Anh-Duc Vu
Implicit assessment of language learning during practice as accurate as explicit testing
Sep 24, 2024
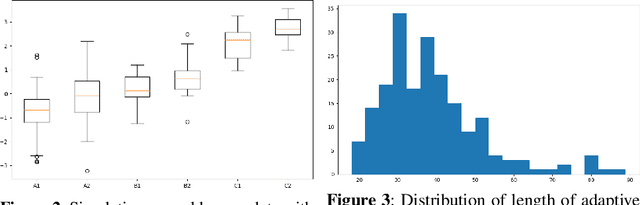
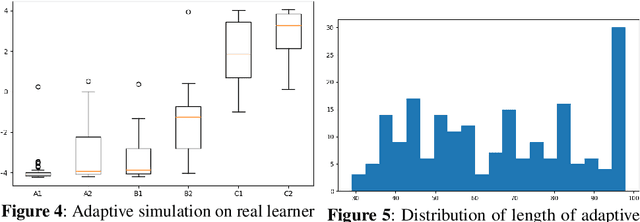
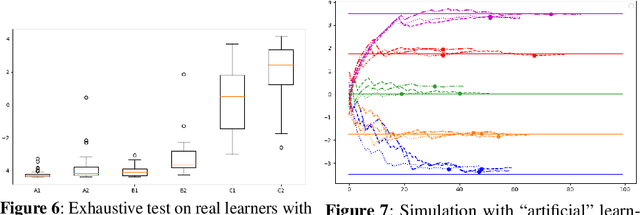
Abstract:Assessment of proficiency of the learner is an essential part of Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS). We use Item Response Theory (IRT) in computer-aided language learning for assessment of student ability in two contexts: in test sessions, and in exercises during practice sessions. Exhaustive testing across a wide range of skills can provide a detailed picture of proficiency, but may be undesirable for a number of reasons. Therefore, we first aim to replace exhaustive tests with efficient but accurate adaptive tests. We use learner data collected from exhaustive tests under imperfect conditions, to train an IRT model to guide adaptive tests. Simulations and experiments with real learner data confirm that this approach is efficient and accurate. Second, we explore whether we can accurately estimate learner ability directly from the context of practice with exercises, without testing. We transform learner data collected from exercise sessions into a form that can be used for IRT modeling. This is done by linking the exercises to {\em linguistic constructs}; the constructs are then treated as "items" within IRT. We present results from large-scale studies with thousands of learners. Using teacher assessments of student ability as "ground truth," we compare the estimates obtained from tests vs. those from exercises. The experiments confirm that the IRT models can produce accurate ability estimation based on exercises.
What do Transformers Know about Government?
Apr 22, 2024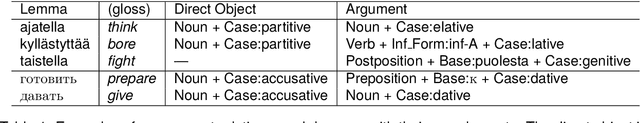
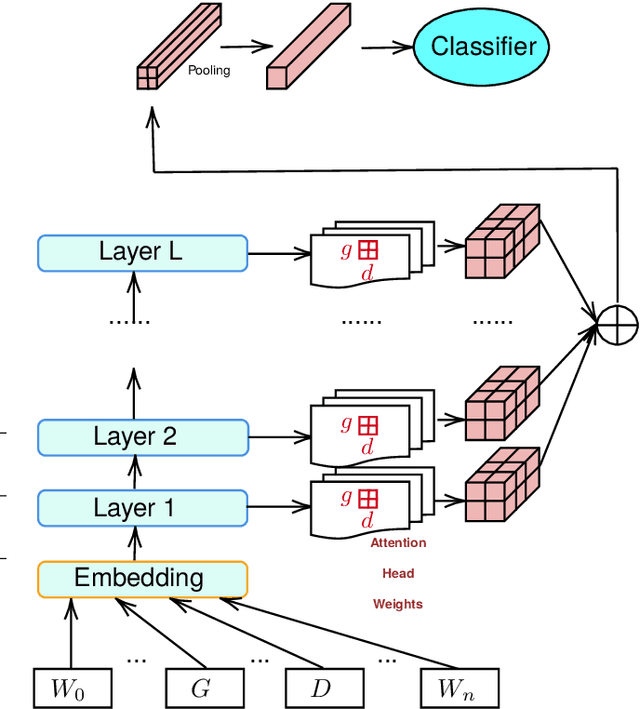
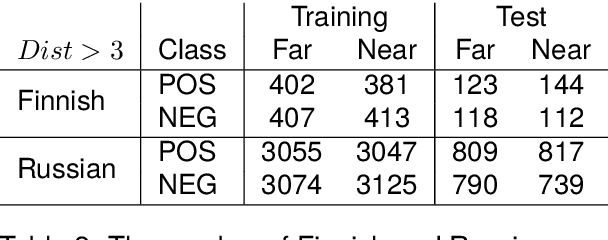
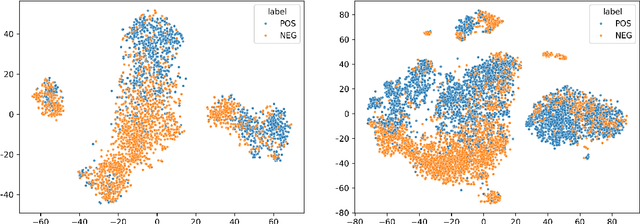
Abstract:This paper investigates what insights about linguistic features and what knowledge about the structure of natural language can be obtained from the encodings in transformer language models.In particular, we explore how BERT encodes the government relation between constituents in a sentence. We use several probing classifiers, and data from two morphologically rich languages. Our experiments show that information about government is encoded across all transformer layers, but predominantly in the early layers of the model. We find that, for both languages, a small number of attention heads encode enough information about the government relations to enable us to train a classifier capable of discovering new, previously unknown types of government, never seen in the training data. Currently, data is lacking for the research community working on grammatical constructions, and government in particular. We release the Government Bank -- a dataset defining the government relations for thousands of lemmas in the languages in our experiments.
Investigating the effect of sub-word segmentation on the performance of transformer language models
May 09, 2023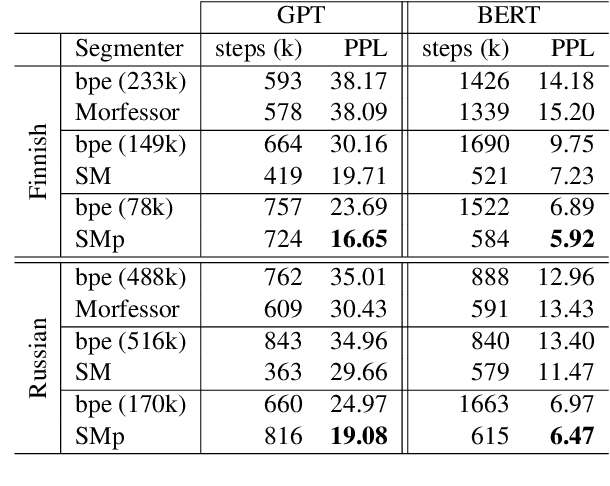
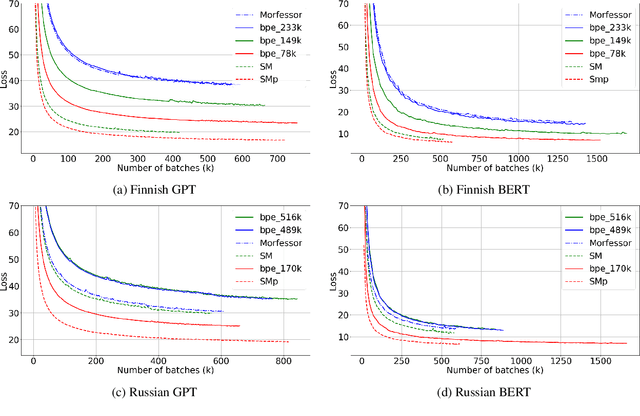
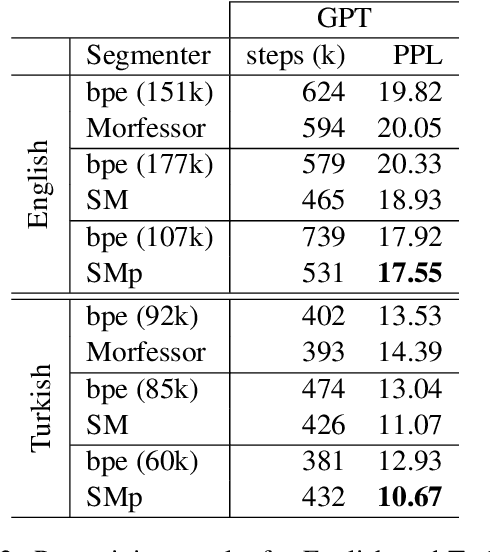
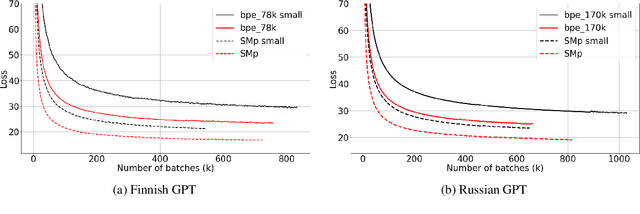
Abstract:We would like to explore how morphemes can affect the performance of a language model. We trained GPT-2 and Bert model with StateMorph for both Finnish and Russian, which is a morpheme segmenting algorithm. As a comparison, we also trained a model with BPE and Morfessor. Our preliminary result shows that StateMorph can help the model to converge more efficiently and achieve a better validation score.
Linguistic Constructs as the Representation of the Domain Model in an Intelligent Language Tutoring System
Dec 03, 2022

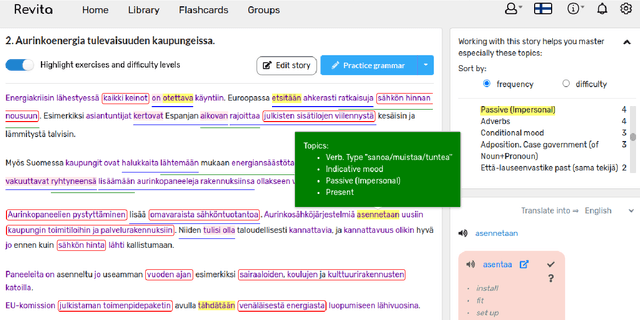
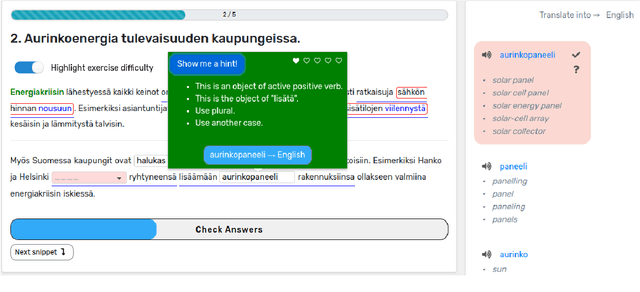
Abstract:This paper presents the development of an AI-based language learning platform Revita. It is a freely available intelligent online tutor, developed to support learners of multiple languages, from low-intermediate to advanced levels. It has been in pilot use by hundreds of students at several universities, whose feedback and needs are shaping the development. One of the main emerging features of Revita is the introduction of a system of linguistic constructs as the representation of domain knowledge. The system of constructs is developed in close collaboration with experts in language teaching. Constructs define the types of exercises, the content of the feedback, and enable the detailed modeling and evaluation of learning progress.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge