can be recovered incrementally using the proposed SCA attack. Finally, we suggest low-overhead countermeasures that can be used to prevent these SCA attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge