Ang Gao
Rethinking Refinement: Correcting Generative Bias without Noise Injection
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Generative models, including diffusion and flow-based models, often exhibit systematic biases that degrade sample quality, particularly in high-dimensional settings. We revisit refinement methods and show that effective bias correction can be achieved as a post-hoc procedure, without noise injection or multi-step resampling of the sampling process. We propose a flow-matching-based \textbf{Bi-stage Flow Refinement (BFR)} framework with two refinement strategies operating at different stages: latent space alignment for approximately invertible generators and data space refinement trained with lightweight augmentations. Unlike previous refiners that perturb sampling dynamics, BFR preserves the original ODE trajectory and applies deterministic corrections to generated samples. Experiments on MNIST, CIFAR-10, and FFHQ at 256x256 resolution demonstrate consistent improvements in fidelity and coverage; notably, starting from base samples with FID 3.95, latent space refinement achieves a \textbf{state-of-the-art} FID of \textbf{1.46} on MNIST using only a single additional function evaluation (1-NFE), while maintaining sample diversity.
Flow Perturbation++: Multi-Step Unbiased Jacobian Estimation for High-Dimensional Boltzmann Sampling
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The scalability of continuous normalizing flows (CNFs) for unbiased Boltzmann sampling remains limited in high-dimensional systems due to the cost of Jacobian-determinant evaluation, which requires $D$ backpropagation passes through the flow layers. Existing stochastic Jacobian estimators such as the Hutchinson trace estimator reduce computation but introduce bias, while the recently proposed Flow Perturbation method is unbiased yet suffers from high variance. We present \textbf{Flow Perturbation++}, a variance-reduced extension of Flow Perturbation that discretizes the probability-flow ODE and performs unbiased stepwise Jacobian estimation at each integration step. This multi-step construction retains the unbiasedness of Flow Perturbation while achieves substantially lower estimator variance. Integrated into a Sequential Monte Carlo framework, Flow Perturbation++ achieves significantly improved equilibrium sampling on a 1000D Gaussian Mixture Model and the all-atom Chignolin protein compared with Hutchinson-based and single-step Flow Perturbation baselines.
Process In-Context Learning: Enhancing Mathematical Reasoning via Dynamic Demonstration Insertion
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) has proven highly effective across diverse large language model (LLM) tasks. However, its potential for enhancing tasks that demand step-by-step logical deduction, such as mathematical reasoning, remains underexplored. A core limitation of existing ICL approaches is their static use of demonstrations: examples are pre-selected before inference and remain fixed, failing to adapt to the dynamic confusion points that often arise during multi-step reasoning such as ambiguous calculations or logical gaps. These unresolved confusion points can lead to cascading errors that degrade final accuracy. To tackle this issue, we propose Process In-Context Learning (PICL), a dynamic demonstration integration framework designed to boost mathematical reasoning by responding to real-time inference needs. PICL operates in two stages: 1)~it identifies potential confusion points by analyzing semantics and entropy in the reasoning process and summarizes their core characteristics; 2)~upon encountering these points, it retrieves relevant demonstrations from the demonstration pool that match the confusion context and inserts them directly into the ongoing reasoning process to guide subsequent steps. Experiments show that PICL outperforms baseline methods by mitigating mid-inference confusion, highlighting the value of adaptive demonstration insertion in complex mathematical reasoning.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Image Denoising Challenge Report
Apr 16, 2025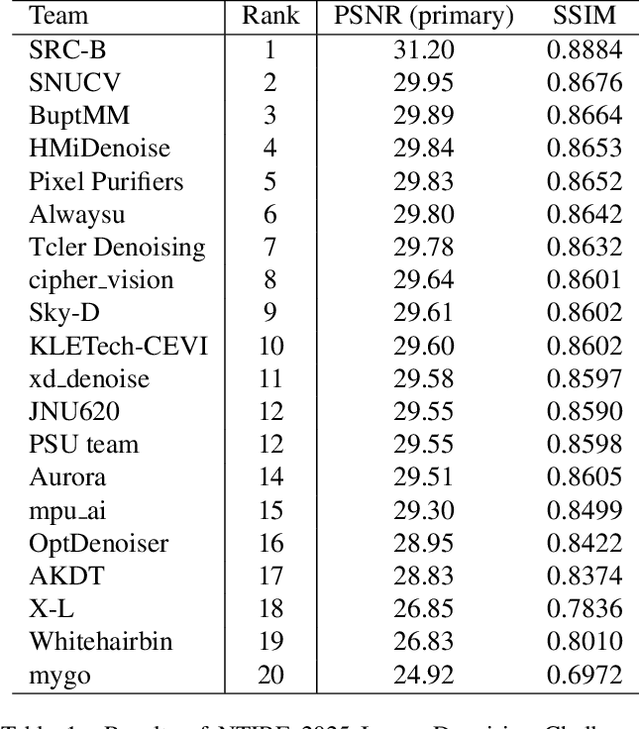

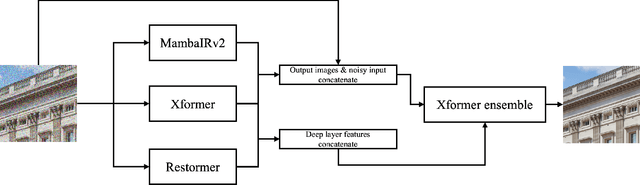

Abstract:This paper presents an overview of the NTIRE 2025 Image Denoising Challenge ({\sigma} = 50), highlighting the proposed methodologies and corresponding results. The primary objective is to develop a network architecture capable of achieving high-quality denoising performance, quantitatively evaluated using PSNR, without constraints on computational complexity or model size. The task assumes independent additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) with a fixed noise level of 50. A total of 290 participants registered for the challenge, with 20 teams successfully submitting valid results, providing insights into the current state-of-the-art in image denoising.
Self-Calibrated Dual Contrasting for Annotation-Efficient Bacteria Raman Spectroscopy Clustering and Classification
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:Raman scattering is based on molecular vibration spectroscopy and provides a powerful technology for pathogenic bacteria diagnosis using the unique molecular fingerprint information of a substance. The integration of deep learning technology has significantly improved the efficiency and accuracy of intelligent Raman spectroscopy (RS) recognition. However, the current RS recognition methods based on deep neural networks still require the annotation of a large amount of spectral data, which is labor-intensive. This paper presents a novel annotation-efficient Self-Calibrated Dual Contrasting (SCDC) method for RS recognition that operates effectively with few or no annotation. Our core motivation is to represent the spectrum from two different perspectives in two distinct subspaces: embedding and category. The embedding perspective captures instance-level information, while the category perspective reflects category-level information. Accordingly, we have implemented a dual contrastive learning approach from two perspectives to obtain discriminative representations, which are applicable for Raman spectroscopy recognition under both unsupervised and semi-supervised learning conditions. Furthermore, a self-calibration mechanism is proposed to enhance robustness. Validation of the identification task on three large-scale bacterial Raman spectroscopy datasets demonstrates that our SCDC method achieves robust recognition performance with very few (5$\%$ or 10$\%$) or no annotations, highlighting the potential of the proposed method for biospectral identification in annotation-efficient clinical scenarios.
DiffRaman: A Conditional Latent Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Bacterial Raman Spectroscopy Identification Under Limited Data Conditions
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Raman spectroscopy has attracted significant attention in various biochemical detection fields, especially in the rapid identification of pathogenic bacteria. The integration of this technology with deep learning to facilitate automated bacterial Raman spectroscopy diagnosis has emerged as a key focus in recent research. However, the diagnostic performance of existing deep learning methods largely depends on a sufficient dataset, and in scenarios where there is a limited availability of Raman spectroscopy data, it is inadequate to fully optimize the numerous parameters of deep neural networks. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a data generation method utilizing deep generative models to expand the data volume and enhance the recognition accuracy of bacterial Raman spectra. Specifically, we introduce DiffRaman, a conditional latent denoising diffusion probability model for Raman spectra generation. Experimental results demonstrate that synthetic bacterial Raman spectra generated by DiffRaman can effectively emulate real experimental spectra, thereby enhancing the performance of diagnostic models, especially under conditions of limited data. Furthermore, compared to existing generative models, the proposed DiffRaman offers improvements in both generation quality and computational efficiency. Our DiffRaman approach offers a well-suited solution for automated bacteria Raman spectroscopy diagnosis in data-scarce scenarios, offering new insights into alleviating the labor of spectroscopic measurements and enhancing rare bacteria identification.
Flow Perturbation to Accelerate Unbiased Sampling of Boltzmann distribution
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:Flow-based generative models have been employed for sampling the Boltzmann distribution, but their application to high-dimensional systems is hindered by the significant computational cost of obtaining the Jacobian of the flow. To overcome this challenge, we introduce the flow perturbation method, which incorporates optimized stochastic perturbations into the flow. By reweighting trajectories generated by the perturbed flow, our method achieves unbiased sampling of the Boltzmann distribution with orders of magnitude speedup compared to both brute force Jacobian calculations and the Hutchinson estimator. Notably, it accurately sampled the Chignolin protein with all atomic Cartesian coordinates explicitly represented, which, to our best knowledge, is the largest molecule ever Boltzmann sampled in such detail using generative models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge