Anisia Katinskaia
An overview of artificial intelligence in computer-assisted language learning
May 04, 2025Abstract:Computer-assisted language learning -- CALL -- is an established research field. We review how artificial intelligence can be applied to support language learning and teaching. The need for intelligent agents that assist language learners and teachers is increasing: the human teacher's time is a scarce and costly resource, which does not scale with growing demand. Further factors contribute to the need for CALL: pandemics and increasing demand for distance learning, migration of large populations, the need for sustainable and affordable support for learning, etc. CALL systems are made up of many components that perform various functions, and AI is applied to many different aspects in CALL, corresponding to their own expansive research areas. Most of what we find in the research literature and in practical use are prototypes or partial implementations -- systems that perform some aspects of the overall desired functionality. Complete solutions -- most of them commercial -- are few, because they require massive resources. Recent advances in AI should result in improvements in CALL, yet there is a lack of surveys that focus on AI in the context of this research field. This paper aims to present a perspective on the AI methods that can be employed for language learning from a position of a developer of a CALL system. We also aim to connect work from different disciplines, to build bridges for interdisciplinary work.
Implicit assessment of language learning during practice as accurate as explicit testing
Sep 24, 2024
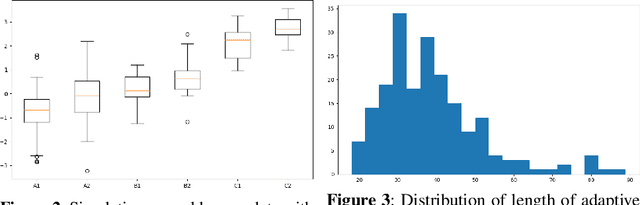
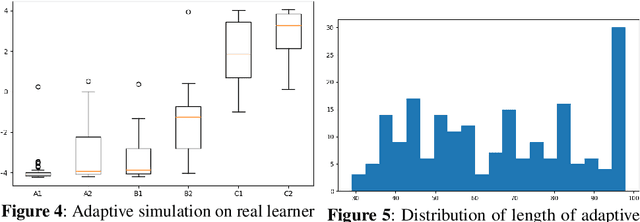
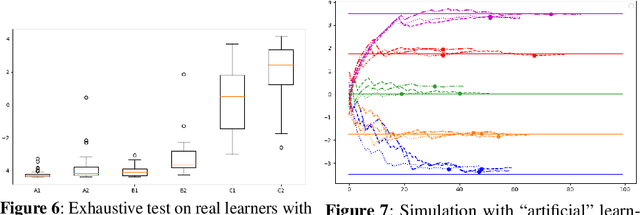
Abstract:Assessment of proficiency of the learner is an essential part of Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS). We use Item Response Theory (IRT) in computer-aided language learning for assessment of student ability in two contexts: in test sessions, and in exercises during practice sessions. Exhaustive testing across a wide range of skills can provide a detailed picture of proficiency, but may be undesirable for a number of reasons. Therefore, we first aim to replace exhaustive tests with efficient but accurate adaptive tests. We use learner data collected from exhaustive tests under imperfect conditions, to train an IRT model to guide adaptive tests. Simulations and experiments with real learner data confirm that this approach is efficient and accurate. Second, we explore whether we can accurately estimate learner ability directly from the context of practice with exercises, without testing. We transform learner data collected from exercise sessions into a form that can be used for IRT modeling. This is done by linking the exercises to {\em linguistic constructs}; the constructs are then treated as "items" within IRT. We present results from large-scale studies with thousands of learners. Using teacher assessments of student ability as "ground truth," we compare the estimates obtained from tests vs. those from exercises. The experiments confirm that the IRT models can produce accurate ability estimation based on exercises.
Probing the Category of Verbal Aspect in Transformer Language Models
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:We investigate how pretrained language models (PLM) encode the grammatical category of verbal aspect in Russian. Encoding of aspect in transformer LMs has not been studied previously in any language. A particular challenge is posed by "alternative contexts": where either the perfective or the imperfective aspect is suitable grammatically and semantically. We perform probing using BERT and RoBERTa on alternative and non-alternative contexts. First, we assess the models' performance on aspect prediction, via behavioral probing. Next, we examine the models' performance when their contextual representations are substituted with counterfactual representations, via causal probing. These counterfactuals alter the value of the "boundedness" feature--a semantic feature, which characterizes the action in the context. Experiments show that BERT and RoBERTa do encode aspect--mostly in their final layers. The counterfactual interventions affect perfective and imperfective in opposite ways, which is consistent with grammar: perfective is positively affected by adding the meaning of boundedness, and vice versa. The practical implications of our probing results are that fine-tuning only the last layers of BERT on predicting aspect is faster and more effective than fine-tuning the whole model. The model has high predictive uncertainty about aspect in alternative contexts, which tend to lack explicit hints about the boundedness of the described action.
GPT-3.5 for Grammatical Error Correction
May 14, 2024



Abstract:This paper investigates the application of GPT-3.5 for Grammatical Error Correction (GEC) in multiple languages in several settings: zero-shot GEC, fine-tuning for GEC, and using GPT-3.5 to re-rank correction hypotheses generated by other GEC models. In the zero-shot setting, we conduct automatic evaluations of the corrections proposed by GPT-3.5 using several methods: estimating grammaticality with language models (LMs), the Scribendi test, and comparing the semantic embeddings of sentences. GPT-3.5 has a known tendency to over-correct erroneous sentences and propose alternative corrections. For several languages, such as Czech, German, Russian, Spanish, and Ukrainian, GPT-3.5 substantially alters the source sentences, including their semantics, which presents significant challenges for evaluation with reference-based metrics. For English, GPT-3.5 demonstrates high recall, generates fluent corrections, and generally preserves sentence semantics. However, human evaluation for both English and Russian reveals that, despite its strong error-detection capabilities, GPT-3.5 struggles with several error types, including punctuation mistakes, tense errors, syntactic dependencies between words, and lexical compatibility at the sentence level.
What do Transformers Know about Government?
Apr 22, 2024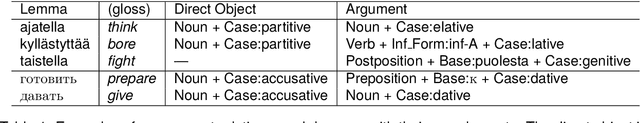
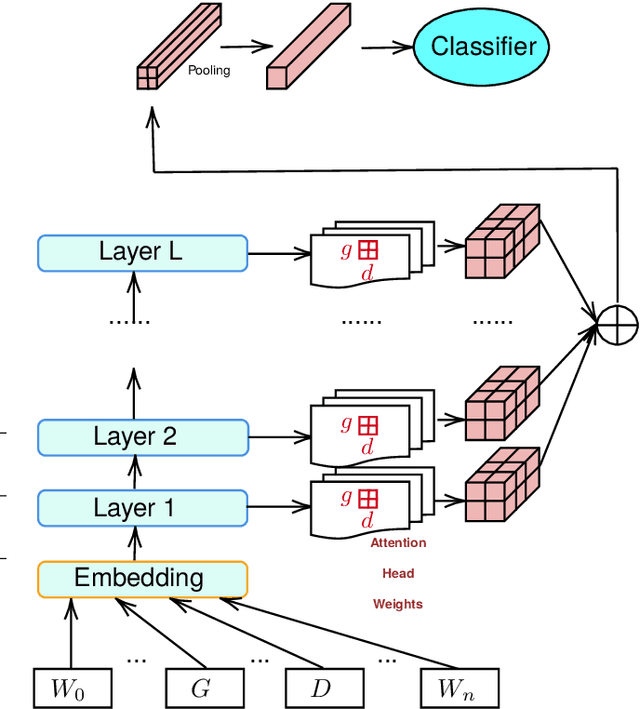
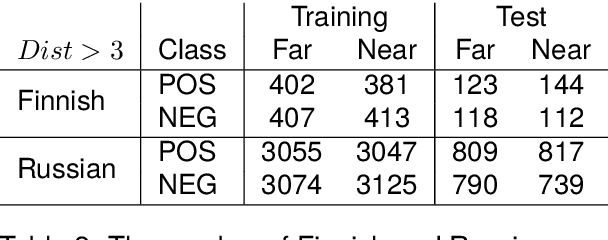
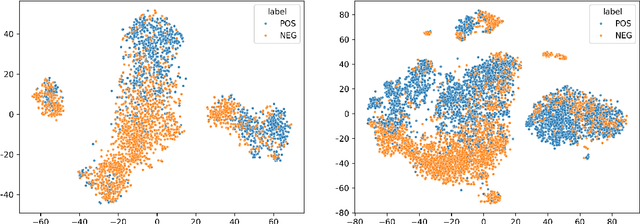
Abstract:This paper investigates what insights about linguistic features and what knowledge about the structure of natural language can be obtained from the encodings in transformer language models.In particular, we explore how BERT encodes the government relation between constituents in a sentence. We use several probing classifiers, and data from two morphologically rich languages. Our experiments show that information about government is encoded across all transformer layers, but predominantly in the early layers of the model. We find that, for both languages, a small number of attention heads encode enough information about the government relations to enable us to train a classifier capable of discovering new, previously unknown types of government, never seen in the training data. Currently, data is lacking for the research community working on grammatical constructions, and government in particular. We release the Government Bank -- a dataset defining the government relations for thousands of lemmas in the languages in our experiments.
Investigating the effect of sub-word segmentation on the performance of transformer language models
May 09, 2023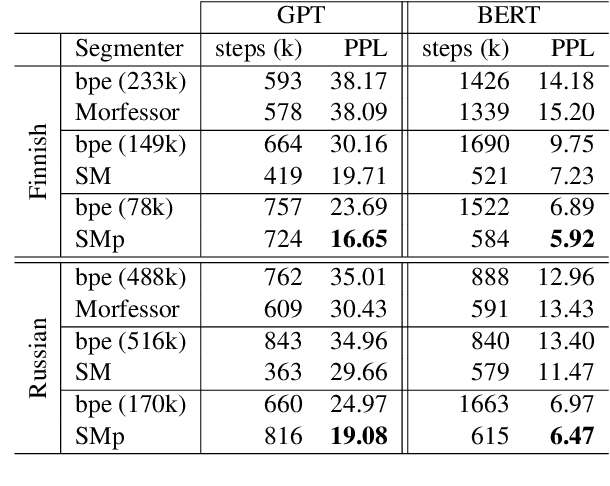
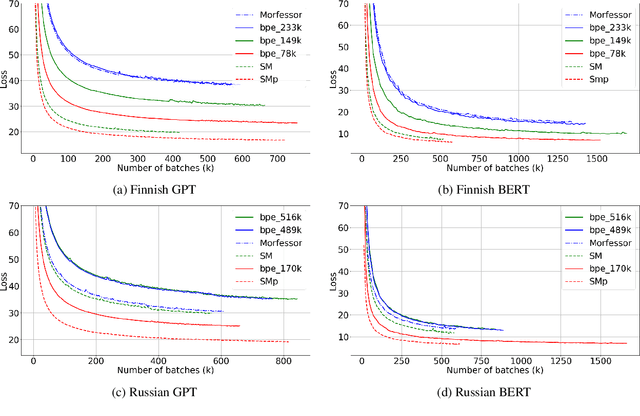
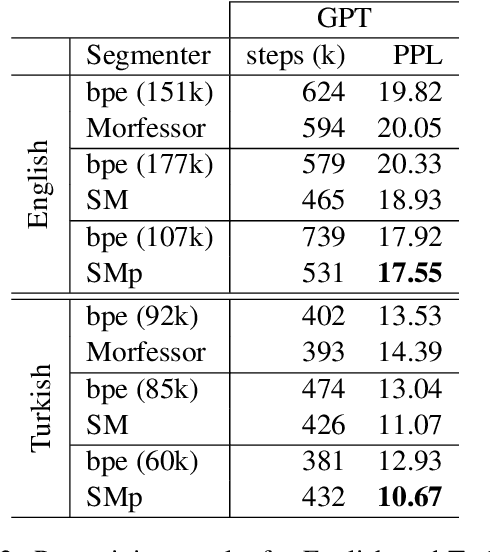
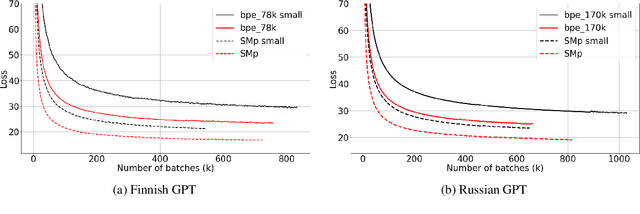
Abstract:We would like to explore how morphemes can affect the performance of a language model. We trained GPT-2 and Bert model with StateMorph for both Finnish and Russian, which is a morpheme segmenting algorithm. As a comparison, we also trained a model with BPE and Morfessor. Our preliminary result shows that StateMorph can help the model to converge more efficiently and achieve a better validation score.
Linguistic Constructs as the Representation of the Domain Model in an Intelligent Language Tutoring System
Dec 03, 2022

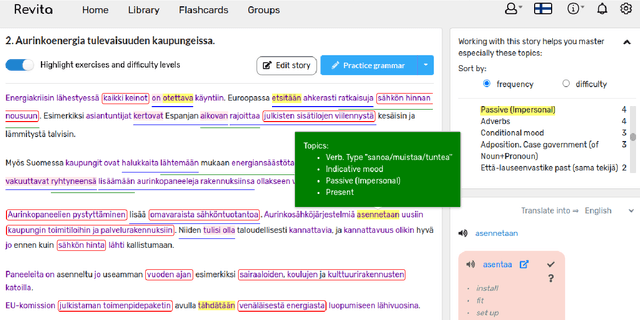
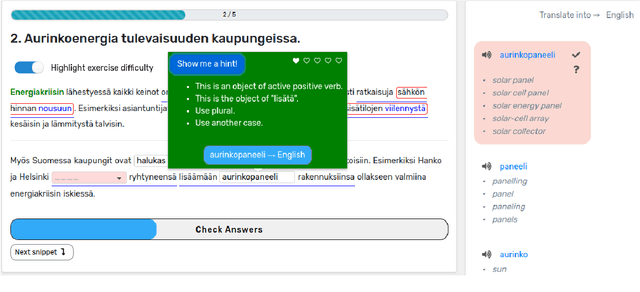
Abstract:This paper presents the development of an AI-based language learning platform Revita. It is a freely available intelligent online tutor, developed to support learners of multiple languages, from low-intermediate to advanced levels. It has been in pilot use by hundreds of students at several universities, whose feedback and needs are shaping the development. One of the main emerging features of Revita is the introduction of a system of linguistic constructs as the representation of domain knowledge. The system of constructs is developed in close collaboration with experts in language teaching. Constructs define the types of exercises, the content of the feedback, and enable the detailed modeling and evaluation of learning progress.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge