Andrew Millard
Particle-Guided Diffusion Models for Partial Differential Equations
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We introduce a guided stochastic sampling method that augments sampling from diffusion models with physics-based guidance derived from partial differential equation (PDE) residuals and observational constraints, ensuring generated samples remain physically admissible. We embed this sampling procedure within a new Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) framework, yielding a scalable generative PDE solver. Across multiple benchmark PDE systems as well as multiphysics and interacting PDE systems, our method produces solution fields with lower numerical error than existing state-of-the-art generative methods.
Investigating Batch Inference in a Sequential Monte Carlo Framework for Neural Networks
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Bayesian inference allows us to define a posterior distribution over the weights of a generic neural network (NN). Exact posteriors are usually intractable, in which case approximations can be employed. One such approximation - variational inference - is computationally efficient when using mini-batch stochastic gradient descent as subsets of the data are used for likelihood and gradient evaluations, though the approach relies on the selection of a variational distribution which sufficiently matches the form of the posterior. Particle-based methods such as Markov chain Monte Carlo and Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) do not assume a parametric family for the posterior by typically require higher computational cost. These sampling methods typically use the full-batch of data for likelihood and gradient evaluations, which contributes to this computational expense. We explore several methods of gradually introducing more mini-batches of data (data annealing) into likelihood and gradient evaluations of an SMC sampler. We find that we can achieve up to $6\times$ faster training with minimal loss in accuracy on benchmark image classification problems using NNs.
Hess-MC2: Sequential Monte Carlo Squared using Hessian Information and Second Order Proposals
Jul 10, 2025
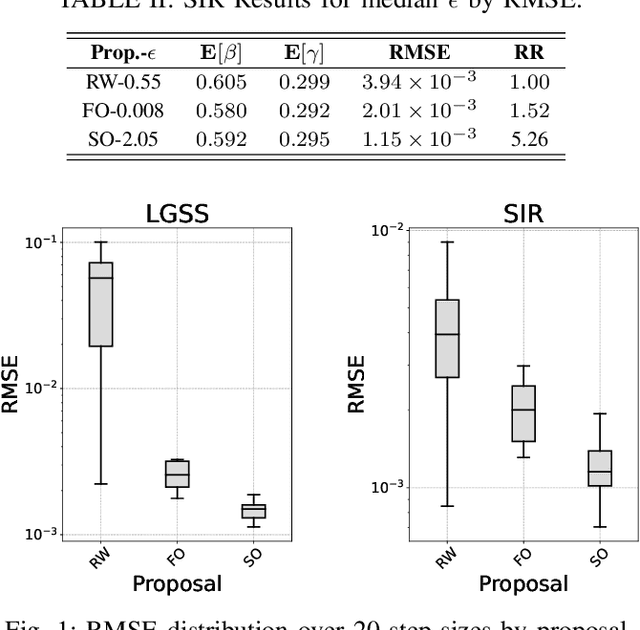
Abstract:When performing Bayesian inference using Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) methods, two considerations arise: the accuracy of the posterior approximation and computational efficiency. To address computational demands, Sequential Monte Carlo Squared (SMC$^2$) is well-suited for high-performance computing (HPC) environments. The design of the proposal distribution within SMC$^2$ can improve accuracy and exploration of the posterior as poor proposals may lead to high variance in importance weights and particle degeneracy. The Metropolis-Adjusted Langevin Algorithm (MALA) uses gradient information so that particles preferentially explore regions of higher probability. In this paper, we extend this idea by incorporating second-order information, specifically the Hessian of the log-target. While second-order proposals have been explored previously in particle Markov Chain Monte Carlo (p-MCMC) methods, we are the first to introduce them within the SMC$^2$ framework. Second-order proposals not only use the gradient (first-order derivative), but also the curvature (second-order derivative) of the target distribution. Experimental results on synthetic models highlight the benefits of our approach in terms of step-size selection and posterior approximation accuracy when compared to other proposals.
Humble your Overconfident Networks: Unlearning Overfitting via Sequential Monte Carlo Tempered Deep Ensembles
May 16, 2025Abstract:Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) methods offer a principled approach to Bayesian uncertainty quantification but are traditionally limited by the need for full-batch gradient evaluations. We introduce a scalable variant by incorporating Stochastic Gradient Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (SGHMC) proposals into SMC, enabling efficient mini-batch based sampling. Our resulting SMCSGHMC algorithm outperforms standard stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and deep ensembles across image classification, out-of-distribution (OOD) detection, and transfer learning tasks. We further show that SMCSGHMC mitigates overfitting and improves calibration, providing a flexible, scalable pathway for converting pretrained neural networks into well-calibrated Bayesian models.
Utilising Gradient-Based Proposals Within Sequential Monte Carlo Samplers for Training of Partial Bayesian Neural Networks
May 01, 2025Abstract:Partial Bayesian neural networks (pBNNs) have been shown to perform competitively with fully Bayesian neural networks while only having a subset of the parameters be stochastic. Using sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) samplers as the inference method for pBNNs gives a non-parametric probabilistic estimation of the stochastic parameters, and has shown improved performance over parametric methods. In this paper we introduce a new SMC-based training method for pBNNs by utilising a guided proposal and incorporating gradient-based Markov kernels, which gives us better scalability on high dimensional problems. We show that our new method outperforms the state-of-the-art in terms of predictive performance and optimal loss. We also show that pBNNs scale well with larger batch sizes, resulting in significantly reduced training times and often better performance.
Incorporating the ChEES Criterion into Sequential Monte Carlo Samplers
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are a powerful but computationally expensive way of performing non-parametric Bayesian inference. MCMC proposals which utilise gradients, such as Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC), can better explore the parameter space of interest if the additional hyper-parameters are chosen well. The No-U-Turn Sampler (NUTS) is a variant of HMC which is extremely effective at selecting these hyper-parameters but is slow to run and is not suited to GPU architectures. An alternative to NUTS, Change in the Estimator of the Expected Square HMC (ChEES-HMC) was shown not only to run faster than NUTS on GPU but also sample from posteriors more efficiently. Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) samplers are another sampling method which instead output weighted samples from the posterior. They are very amenable to parallelisation and therefore being run on GPUs while having additional flexibility in their choice of proposal over MCMC. We incorporate (ChEEs-HMC) as a proposal into SMC samplers and demonstrate competitive but faster performance than NUTS on a number of tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge