Anne Juuti
Nonparametric modeling of the composite effect of multiple nutrients on blood glucose dynamics
Nov 06, 2023



Abstract:In biomedical applications it is often necessary to estimate a physiological response to a treatment consisting of multiple components, and learn the separate effects of the components in addition to the joint effect. Here, we extend existing probabilistic nonparametric approaches to explicitly address this problem. We also develop a new convolution-based model for composite treatment-response curves that is more biologically interpretable. We validate our models by estimating the impact of carbohydrate and fat in meals on blood glucose. By differentiating treatment components, incorporating their dosages, and sharing statistical information across patients via a hierarchical multi-output Gaussian process, our method improves prediction accuracy over existing approaches, and allows us to interpret the different effects of carbohydrates and fat on the overall glucose response.
Temporal Causal Mediation through a Point Process: Direct and Indirect Effects of Healthcare Interventions
Jun 16, 2023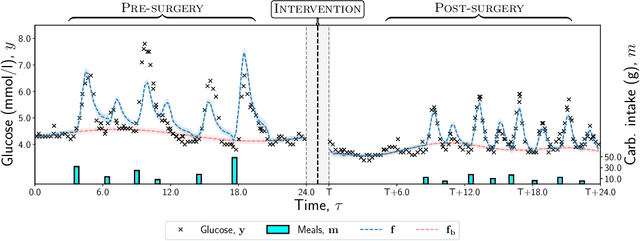
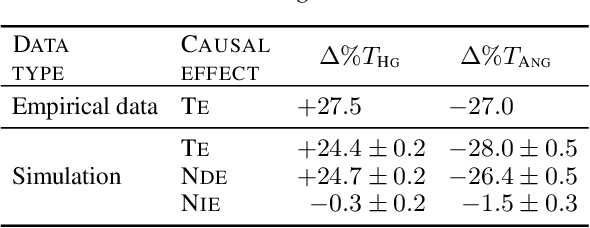
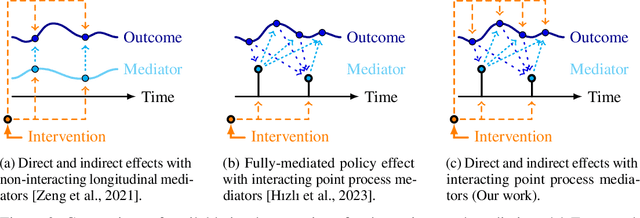
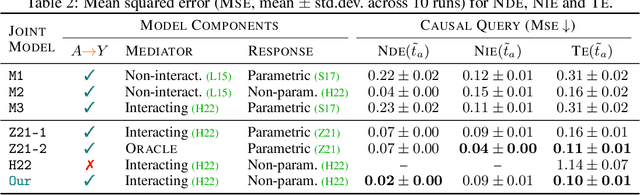
Abstract:Deciding on an appropriate intervention requires a causal model of a treatment, the outcome, and potential mediators. Causal mediation analysis lets us distinguish between direct and indirect effects of the intervention, but has mostly been studied in a static setting. In healthcare, data come in the form of complex, irregularly sampled time-series, with dynamic interdependencies between a treatment, outcomes, and mediators across time. Existing approaches to dynamic causal mediation analysis are limited to regular measurement intervals, simple parametric models, and disregard long-range mediator--outcome interactions. To address these limitations, we propose a non-parametric mediator--outcome model where the mediator is assumed to be a temporal point process that interacts with the outcome process. With this model, we estimate the direct and indirect effects of an external intervention on the outcome, showing how each of these affects the whole future trajectory. We demonstrate on semi-synthetic data that our method can accurately estimate direct and indirect effects. On real-world healthcare data, our model infers clinically meaningful direct and indirect effect trajectories for blood glucose after a surgery.
Joint Non-parametric Point Process model for Treatments and Outcomes: Counterfactual Time-series Prediction Under Policy Interventions
Sep 09, 2022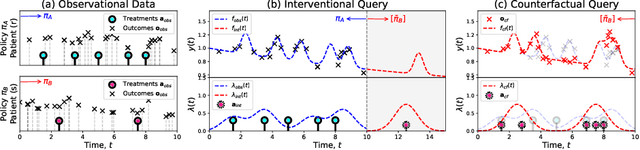
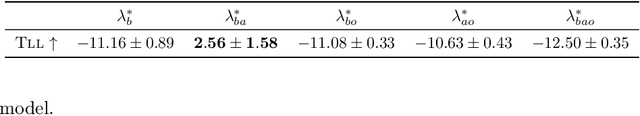
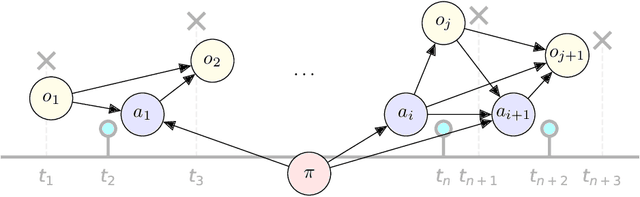
Abstract:Policy makers need to predict the progression of an outcome before adopting a new treatment policy, which defines when and how a sequence of treatments affecting the outcome occurs in continuous time. Commonly, algorithms that predict interventional future outcome trajectories take a fixed sequence of future treatments as input. This either neglects the dependence of future treatments on outcomes preceding them or implicitly assumes the treatment policy is known, and hence excludes scenarios where the policy is unknown or a counterfactual analysis is needed. To handle these limitations, we develop a joint model for treatments and outcomes, which allows for the estimation of treatment policies and effects from sequential treatment--outcome data. It can answer interventional and counterfactual queries about interventions on treatment policies, as we show with real-world data on blood glucose progression and a simulation study building on top of this.
Errors-in-variables Modeling of Personalized Treatment-Response Trajectories
Jun 10, 2019



Abstract:Estimating the effect of a treatment on a given outcome, conditioned on a vector of covariates, is central in many applications. However, learning the impact of a treatment on a continuous temporal response, when the covariates suffer extensively from measurement error and even the timing of the treatments is uncertain, has not been addressed. We introduce a novel data-driven method that can estimate treatment-response trajectories in this challenging scenario. We model personalized treatment-response curves as a combination of parametric response functions, hierarchically sharing information across individuals, and a sparse Gaussian process for the baseline trend. Importantly, our model considers measurement error not only in treatment covariates, but also in treatment times, a problem which arises in practice for example when treatment information is based on self-reporting. In a challenging and timely problem of estimating the impact of diet on continuous blood glucose measurements, our model leads to significant improvements in estimation accuracy and prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge