Andrei Polzounov
WordFence: Text Detection in Natural Images with Border Awareness
May 15, 2017
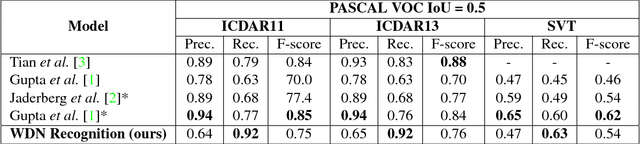
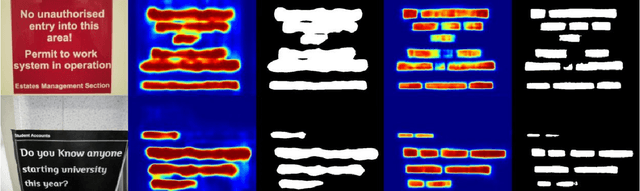
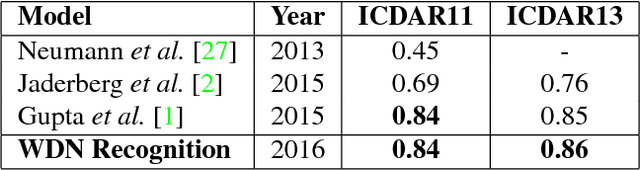
Abstract:In recent years, text recognition has achieved remarkable success in recognizing scanned document text. However, word recognition in natural images is still an open problem, which generally requires time consuming post-processing steps. We present a novel architecture for individual word detection in scene images based on semantic segmentation. Our contributions are twofold: the concept of WordFence, which detects border areas surrounding each individual word and a novel pixelwise weighted softmax loss function which penalizes background and emphasizes small text regions. WordFence ensures that each word is detected individually, and the new loss function provides a strong training signal to both text and word border localization. The proposed technique avoids intensive post-processing, producing an end-to-end word detection system. We achieve superior localization recall on common benchmark datasets - 92% recall on ICDAR11 and ICDAR13 and 63% recall on SVT. Furthermore, our end-to-end word recognition system achieves state-of-the-art 86% F-Score on ICDAR13.
Right whale recognition using convolutional neural networks
Apr 19, 2016



Abstract:We studied the feasibility of recognizing individual right whales (Eubalaena glacialis) using convolutional neural networks. Prior studies have shown that CNNs can be used in wide range of classification and categorization tasks such as automated human face recognition. To test applicability of deep learning to whale recognition we have developed several models based on best practices from literature. Here, we describe the performance of the models. We conclude that machine recognition of whales is feasible and comment on the difficulty of the problem
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge