Anil Kumar Tiwari
Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur
DAAL: Density-Aware Adaptive Line Margin Loss for Multi-Modal Deep Metric Learning
Oct 07, 2024Abstract:Multi-modal deep metric learning is crucial for effectively capturing diverse representations in tasks such as face verification, fine-grained object recognition, and product search. Traditional approaches to metric learning, whether based on distance or margin metrics, primarily emphasize class separation, often overlooking the intra-class distribution essential for multi-modal feature learning. In this context, we propose a novel loss function called Density-Aware Adaptive Margin Loss(DAAL), which preserves the density distribution of embeddings while encouraging the formation of adaptive sub-clusters within each class. By employing an adaptive line strategy, DAAL not only enhances intra-class variance but also ensures robust inter-class separation, facilitating effective multi-modal representation. Comprehensive experiments on benchmark fine-grained datasets demonstrate the superior performance of DAAL, underscoring its potential in advancing retrieval applications and multi-modal deep metric learning.
ARNN: Attentive Recurrent Neural Network for Multi-channel EEG Signals to Identify Epileptic Seizures
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:We proposed an Attentive Recurrent Neural Network (ARNN), which recurrently applies attention layers along a sequence and has linear complexity with respect to the sequence length. The proposed model operates on multi-channel EEG signals rather than single channel signals and leverages parallel computation. In this cell, the attention layer is a computational unit that efficiently applies self-attention and cross-attention mechanisms to compute a recurrent function over a wide number of state vectors and input signals. Our architecture is inspired in part by the attention layer and long short-term memory (LSTM) cells, and it uses long-short style gates, but it scales this typical cell up by several orders to parallelize for multi-channel EEG signals. It inherits the advantages of attention layers and LSTM gate while avoiding their respective drawbacks. We evaluated the model effectiveness through extensive experiments with heterogeneous datasets, including the CHB-MIT and UPenn and Mayos Clinic, CHB-MIT datasets. The empirical findings suggest that the ARNN model outperforms baseline methods such as LSTM, Vision Transformer (ViT), Compact Convolution Transformer (CCT), and R-Transformer (RT), showcasing superior performance and faster processing capabilities across a wide range of tasks. The code has been made publicly accessible at \url{https://github.com/Salim-Lysiun/ARNN}.
Stacked Deep Multi-Scale Hierarchical Network for Fast Bokeh Effect Rendering from a Single Image
May 15, 2021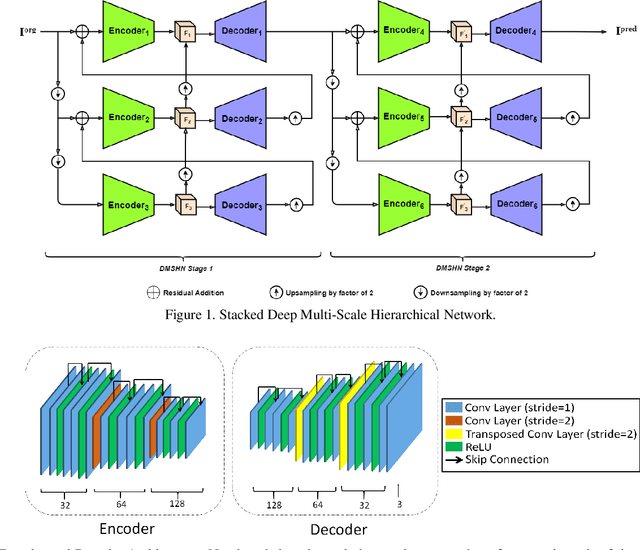
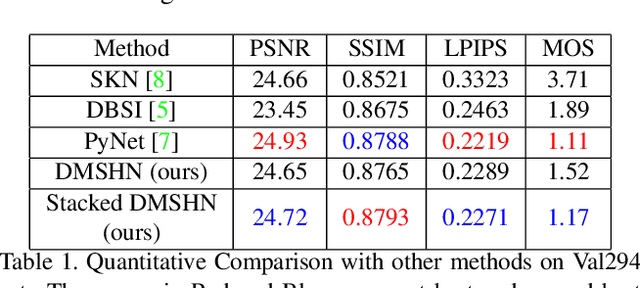
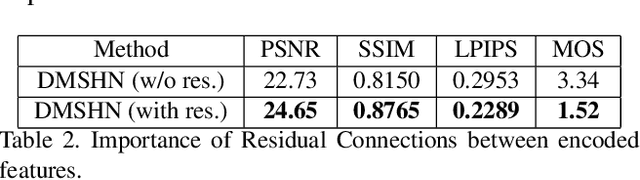

Abstract:The Bokeh Effect is one of the most desirable effects in photography for rendering artistic and aesthetic photos. Usually, it requires a DSLR camera with different aperture and shutter settings and certain photography skills to generate this effect. In smartphones, computational methods and additional sensors are used to overcome the physical lens and sensor limitations to achieve such effect. Most of the existing methods utilized additional sensor's data or pretrained network for fine depth estimation of the scene and sometimes use portrait segmentation pretrained network module to segment salient objects in the image. Because of these reasons, networks have many parameters, become runtime intensive and unable to run in mid-range devices. In this paper, we used an end-to-end Deep Multi-Scale Hierarchical Network (DMSHN) model for direct Bokeh effect rendering of images captured from the monocular camera. To further improve the perceptual quality of such effect, a stacked model consisting of two DMSHN modules is also proposed. Our model does not rely on any pretrained network module for Monocular Depth Estimation or Saliency Detection, thus significantly reducing the size of model and run time. Stacked DMSHN achieves state-of-the-art results on a large scale EBB! dataset with around 6x less runtime compared to the current state-of-the-art model in processing HD quality images.
Detector-SegMentor Network for Skin Lesion Localization and Segmentation
May 13, 2020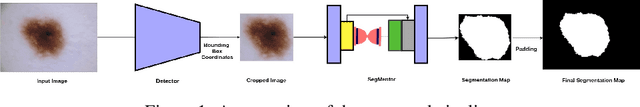
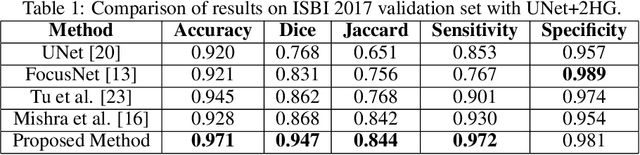
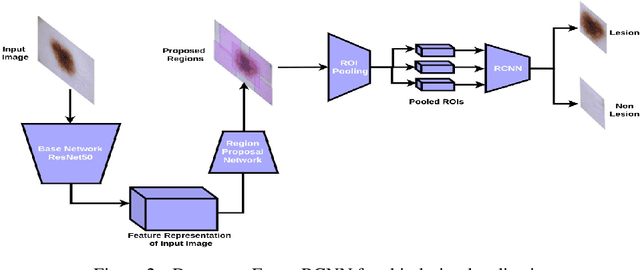
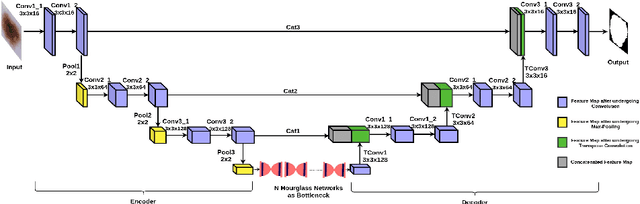
Abstract:Melanoma is a life-threatening form of skin cancer when left undiagnosed at the early stages. Although there are more cases of non-melanoma cancer than melanoma cancer, melanoma cancer is more deadly. Early detection of melanoma is crucial for the timely diagnosis of melanoma cancer and prohibit its spread to distant body parts. Segmentation of skin lesion is a crucial step in the classification of melanoma cancer from the cancerous lesions in dermoscopic images. Manual segmentation of dermoscopic skin images is very time consuming and error-prone resulting in an urgent need for an intelligent and accurate algorithm. In this study, we propose a simple yet novel network-in-network convolution neural network(CNN) based approach for segmentation of the skin lesion. A Faster Region-based CNN (Faster RCNN) is used for preprocessing to predict bounding boxes of the lesions in the whole image which are subsequently cropped and fed into the segmentation network to obtain the lesion mask. The segmentation network is a combination of the UNet and Hourglass networks. We trained and evaluated our models on ISIC 2018 dataset and also cross-validated on PH\textsuperscript{2} and ISBI 2017 datasets. Our proposed method surpassed the state-of-the-art with Dice Similarity Coefficient of 0.915 and Accuracy 0.959 on ISIC 2018 dataset and Dice Similarity Coefficient of 0.947 and Accuracy 0.971 on ISBI 2017 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge