Anna Fedyukova
Explainable Machine Learning for ICU Readmission Prediction
Sep 27, 2023



Abstract:The intensive care unit (ICU) comprises a complex hospital environment, where decisions made by clinicians have a high level of risk for the patients' lives. A comprehensive care pathway must then be followed to reduce p complications. Uncertain, competing and unplanned aspects within this environment increase the difficulty in uniformly implementing the care pathway. Readmission contributes to this pathway's difficulty, occurring when patients are admitted again to the ICU in a short timeframe, resulting in high mortality rates and high resource utilisation. Several works have tried to predict readmission through patients' medical information. Although they have some level of success while predicting readmission, those works do not properly assess, characterise and understand readmission prediction. This work proposes a standardised and explainable machine learning pipeline to model patient readmission on a multicentric database (i.e., the eICU cohort with 166,355 patients, 200,859 admissions and 6,021 readmissions) while validating it on monocentric (i.e., the MIMIC IV cohort with 382,278 patients, 523,740 admissions and 5,984 readmissions) and multicentric settings. Our machine learning pipeline achieved predictive performance in terms of the area of the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) up to 0.7 with a Random Forest classification model, yielding an overall good calibration and consistency on validation sets. From explanations provided by the constructed models, we could also derive a set of insightful conclusions, primarily on variables related to vital signs and blood tests (e.g., albumin, blood urea nitrogen and hemoglobin levels), demographics (e.g., age, and admission height and weight), and ICU-associated variables (e.g., unit type). These insights provide an invaluable source of information during clinicians' decision-making while discharging ICU patients.
Quantifying machine learning-induced overdiagnosis in sepsis
Jul 03, 2021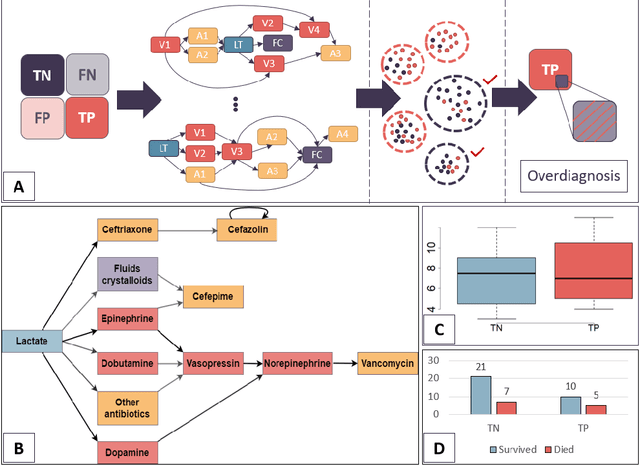
Abstract:The proliferation of early diagnostic technologies, including self-monitoring systems and wearables, coupled with the application of these technologies on large segments of healthy populations may significantly aggravate the problem of overdiagnosis. This can lead to unwanted consequences such as overloading health care systems and overtreatment, with potential harms to healthy individuals. The advent of machine-learning tools to assist diagnosis -- while promising rapid and more personalised patient management and screening -- might contribute to this issue. The identification of overdiagnosis is usually post hoc and demonstrated after long periods (from years to decades) and costly randomised control trials. In this paper, we present an innovative approach that allows us to preemptively detect potential cases of overdiagnosis during predictive model development. This approach is based on the combination of labels obtained from a prediction model and clustered medical trajectories, using sepsis in adults as a test case. This is one of the first attempts to quantify machine-learning induced overdiagnosis and we believe will serves as a platform for further development, leading to guidelines for safe deployment of computational diagnostic tools.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge