Anna Kozak
Best Practices For Empirical Meta-Algorithmic Research: Guidelines from the COSEAL Research Network
Dec 19, 2025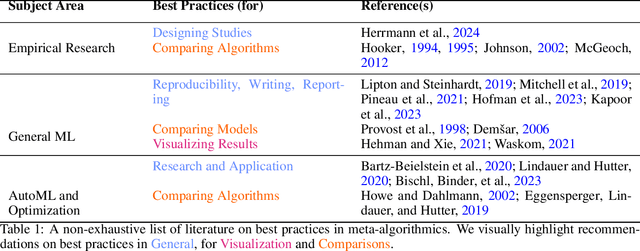
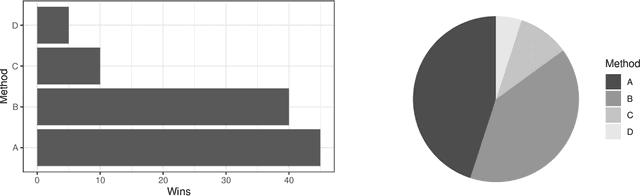
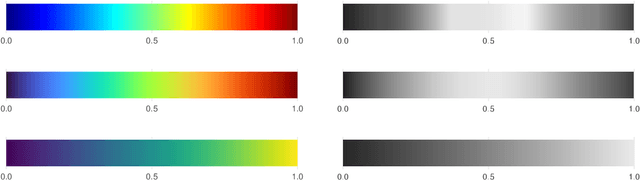
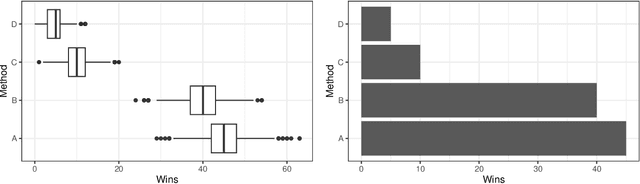
Abstract:Empirical research on meta-algorithmics, such as algorithm selection, configuration, and scheduling, often relies on extensive and thus computationally expensive experiments. With the large degree of freedom we have over our experimental setup and design comes a plethora of possible error sources that threaten the scalability and validity of our scientific insights. Best practices for meta-algorithmic research exist, but they are scattered between different publications and fields, and continue to evolve separately from each other. In this report, we collect good practices for empirical meta-algorithmic research across the subfields of the COSEAL community, encompassing the entire experimental cycle: from formulating research questions and selecting an experimental design, to executing experiments, and ultimately, analyzing and presenting results impartially. It establishes the current state-of-the-art practices within meta-algorithmic research and serves as a guideline to both new researchers and practitioners in meta-algorithmic fields.
Divide, Specialize, and Route: A New Approach to Efficient Ensemble Learning
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Ensemble learning has proven effective in boosting predictive performance, but traditional methods such as bagging, boosting, and dynamic ensemble selection (DES) suffer from high computational cost and limited adaptability to heterogeneous data distributions. To address these limitations, we propose Hellsemble, a novel and interpretable ensemble framework for binary classification that leverages dataset complexity during both training and inference. Hellsemble incrementally partitions the dataset into circles of difficulty by iteratively passing misclassified instances from simpler models to subsequent ones, forming a committee of specialised base learners. Each model is trained on increasingly challenging subsets, while a separate router model learns to assign new instances to the most suitable base model based on inferred difficulty. Hellsemble achieves strong classification accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency and interpretability. Experimental results on OpenML-CC18 and Tabzilla benchmarks demonstrate that Hellsemble often outperforms classical ensemble methods. Our findings suggest that embracing instance-level difficulty offers a promising direction for constructing efficient and robust ensemble systems.
forester: A Tree-Based AutoML Tool in R
Sep 07, 2024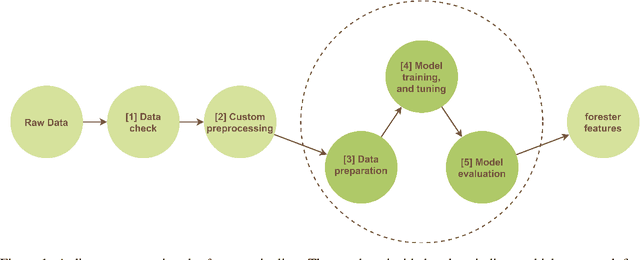


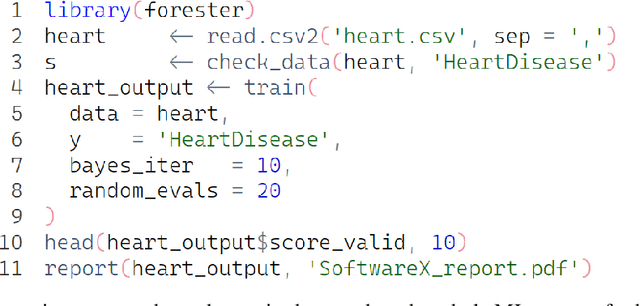
Abstract:The majority of automated machine learning (AutoML) solutions are developed in Python, however a large percentage of data scientists are associated with the R language. Unfortunately, there are limited R solutions available. Moreover high entry level means they are not accessible to everyone, due to required knowledge about machine learning (ML). To fill this gap, we present the forester package, which offers ease of use regardless of the user's proficiency in the area of machine learning. The forester is an open-source AutoML package implemented in R designed for training high-quality tree-based models on tabular data. It fully supports binary and multiclass classification, regression, and partially survival analysis tasks. With just a few functions, the user is capable of detecting issues regarding the data quality, preparing the preprocessing pipeline, training and tuning tree-based models, evaluating the results, and creating the report for further analysis.
Deciphering AutoML Ensembles: cattleia's Assistance in Decision-Making
Mar 19, 2024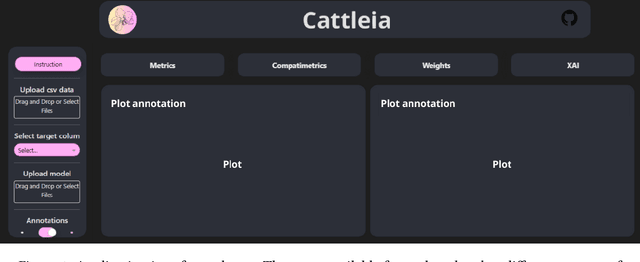
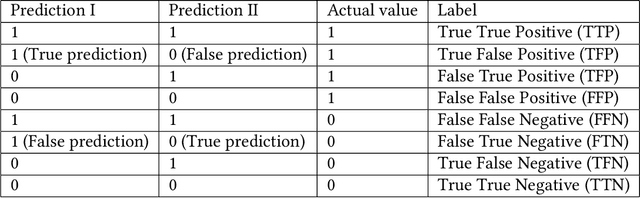
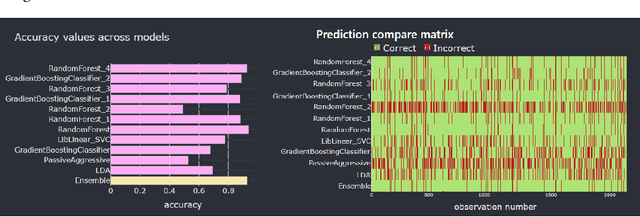

Abstract:In many applications, model ensembling proves to be better than a single predictive model. Hence, it is the most common post-processing technique in Automated Machine Learning (AutoML). The most popular frameworks use ensembles at the expense of reducing the interpretability of the final models. In our work, we propose cattleia - an application that deciphers the ensembles for regression, multiclass, and binary classification tasks. This tool works with models built by three AutoML packages: auto-sklearn, AutoGluon, and FLAML. The given ensemble is analyzed from different perspectives. We conduct a predictive performance investigation through evaluation metrics of the ensemble and its component models. We extend the validation perspective by introducing new measures to assess the diversity and complementarity of the model predictions. Moreover, we apply explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) techniques to examine the importance of variables. Summarizing obtained insights, we can investigate and adjust the weights with a modification tool to tune the ensemble in the desired way. The application provides the aforementioned aspects through dedicated interactive visualizations, making it accessible to a diverse audience. We believe the cattleia can support users in decision-making and deepen the comprehension of AutoML frameworks.
Rethinking of Encoder-based Warm-start Methods in Hyperparameter Optimization
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Effectively representing heterogeneous tabular datasets for meta-learning remains an open problem. Previous approaches rely on predefined meta-features, for example, statistical measures or landmarkers. Encoder-based models, such as Dataset2Vec, allow us to extract significant meta-features automatically without human intervention. This research introduces a novel encoder-based representation of tabular datasets implemented within the liltab package available on GitHub https://github.com/azoz01/liltab. Our package is based on an established model for heterogeneous tabular data proposed in [Iwata and Kumagai, 2020]. The proposed approach employs a different model for encoding feature relationships, generating alternative representations compared to existing methods like Dataset2Vec. Both of them leverage the fundamental assumption of dataset similarity learning. In this work, we evaluate Dataset2Vec and liltab on two common meta-tasks - representing entire datasets and hyperparameter optimization warm-start. However, validation on an independent metaMIMIC dataset highlights the nuanced challenges in representation learning. We show that general representations may not suffice for some meta-tasks where requirements are not explicitly considered during extraction. [Iwata and Kumagai, 2020] Tomoharu Iwata and Atsutoshi Kumagai. Meta-learning from Tasks with Heterogeneous Attribute Spaces. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020.
Enabling Machine Learning Algorithms for Credit Scoring -- Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) methods for clear understanding complex predictive models
Apr 14, 2021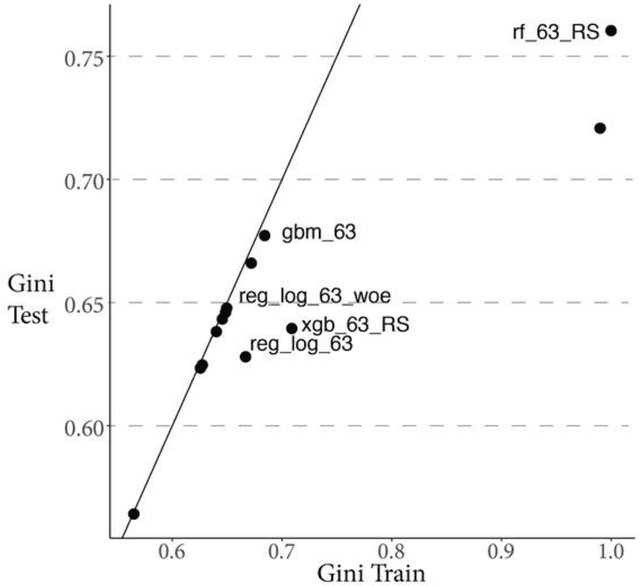
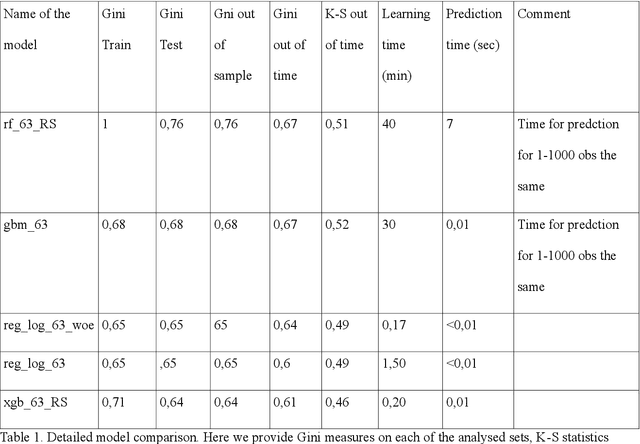
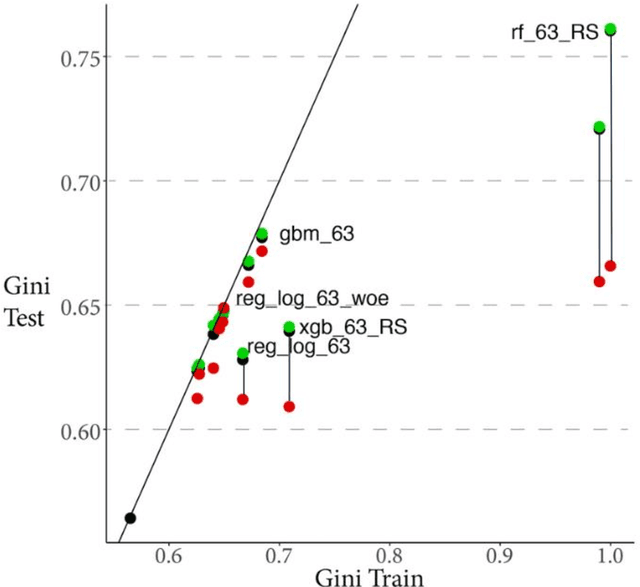
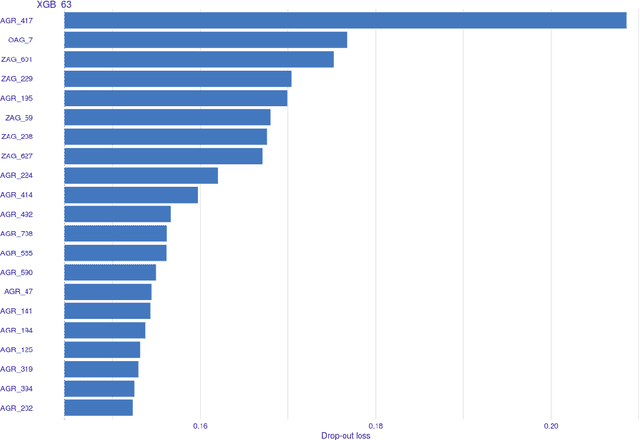
Abstract:Rapid development of advanced modelling techniques gives an opportunity to develop tools that are more and more accurate. However as usually, everything comes with a price and in this case, the price to pay is to loose interpretability of a model while gaining on its accuracy and precision. For managers to control and effectively manage credit risk and for regulators to be convinced with model quality the price to pay is too high. In this paper, we show how to take credit scoring analytics in to the next level, namely we present comparison of various predictive models (logistic regression, logistic regression with weight of evidence transformations and modern artificial intelligence algorithms) and show that advanced tree based models give best results in prediction of client default. What is even more important and valuable we also show how to boost advanced models using techniques which allow to interpret them and made them more accessible for credit risk practitioners, resolving the crucial obstacle in widespread deployment of more complex, 'black box' models like random forests, gradient boosted or extreme gradient boosted trees. All this will be shown on the large dataset obtained from the Polish Credit Bureau to which all the banks and most of the lending companies in the country do report the credit files. In this paper the data from lending companies were used. The paper then compares state of the art best practices in credit risk modelling with new advanced modern statistical tools boosted by the latest developments in the field of interpretability and explainability of artificial intelligence algorithms. We believe that this is a valuable contribution when it comes to presentation of different modelling tools but what is even more important it is showing which methods might be used to get insight and understanding of AI methods in credit risk context.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge