Antoine Boniface
Physics-based neural network for non-invasive control of coherent light in scattering media
Jun 01, 2022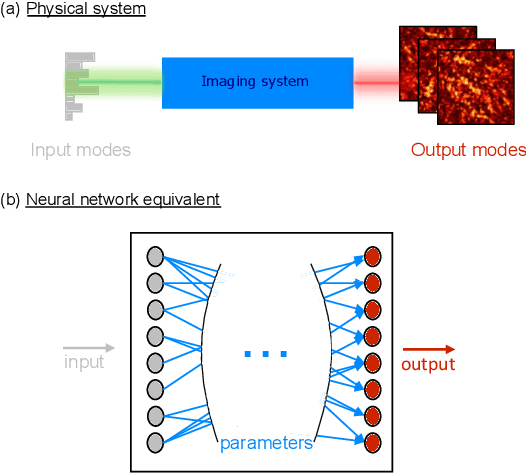
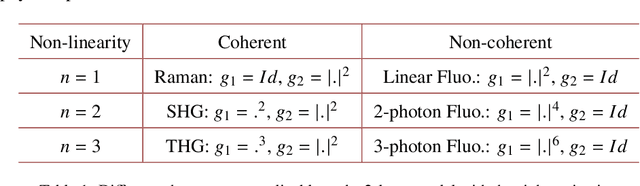
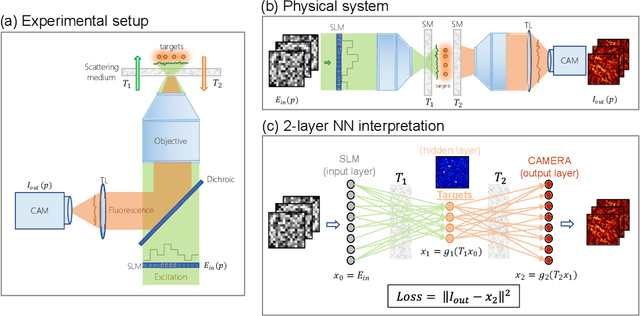
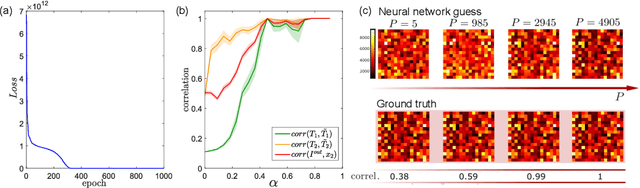
Abstract:Optical imaging through complex media, such as biological tissues or fog, is challenging due to light scattering. In the multiple scattering regime, wavefront shaping provides an effective method to retrieve information; it relies on measuring how the propagation of different optical wavefronts are impacted by scattering. Based on this principle, several wavefront shaping techniques were successfully developed, but most of them are highly invasive and limited to proof-of-principle experiments. Here, we propose to use a neural network approach to non-invasively characterize and control light scattering inside the medium and also to retrieve information of hidden objects buried within it. Unlike most of the recently-proposed approaches, the architecture of our neural network with its layers, connected nodes and activation functions has a true physical meaning as it mimics the propagation of light in our optical system. It is trained with an experimentally-measured input/output dataset built from a series of incident light patterns and corresponding camera snapshots. We apply our physics-based neural network to a fluorescence microscope in epi-configuration and demonstrate its performance through numerical simulations and experiments. This flexible method can include physical priors and we show that it can be applied to other systems as, for example, non-linear or coherent contrast mechanisms.
Large field-of-view non-invasive imaging through scattering layers using fluctuating random illumination
Jul 17, 2021



Abstract:On-invasive optical imaging techniques are essential diagnostic tools in many fields. Although various recent methods have been proposed to utilize and control light in multiple scattering media, non-invasive optical imaging through and inside scattering layers across a large field of view remains elusive due to the physical limits set by the optical memory effect, especially without wavefront shaping techniques. Here, we demonstrate an approach that enables non-invasive fluorescence imaging behind scattering layers with field-of-views extending well beyond the optical memory effect. The method consists in demixing the speckle patterns emitted by a fluorescent object under variable unknown random illumination, using matrix factorization and a novel fingerprint-based reconstruction. Experimental validation shows the efficiency and robustness of the method with various fluorescent samples, covering a field of view up to three times the optical memory effect range. Our non-invasive imaging technique is simple, neither requires a spatial light modulator nor a guide star, and can be generalized to a wide range of incoherent contrast mechanisms and illumination schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge